
- Overview of Public Administration
- Public Administration Bachelor Degree Programs
- Skills and Knowledge Acquired Through a Public Administration Degree
- The Role of Public Administration in Policy Formulation and Implementation
- Ethics and Accountability in Public Administration
- Emerging Trends in Public Administration
- Final Wrap-Up
- FAQ Explained: Public Administration Bachelor Degree
A Public Administration Bachelor Degree opens doors to a fulfilling career dedicated to serving the public good. This degree equips individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate the complexities of government and non-profit organizations, fostering a positive impact on communities and society as a whole.
From understanding the core principles of public administration and its historical evolution to exploring diverse career paths and the ethical considerations that guide public service, this degree provides a comprehensive foundation for those seeking to make a difference in the world.
Overview of Public Administration
Public administration is a vital field that governs the implementation of public policy and ensures the efficient and effective delivery of public services. It encompasses a broad range of activities, from managing government agencies to providing essential services like healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
Core Principles of Public Administration
The core principles of public administration provide a framework for ethical and effective governance. These principles guide public administrators in their decision-making and actions, ensuring accountability, transparency, and responsiveness to the public.
- Public Interest: Public administrators are entrusted with serving the public interest, prioritizing the well-being of the community over personal gain or political agendas. They are expected to act in a way that benefits the majority and promotes social justice.
- Accountability: Public administrators are accountable for their actions and decisions. They must be transparent in their operations and provide justifications for their choices. This accountability extends to both the public and elected officials.
- Efficiency and Effectiveness: Public administration aims to maximize the use of resources and achieve desired outcomes. This involves optimizing processes, minimizing waste, and ensuring that public services are delivered effectively.
- Neutrality: Public administrators should remain impartial and objective in their decision-making. They should not be influenced by personal biases, political affiliations, or external pressures. This neutrality ensures fairness and equity in the delivery of public services.
- Rule of Law: Public administration operates within a legal framework, adhering to established laws, regulations, and procedures. This adherence to the rule of law ensures consistency, predictability, and accountability in governance.
Historical Evolution of Public Administration, Public administration bachelor degree
Public administration has evolved significantly over time, adapting to changing societal needs and technological advancements.
- Ancient Civilizations: The earliest forms of public administration can be traced back to ancient civilizations like Egypt, Mesopotamia, and Greece. These societies had established systems for managing public works, collecting taxes, and maintaining order.
- Medieval Period: During the medieval period, public administration was largely centralized under monarchs and feudal lords. This system emphasized hierarchical structures and the collection of resources for military campaigns and royal patronage.
- Modern Era: The modern era saw a shift towards more democratic forms of governance. The rise of nation-states and the development of bureaucratic structures led to the emergence of professional public administration. This era witnessed the development of theories and principles that emphasized efficiency, effectiveness, and accountability.
- 20th Century: The 20th century witnessed significant advancements in public administration, including the development of new management techniques, the growth of the welfare state, and the increasing importance of public policy. These advancements were driven by factors such as globalization, technological change, and the need for social reform.
Significance of Public Administration in Modern Society
Public administration plays a crucial role in modern society, ensuring the smooth functioning of governments and the delivery of essential services to citizens.
- Economic Development: Public administration plays a vital role in promoting economic development by providing infrastructure, regulating markets, and fostering innovation. This includes managing transportation systems, providing education and healthcare, and supporting businesses.
- Social Welfare: Public administration is responsible for delivering essential social services such as healthcare, education, and social security. These services help to improve the well-being of citizens and reduce inequality.
- National Security: Public administration is crucial for maintaining national security by managing law enforcement agencies, providing defense capabilities, and responding to emergencies. This includes protecting citizens from threats and ensuring the stability of the nation.
- Environmental Protection: Public administration plays a critical role in protecting the environment by setting regulations, managing natural resources, and promoting sustainable practices. This includes addressing climate change, protecting biodiversity, and ensuring clean air and water.
- Democracy and Governance: Public administration is essential for ensuring democratic governance by implementing public policy, holding elections, and providing transparency and accountability. This includes ensuring the rule of law, protecting civil liberties, and promoting citizen participation.
