
- Definition of a Bachelor’s Degree
- Types of Bachelor’s Degrees
- Benefits of Obtaining a Bachelor’s Degree
- The Bachelor’s Degree Process
- Choosing a Bachelor’s Degree Program: What’s A Bachelor’s Degree
- The Importance of Choosing a Field of Study
- The Future of Bachelor’s Degrees
- Outcome Summary
- Essential FAQs
What’s a bachelor’s degree? It’s more than just a piece of paper – it’s a gateway to countless opportunities, personal growth, and a brighter future. This degree, earned after years of dedicated study, signifies a commitment to knowledge and prepares individuals for the challenges and rewards of the professional world.
From the traditional Bachelor of Arts (BA) to the specialized Bachelor of Science (BS), there’s a degree for everyone. Each type offers a unique curriculum, focusing on specific disciplines and preparing graduates for diverse career paths. The bachelor’s degree is a testament to a student’s hard work and dedication, opening doors to a world of possibilities.
Definition of a Bachelor’s Degree
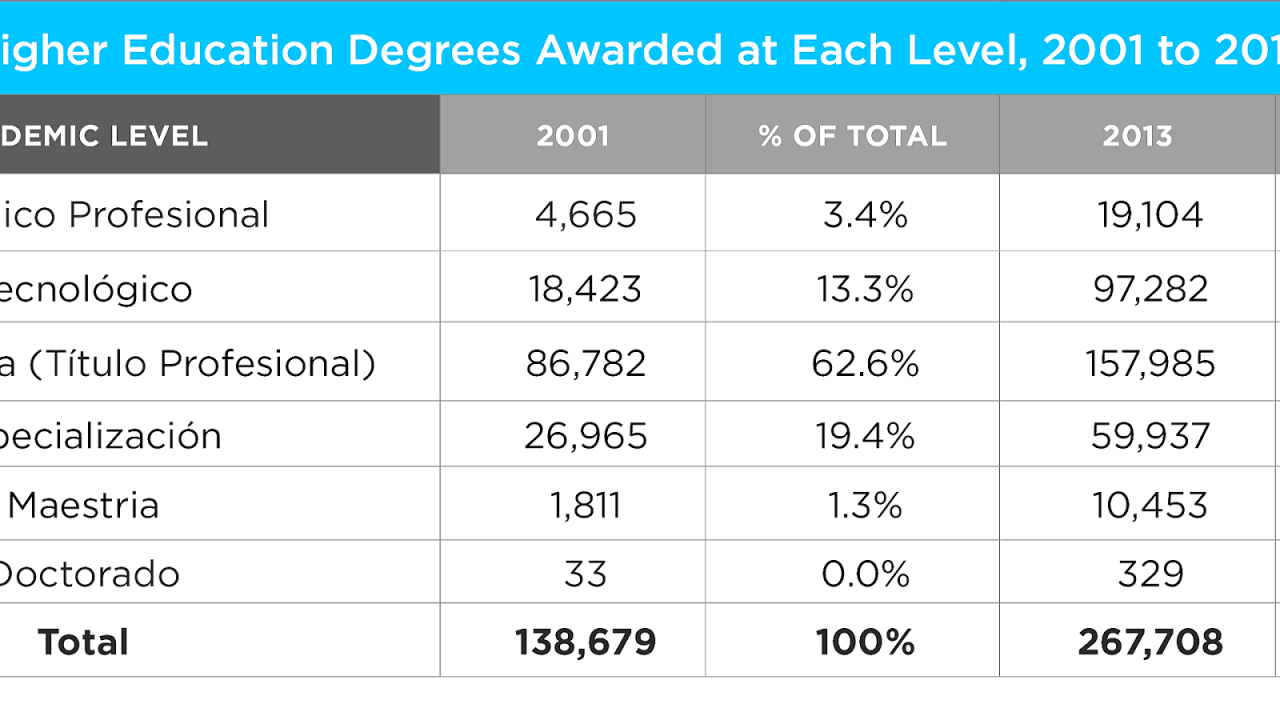
A bachelor’s degree is a post-secondary academic degree awarded by colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study. It signifies that the recipient has successfully acquired a broad and foundational understanding of a particular subject area.