Public Administration Bachelor Degree Programs
A bachelor’s degree in public administration (MPA) provides a comprehensive understanding of the principles, theories, and practices of public service. It equips graduates with the necessary skills and knowledge to excel in various public sector roles. These programs offer a solid foundation for careers in government, non-profit organizations, and international development.
Common Core Courses
Core courses in public administration bachelor programs cover fundamental concepts and principles that are essential for effective public service. These courses provide a broad understanding of the field, its history, and its evolving role in society.
- Introduction to Public Administration: This course introduces the fundamental concepts, principles, and history of public administration, exploring the role of government and its relationship with citizens.
- Public Policy Analysis: This course teaches students how to analyze public policies, evaluate their effectiveness, and develop recommendations for improvement.
- Public Finance and Budgeting: This course covers the principles of public finance, including budgeting, taxation, and public debt management.
- Organizational Behavior and Management: This course examines the dynamics of organizations, including leadership, motivation, and decision-making processes.
- Ethics in Public Service: This course explores ethical dilemmas and challenges faced by public administrators, emphasizing the importance of integrity, accountability, and public trust.
- Research Methods in Public Administration: This course introduces students to research methodologies and data analysis techniques used in public administration.
Specialization Tracks
Public administration bachelor programs often offer specialization tracks that allow students to focus their studies on specific areas of interest. These tracks provide in-depth knowledge and skills relevant to particular career paths within the public sector.
- Public Policy: This track focuses on the development, analysis, and implementation of public policies. Students learn about policy analysis techniques, advocacy strategies, and the political process.
- Non-Profit Management: This track prepares students for leadership roles in non-profit organizations. Students gain knowledge of non-profit governance, fundraising, program development, and community engagement.
- Public Health Administration: This track focuses on the management and delivery of public health services. Students learn about health policy, epidemiology, health promotion, and disease prevention.
- Environmental Policy and Management: This track explores the intersection of public policy and environmental issues. Students gain knowledge of environmental regulations, sustainable development, and environmental impact assessment.
- Urban Planning and Development: This track focuses on the planning and development of urban areas. Students learn about land use planning, transportation systems, and community development strategies.
Comparison of Public Administration Programs
Public administration bachelor programs vary across universities in terms of curriculum, faculty expertise, and program emphasis. Students should carefully consider their career goals and interests when choosing a program.
- Curriculum: Some programs may offer more specialized courses or elective options than others. Students should review the course catalogs and syllabuses to ensure the program aligns with their academic and professional aspirations.
- Faculty Expertise: The faculty members in a public administration program can significantly impact the quality of education. Students should research the faculty’s credentials, research interests, and teaching experience.
- Program Emphasis: Some programs may have a stronger emphasis on policy analysis, while others may focus more on management or public service delivery. Students should choose a program that aligns with their career goals and interests.
Skills and Knowledge Acquired Through a Public Administration Degree
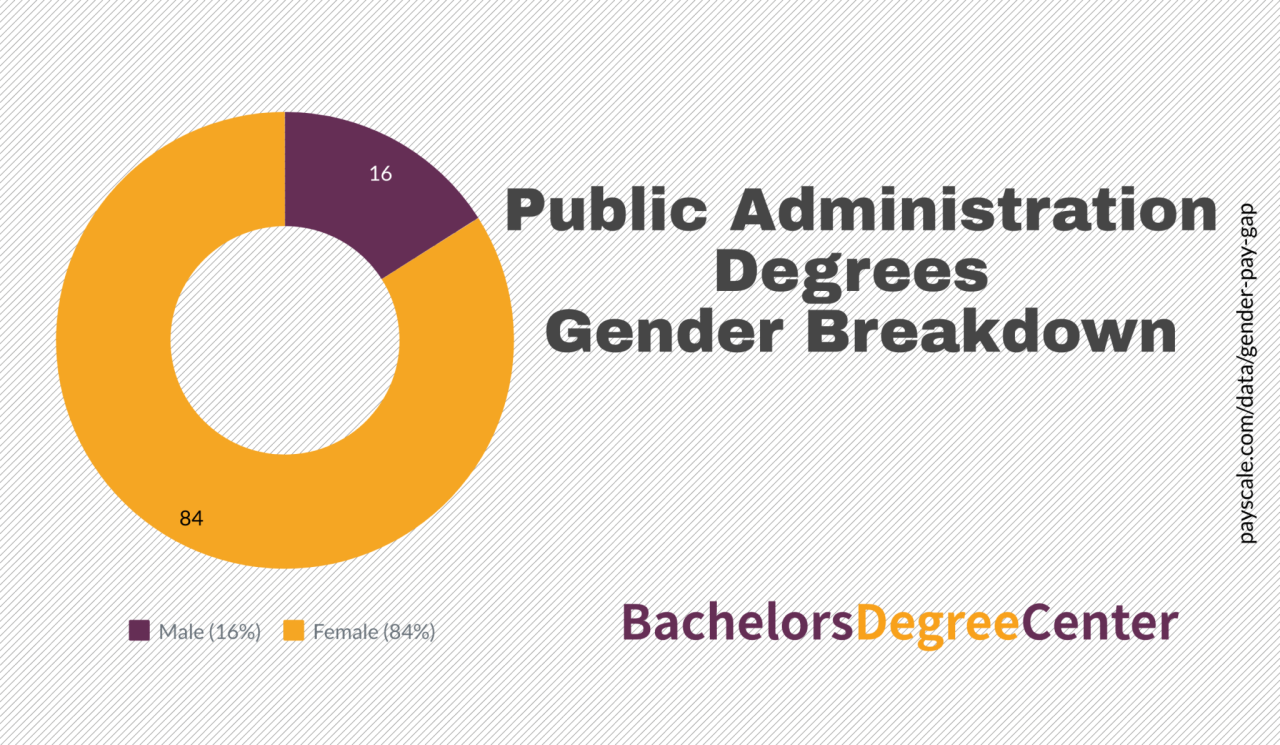
A public administration degree equips individuals with a comprehensive set of skills and knowledge essential for navigating the complex world of government and public service. The curriculum encompasses a broad range of disciplines, providing students with the tools and insights needed to effectively address public policy challenges and manage public organizations.
Key Skills Developed
The curriculum emphasizes the development of essential skills that are highly valued in public service and various other sectors.
- Analytical Skills: Public administration professionals are expected to analyze complex problems, gather and interpret data, and identify potential solutions. They must be able to evaluate policy options, assess their feasibility, and predict their potential impact. This requires strong analytical skills, including critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making abilities.
- Communication Skills: Effective communication is paramount in public administration. Professionals must be able to communicate complex ideas clearly and concisely, both orally and in writing. They need to engage with diverse stakeholders, including elected officials, community members, and other government agencies, and effectively convey information and build consensus. This involves mastering various communication styles, including public speaking, report writing, and negotiation.
- Leadership Skills: Public administration often involves leading and managing teams of individuals. Professionals need to motivate, inspire, and guide their teams towards shared goals. This requires strong leadership skills, including delegation, conflict resolution, and team-building abilities. They also need to understand and adapt to different leadership styles and situations.
- Organizational Skills: Public administration involves managing complex organizations with diverse stakeholders and competing priorities. Professionals must be able to effectively plan, organize, and implement programs and projects. They need to understand organizational structures, manage resources efficiently, and navigate bureaucratic processes. This requires strong organizational skills, including time management, project management, and resource allocation.
The Importance of Critical Thinking, Problem-Solving, and Communication Skills
Critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills are fundamental to effective public administration. These skills enable professionals to identify and analyze complex issues, develop innovative solutions, and effectively communicate their findings and recommendations to stakeholders.
- Critical Thinking: Public administration professionals are constantly faced with complex problems that require critical thinking skills. They must be able to analyze information, identify biases, evaluate assumptions, and draw logical conclusions. Critical thinking allows them to objectively assess situations, consider multiple perspectives, and make informed decisions.