History of the Bachelor’s Degree
The bachelor’s degree originated in medieval Europe, evolving from the “baccalaureate” degree awarded to students who had completed the first stage of their education. Initially, the bachelor’s degree was primarily focused on theology, law, and medicine. However, over time, the scope of the bachelor’s degree expanded to include other subjects, such as the arts, sciences, and humanities.
Significance of a Bachelor’s Degree in Today’s Society
In today’s competitive job market, a bachelor’s degree has become increasingly important for career advancement and personal growth. It provides individuals with the knowledge, skills, and credentials necessary to succeed in a wide range of industries.
“A bachelor’s degree is a valuable investment in your future, providing you with the foundation for a successful career and a fulfilling life.”
Types of Bachelor’s Degrees
There are many different types of bachelor’s degrees available, depending on the field of study. Some of the most common types include:
- Bachelor of Arts (BA): Typically awarded in fields like humanities, social sciences, and the arts.
- Bachelor of Science (BS): Usually awarded in fields like science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
- Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA): Awarded in fields like art, design, music, and theater.
- Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA): Awarded in fields like business, management, and finance.
Benefits of Earning a Bachelor’s Degree
Earning a bachelor’s degree offers a variety of benefits, including:
- Increased earning potential: Individuals with a bachelor’s degree typically earn significantly more than those with only a high school diploma.
- Improved job prospects: A bachelor’s degree can open doors to a wider range of career opportunities.
- Enhanced critical thinking and problem-solving skills: The rigorous coursework and research involved in earning a bachelor’s degree develop these essential skills.
- Personal growth and development: The experience of pursuing a bachelor’s degree can broaden perspectives and foster intellectual curiosity.
Choosing a Bachelor’s Degree Program
Choosing the right bachelor’s degree program is an important decision. Consider your interests, career goals, and the job market when making this choice.
“Research different programs, talk to advisors, and explore your options carefully to find the best fit for your needs and aspirations.”
Types of Bachelor’s Degrees
While the term “Bachelor’s Degree” is commonly used, there are various types, each offering a distinct educational path and career trajectory. Understanding the differences between these degrees is crucial for choosing the right program for your goals and interests.
Categorization of Bachelor’s Degrees
Bachelor’s degrees are broadly categorized into two main types: Bachelor of Arts (BA) and Bachelor of Science (BS). The choice between these degrees often depends on the field of study and the desired career path.
| Degree Type | Focus | Common Majors | Typical Career Paths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bachelor of Arts (BA) | Liberal arts, humanities, social sciences, and the arts | English, History, Philosophy, Sociology, Psychology, Music, Art | Teaching, Journalism, Writing, Research, Marketing, Public Relations, Human Resources |
| Bachelor of Science (BS) | Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields | Biology, Chemistry, Physics, Computer Science, Engineering, Mathematics, Nursing | Science and Engineering Research, Software Development, Data Analysis, Healthcare, Education, Management |
Other Types of Bachelor’s Degrees
Besides the BA and BS, several other types of bachelor’s degrees exist, each tailored to specific fields of study and career paths.
- Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA): This degree focuses on creative and artistic disciplines, such as visual arts, performing arts, and design. It emphasizes practical skills and studio work, preparing graduates for careers in art, design, and entertainment industries.
- Bachelor of Music (BM): This degree is designed for aspiring musicians, providing a comprehensive understanding of music theory, performance, and composition. Graduates may pursue careers as performers, composers, educators, or music therapists.
- Bachelor of Education (BEd): This degree prepares individuals for teaching careers in various educational settings. The curriculum includes pedagogical theory, classroom management, and subject-specific knowledge.
- Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA): This degree focuses on the principles and practices of business management, including finance, marketing, accounting, and operations. Graduates may pursue careers in various business sectors, including management, consulting, and entrepreneurship.