- Problem-Solving: Public administration is inherently problem-oriented. Professionals are expected to identify and address public policy challenges, implement programs to improve public services, and manage organizational issues. Effective problem-solving requires a systematic approach, including defining the problem, exploring potential solutions, evaluating their feasibility, and implementing the chosen solution.
- Communication Skills: Communication skills are essential for building relationships, fostering collaboration, and ensuring effective public service delivery. Professionals must be able to communicate effectively with diverse stakeholders, including elected officials, community members, and other government agencies. This involves being able to clearly articulate ideas, listen attentively, and respond appropriately to feedback.
Knowledge Base in Public Administration
Public administration programs provide students with a comprehensive knowledge base in key areas relevant to public service.
- Policy Analysis: Public administration professionals need to understand the policy process, from policy formulation to implementation and evaluation. They must be able to analyze policy options, assess their impact, and recommend effective solutions. This involves understanding the principles of policy analysis, including cost-benefit analysis, stakeholder analysis, and program evaluation.
- Public Finance: Public administration professionals need to understand the principles of public finance, including budgeting, taxation, and debt management. They must be able to manage public resources effectively, allocate funds appropriately, and ensure fiscal responsibility. This involves understanding the concepts of revenue generation, expenditure control, and financial reporting.
- Organizational Management: Public administration professionals need to understand the principles of organizational management, including leadership, organizational structure, and human resource management. They must be able to effectively manage public organizations, motivate employees, and foster a productive work environment. This involves understanding the concepts of organizational design, strategic planning, and performance management.
The Role of Public Administration in Policy Formulation and Implementation

Public administration plays a pivotal role in the process of policy formulation and implementation, ensuring that government policies are effectively translated into action and achieve their intended outcomes. Public administration professionals are involved in every stage of the policy cycle, from identifying problems and formulating solutions to implementing and evaluating policies.
Steps Involved in the Policy-Making Process
The policy-making process is a complex and iterative cycle that involves various actors and stages. Understanding these steps is crucial for comprehending the role of public administration in policy development and implementation.
- Problem Identification and Agenda Setting: This initial stage involves identifying societal issues that require government attention. Public administrators gather data, analyze trends, and engage with stakeholders to understand the nature and scope of the problem.
- Policy Formulation: Once a problem is identified, policy options are developed. Public administrators conduct research, consult with experts, and consider various perspectives to propose potential solutions. This stage involves drafting policy proposals, analyzing their feasibility, and assessing their potential impact.
- Policy Legitimization: This stage involves gaining political support for the proposed policy. Public administrators engage in lobbying, public relations, and advocacy to build consensus among policymakers and the public. This may involve presenting policy proposals to legislative bodies, securing funding, and obtaining necessary approvals.
- Policy Implementation: Once a policy is approved, public administrators play a critical role in putting it into action. This involves developing detailed plans, allocating resources, and coordinating with various agencies and stakeholders. Public administrators also monitor implementation progress and address any challenges that arise.
- Policy Evaluation: The final stage involves assessing the effectiveness of the policy. Public administrators collect data, analyze outcomes, and identify areas for improvement. This feedback loop informs future policy development and ensures that policies remain relevant and responsive to evolving needs.
Contributions of Public Administration Professionals to Policy Development and Implementation
Public administration professionals contribute significantly to the policy-making process by:
- Providing technical expertise: Public administrators possess specialized knowledge in areas such as budgeting, program evaluation, and policy analysis. They leverage this expertise to inform policy development, assess the feasibility of proposed solutions, and identify potential challenges.
- Facilitating stakeholder engagement: Public administrators act as intermediaries between government agencies, the public, and other stakeholders. They facilitate dialogue, gather input, and ensure that diverse perspectives are considered in policy development and implementation.
- Developing and implementing program plans: Public administrators are responsible for translating policy into concrete action plans. They develop detailed program guidelines, allocate resources, and monitor implementation progress to ensure that policies are effectively carried out.
- Conducting program evaluations: Public administrators assess the effectiveness of policies and programs through data collection, analysis, and reporting. They identify areas for improvement and provide recommendations for future policy development.
Challenges in Translating Policy into Practice
While public administration plays a vital role in policy implementation, several challenges can arise in translating policy into practice:
- Resource constraints: Limited funding and personnel can hinder effective implementation. Public administrators must prioritize resources, make tough decisions, and ensure that available resources are used efficiently.
- Political pressures: Policy implementation can be influenced by political factors, such as changing priorities, electoral cycles, and pressure from special interest groups. Public administrators must navigate these pressures while adhering to the principles of good governance and public service.
- Bureaucratic inertia: Established procedures and regulations can create obstacles to policy implementation. Public administrators must work within existing systems, but also identify opportunities for streamlining processes and improving efficiency.
- Public resistance: Policy implementation can face resistance from the public if they perceive the policy as unfair, ineffective, or contrary to their interests. Public administrators must engage with the public, address concerns, and build trust in order to facilitate policy acceptance.
Ethics and Accountability in Public Administration
Public administration is a field that demands the highest ethical standards. Public administrators are entrusted with the responsibility of serving the public interest, and their actions have a direct impact on the lives of citizens. Therefore, ethical principles are essential to guide their conduct and ensure that they uphold the values of integrity, fairness, and accountability.
Ethical Principles in Public Administration
Public administration is governed by a set of ethical principles that guide the conduct of public administrators. These principles are designed to ensure that public administrators act in a way that is consistent with the public interest and that they are accountable for their actions.
- Public Interest: Public administrators must prioritize the needs of the public over their own personal interests. They should make decisions that are in the best interest of the community and avoid actions that could benefit them personally or their friends and family.
- Integrity: Public administrators must be honest and trustworthy. They should avoid conflicts of interest and act with transparency and accountability.
- Impartiality: Public administrators must treat all individuals fairly and equitably, regardless of their race, religion, gender, or other personal characteristics. They should avoid bias and discrimination in their decision-making.
- Accountability: Public administrators are accountable for their actions and decisions. They should be transparent about their activities and be willing to answer for their choices.
- Professionalism: Public administrators should maintain a high standard of professional conduct. They should be respectful of others, be honest in their dealings, and avoid any actions that could damage the reputation of the public service.
Transparency and Accountability in Public Service
Transparency and accountability are crucial for maintaining public trust in government. When public administrators are transparent about their decisions and actions, citizens can hold them accountable for their performance. This helps to ensure that government is responsive to the needs of the people and that it operates in a fair and ethical manner.
- Openness and Disclosure: Public administrators should make information about their activities readily available to the public. This includes information about their budgets, their policies, and their decision-making processes.
- Public Participation: Citizens should have opportunities to participate in the decision-making process. This can be done through public hearings, online forums, and other mechanisms that allow citizens to express their views and concerns.
- Independent Oversight: Independent oversight bodies, such as audit offices and ethics commissions, can help to ensure that public administrators are accountable for their actions. These bodies can investigate complaints of misconduct and make recommendations for improvements.
Ethical Dilemmas Faced by Public Administrators
Public administrators often face ethical dilemmas in their work. These dilemmas can arise from conflicts of interest, pressure from special interest groups, or the need to balance competing values.
- Conflicts of Interest: Public administrators may be faced with situations where their personal interests conflict with their duty to serve the public interest. For example, a public administrator may be asked to approve a project that would benefit a company in which they have a financial stake.
- Pressure from Special Interest Groups: Public administrators may be pressured by special interest groups to make decisions that benefit their own interests, even if those decisions are not in the best interest of the public. For example, a public administrator may be pressured by a developer to approve a zoning change that would allow them to build a large shopping mall, even if the mall would have a negative impact on the local community.
- Balancing Competing Values: Public administrators may be faced with situations where they need to balance competing values. For example, a public administrator may need to balance the need for economic development with the need to protect the environment.
Emerging Trends in Public Administration

Public administration is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of society. Technological advancements, demographic shifts, and global challenges are reshaping the landscape of public service. Understanding emerging trends in public administration is crucial for professionals to adapt and innovate, ensuring effective and efficient service delivery.