- Bachelor of Laws (LLB): This degree is a professional qualification for lawyers, providing a comprehensive understanding of legal principles, procedures, and ethics. Graduates can work as lawyers, legal professionals, or legal researchers.
Distinction Between BA and BS
While both BA and BS degrees are valuable, they differ in their focus and curriculum, leading to distinct career paths.
- Focus: BA programs typically emphasize critical thinking, communication, and analytical skills, while BS programs emphasize scientific inquiry, technical skills, and problem-solving abilities.
- Curriculum: BA programs include a broader range of humanities and social science courses, while BS programs offer more specialized courses in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
- Career Paths: BA degrees often lead to careers in fields like education, journalism, marketing, and social work, while BS degrees are more common in science, technology, engineering, and healthcare fields.
Choosing the Right Degree
The decision between a BA and BS degree depends on individual goals, interests, and career aspirations. Consider the following factors:
- Career Goals: What kind of career do you envision for yourself? Research the educational requirements and typical degree paths for your desired profession.
- Interests: What subjects do you enjoy studying? Choose a degree that aligns with your passions and intellectual curiosity.
- Skills and Abilities: What skills and abilities do you possess? Consider how a particular degree can help you develop and enhance these skills.
Benefits of Obtaining a Bachelor’s Degree
A bachelor’s degree is a valuable investment in your future. It opens doors to a wide range of opportunities and equips you with the knowledge and skills necessary to succeed in today’s competitive job market. Obtaining a bachelor’s degree offers numerous advantages, including increased earning potential, career advancement opportunities, and personal growth.
Increased Earning Potential
Individuals with a bachelor’s degree generally earn significantly more than those with only a high school diploma. The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that workers with a bachelor’s degree earn an average of 67% more than those with only a high school diploma. This significant income difference highlights the financial benefits of pursuing a bachelor’s degree.
Career Advancement Opportunities
A bachelor’s degree can open doors to a wider range of career options and enhance your chances of promotion within your chosen field. Many employers require a bachelor’s degree for entry-level positions and higher-level roles. For example, a bachelor’s degree in engineering can lead to a career as a project manager, while a degree in business administration can open doors to leadership positions in various industries.
Personal Growth
Beyond the professional benefits, a bachelor’s degree can also contribute to personal growth and development. It challenges you intellectually, expands your knowledge base, and helps you develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills. These skills are valuable not only in the workplace but also in your personal life.
Higher Levels of Education and Research Opportunities
A bachelor’s degree can be a stepping stone to higher levels of education, such as a master’s or doctoral degree. This can open up further career opportunities and research possibilities. For instance, a bachelor’s degree in biology can be followed by a master’s or Ph.D. in a specialized area of biology, leading to a career in research or academia.
The Bachelor’s Degree Process
Earning a bachelor’s degree is a journey that involves several steps, from choosing a major to walking across the stage at graduation. The process can vary depending on the institution you choose, but the core elements remain consistent. Let’s explore the typical steps involved in obtaining a bachelor’s degree.
Choosing a Major
Choosing a major is a crucial first step. It’s essential to select a field that aligns with your interests, skills, and career aspirations. Many universities offer academic advisors to guide students through the major selection process. You can explore various academic disciplines, consider your career goals, and conduct research on different programs to find the best fit for your aspirations.
Admission Requirements and Application Process
Admission requirements and the application process vary significantly across universities and colleges. Some institutions may require standardized test scores like the SAT or ACT, while others may emphasize GPA or extracurricular activities.
Here are some common admission requirements:
* Academic transcripts: High school transcripts are essential for demonstrating your academic performance.
* Letters of recommendation: Letters from teachers or counselors can provide insights into your character, work ethic, and potential.
* Personal statement: This essay allows you to articulate your academic goals, interests, and reasons for choosing a particular institution.
* Standardized test scores: Some universities may require standardized test scores, such as the SAT or ACT.
* Application fees: Most institutions charge application fees, which can vary in amount.
The application process typically involves submitting an online application form, along with the required documents. It’s crucial to carefully review the specific requirements and deadlines for each institution you apply to.
Course Load, Credit Requirements, and Graduation Criteria
Once admitted, you’ll begin your journey towards earning your bachelor’s degree. The course load, credit requirements, and graduation criteria are Artikeld by the university.
* Course Load: Universities typically require students to take a specific number of credit hours per semester. A full-time course load is generally 12-18 credit hours.
* Credit Requirements: The number of credit hours required for graduation varies depending on the institution and the chosen major. A typical bachelor’s degree requires around 120-130 credit hours.
* Graduation Criteria: To graduate, students must complete all required courses, maintain a minimum GPA, and fulfill any other institution-specific requirements.
Financial Aid and Scholarships
Financing your education is a significant consideration. Many universities offer financial aid and scholarship programs to help students pay for tuition, fees, and other expenses.
Here are some common financial aid options:
* Federal grants: Grants are free money that doesn’t need to be repaid.
* Federal loans: Loans provide financial assistance that needs to be repaid with interest.
* Scholarships: Scholarships are awarded based on academic merit, extracurricular activities, or other criteria.
* Work-study programs: Work-study programs allow students to work part-time on campus to earn money for their education.
It’s essential to research and apply for financial aid and scholarships to reduce the financial burden of obtaining a bachelor’s degree.
Choosing a Bachelor’s Degree Program: What’s A Bachelor’s Degree
Choosing the right bachelor’s degree program is a significant decision that can shape your future career path and personal development. It’s crucial to consider your interests, skills, and career goals to make an informed choice that aligns with your aspirations.
Factors to Consider
This section delves into the key factors to consider when choosing a bachelor’s degree program. Understanding these aspects can help you narrow down your options and select a program that best suits your needs.
- Program Curriculum: The curriculum Artikels the courses you’ll take and the knowledge and skills you’ll gain. It’s essential to review the course descriptions and ensure they align with your interests and career goals. For example, if you’re interested in a career in computer science, you’ll want to look for a program that offers courses in programming, data structures, and algorithms. You can also check if the program offers elective courses that allow you to specialize in a specific area of interest, such as artificial intelligence or cybersecurity.
- Faculty Expertise: The faculty members are responsible for teaching and mentoring students. It’s important to research the faculty’s credentials, research interests, and teaching experience. Look for faculty members who are active in their field and have a strong reputation for teaching and scholarship. You can often find this information on the university’s website or by contacting the department directly.
- Career Placement Services: Many universities offer career placement services to help students find jobs after graduation. These services can include career counseling, job fairs, and internship opportunities. It’s important to consider the university’s track record in placing graduates in their desired fields. You can find this information on the university’s website or by contacting the career services office.
Researching and Comparing Programs, What’s a bachelor’s degree
This section provides tips for researching and comparing different bachelor’s degree programs to make an informed decision.
- University Websites: Start by visiting the websites of universities that offer programs that interest you. Look for information about the program curriculum, faculty, career placement services, and student life. Many universities also offer virtual tours of their campuses and online resources for prospective students.
- Professional Organizations: If you’re interested in a specific career field, consider contacting professional organizations in that field. They can provide information about the skills and knowledge required for entry-level positions and recommend programs that align with industry standards.
- Networking: Talk to people who work in the field you’re interested in. Ask them about their educational background and what skills they consider essential for success. You can also ask for recommendations for programs that they believe are strong in their field.
The Importance of Choosing a Field of Study

Choosing a field of study is a crucial decision that can have a profound impact on your future career and overall life satisfaction. It’s not just about picking a subject you find interesting; it’s about finding a path that aligns with your passions, skills, and career aspirations.
The Impact of Choosing a Field That’s Not a Good Fit
Selecting a field of study that doesn’t resonate with your interests or career goals can lead to a variety of challenges. You might find yourself feeling unmotivated, unfulfilled, and even trapped in a career path that doesn’t align with your true passions.