The Impact of Technology on Public Administration
Technological advancements have profoundly impacted public administration, transforming how governments operate and interact with citizens. The rise of e-governance, big data analytics, artificial intelligence, and social media platforms has created new opportunities and challenges for public administrators.
- E-governance: Online platforms and mobile applications have enabled governments to provide services, collect data, and engage with citizens more efficiently. This has led to increased transparency, accountability, and accessibility to public services.
- Big Data Analytics: The ability to collect and analyze vast amounts of data allows governments to make more informed decisions based on evidence and insights. This can help in areas such as resource allocation, policy development, and public safety.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI technologies, such as chatbots and machine learning algorithms, can automate tasks, improve efficiency, and personalize public services. This can help governments to provide tailored services and address individual needs more effectively.
- Social Media: Social media platforms have become important tools for public engagement, allowing governments to communicate with citizens, gather feedback, and respond to concerns in real-time.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
Data-driven decision-making is becoming increasingly important in public administration, as governments strive to allocate resources effectively and address complex challenges based on evidence. This approach involves using data analysis to inform policy development, program evaluation, and resource allocation.
- Performance Measurement: Data analytics can be used to track the effectiveness of public programs and services, allowing governments to identify areas for improvement and optimize resource allocation.
- Predictive Analytics: Data can be used to forecast future trends and anticipate potential problems, enabling governments to proactively address challenges and allocate resources accordingly.
- Citizen Feedback: Online surveys, social media monitoring, and other data collection methods can be used to gather feedback from citizens, providing insights into public needs and preferences.
Citizen Engagement
Citizen engagement is a key trend in public administration, as governments recognize the importance of involving citizens in decision-making processes. This approach aims to empower citizens, foster transparency, and improve the effectiveness of public services.
- Participatory Budgeting: This approach allows citizens to directly influence how public funds are allocated, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability.
- Open Data Initiatives: Governments are increasingly making public data available to citizens, empowering them to analyze information and hold governments accountable.
- Citizen Feedback Mechanisms: Online platforms and mobile applications provide channels for citizens to provide feedback, report problems, and participate in public consultations.
Final Wrap-Up
By pursuing a Public Administration Bachelor Degree, individuals gain valuable skills and knowledge, becoming equipped to address critical challenges and contribute to the well-being of society. From policy analysis and implementation to fostering citizen engagement and ethical leadership, this degree prepares graduates to navigate the evolving landscape of public service and make a meaningful impact on the world around them.
FAQ Explained: Public Administration Bachelor Degree
What are the job prospects for public administration graduates?
Public administration graduates are highly sought after in various sectors, including government, non-profit organizations, and private companies. They can pursue careers in policy analysis, program management, community development, and more.
Is a public administration degree worth it?
A public administration degree can be highly valuable, equipping individuals with the skills and knowledge to make a difference in the world. It opens doors to fulfilling careers and opportunities for personal and professional growth.
What are the admission requirements for public administration programs?
Admission requirements vary depending on the university and program. Typically, a high school diploma or equivalent is required, along with specific academic prerequisites and standardized test scores.





Thanks for posting. I really enjoyed reading it, especially because it addressed my problem. http://www.hairstylesvip.com It helped me a lot and I hope it will help others too.
Good day! This is my first visit to your blog! We are a team of volunteers and starting a new project in a community in the same niche. Your blog provided us valuable information to work on. You have done a marvellous job!
What i don’t realize is actually how you are not actually much more well-liked than you might be right now. You are so intelligent. You realize thus considerably relating to this subject, produced me personally consider it from a lot of varied angles. Its like women and men aren’t fascinated unless it抯 one thing to accomplish with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs nice. Always maintain it up!
We’re a bunch of volunteers and starting a brand new scheme in our community. Your website provided us with valuable info to work on. You’ve performed a formidable task and our entire group will probably be thankful to you.
I want to thank you for your assistance and this post. It’s been great. http://www.hairstylesvip.com