- Dissatisfaction and Burnout: When you’re not genuinely interested in your field of study, it’s easy to become disengaged and lose motivation. This can lead to burnout, low productivity, and a lack of satisfaction in your work.
- Limited Career Opportunities: If you choose a field that doesn’t match your skills or interests, you may find yourself limited in terms of career opportunities. You might struggle to find jobs that utilize your skills or that provide you with the level of challenge and growth you desire.
- Financial Instability: A career in a field that doesn’t align with your passions can also lead to financial instability. If you’re not passionate about your work, you may be less motivated to advance your career, which can impact your earning potential.
The Future of Bachelor’s Degrees
The landscape of higher education is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, shifting workforce demands, and evolving societal needs. These changes are shaping the future of bachelor’s degrees, influencing their relevance, value, and accessibility.
Emerging Trends in Higher Education
The changing dynamics of higher education are impacting the traditional bachelor’s degree model.
- Online Learning: Online learning platforms are becoming increasingly popular, offering flexibility and accessibility to students worldwide. This trend is likely to continue, with universities offering more hybrid and fully online programs, potentially leading to a shift in the delivery and format of bachelor’s degrees.
- Micro-credentials and Stackable Credentials: The demand for specialized skills is growing, leading to the rise of micro-credentials and stackable credentials. These shorter, focused programs allow learners to acquire specific skills and knowledge, potentially offering an alternative or supplement to traditional bachelor’s degrees.
- Personalized Learning: Personalized learning pathways are gaining traction, allowing students to tailor their education to their individual interests and career goals. This trend could lead to more flexible and customizable bachelor’s degree programs, allowing students to acquire the specific knowledge and skills they need for their chosen field.
The Growing Demand for Specialized Skills
The future workforce will require individuals with specialized skills and the ability to adapt to changing technologies and work environments.
- Technical Skills: In fields like data science, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence, employers are seeking individuals with strong technical skills. Bachelor’s degree programs are adapting to meet this demand by incorporating these skills into their curricula.
- Soft Skills: Alongside technical skills, soft skills such as communication, critical thinking, and problem-solving are becoming increasingly valuable. Bachelor’s degree programs are emphasizing the development of these skills, recognizing their importance in today’s collaborative and dynamic work environments.
The Role of Bachelor’s Degrees in the Future Workforce
While the future of work is uncertain, bachelor’s degrees are likely to remain a valuable asset for individuals seeking to advance their careers.
- Higher Earning Potential: Individuals with a bachelor’s degree typically earn significantly more than those with only a high school diploma. This trend is expected to continue, as higher education remains a key factor in securing well-paying jobs.
- Career Advancement: A bachelor’s degree can open doors to more senior roles and leadership positions. In many industries, a bachelor’s degree is considered a prerequisite for career advancement.
- Lifelong Learning: The future workforce will require continuous learning and professional development. A bachelor’s degree can provide a foundation for lifelong learning, equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills to adapt to evolving job markets.
Outcome Summary
In a world that’s constantly evolving, a bachelor’s degree remains a valuable asset. It’s a symbol of intellectual curiosity, a foundation for lifelong learning, and a key to unlocking professional success. Whether you’re pursuing a passion, seeking career advancement, or simply striving for personal growth, a bachelor’s degree can be the stepping stone to achieving your goals.
Essential FAQs
What are the most common bachelor’s degree majors?
Some of the most popular majors include Business Administration, Nursing, Engineering, Education, and Psychology.
How long does it take to earn a bachelor’s degree?
A typical bachelor’s degree program takes four years of full-time study to complete.
Is a bachelor’s degree necessary for all careers?
While some professions require a bachelor’s degree, others may accept experience or specialized training. It’s best to research specific career paths to determine the required qualifications.
What are some alternative options to a bachelor’s degree?
There are alternative pathways to career success, such as vocational training, apprenticeships, or associate degrees.




