- Definition and Scope of Pre-Authorization
-
Pre-Authorization in Healthcare
- The Role of Pre-Authorization in Managing Healthcare Costs
- The Process of Obtaining Pre-Authorization for Medical Procedures
- Common Reasons for Pre-Authorization Denials in Healthcare
- Best Practices for Healthcare Providers to Navigate Pre-Authorization Requirements
- A Typical Healthcare Pre-Authorization Process Flowchart
-
Legal and Regulatory Aspects of Pre-Authorization
- Relevant Laws and Regulations Governing Pre-Authorization
- Implications of Non-Compliance with Pre-Authorization Requirements
- Ethical Considerations Related to Pre-Authorization Practices
- Examples of Legal Cases Involving Disputes Over Pre-Authorization
- Key Legal Considerations for Businesses Using Pre-Authorization
- Technological Aspects of Pre-Authorization
-
Future Trends in Pre-Authorization
- Emerging Trends in Pre-Authorization Technology and Processes
- Challenges and Opportunities in Pre-Authorization
- Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning on Pre-Authorization
- Predictions for the Evolution of Pre-Authorization in Different Industries
- Scenario: Impact of a Significant Technological Advancement
- Final Review
- Commonly Asked Questions
Pre-authorization, a seemingly simple term, underpins a vast and complex web of processes across numerous industries. From securing healthcare procedures to authorizing financial transactions, pre-authorization acts as a gatekeeper, ensuring legitimacy and mitigating risk. This exploration delves into the multifaceted world of pre-authorization, examining its various applications, benefits, and challenges.
We’ll journey through healthcare’s intricate pre-authorization landscape, navigating the complexities of securing approvals for medical treatments and understanding the potential for denials. Then, we’ll shift our focus to the financial realm, exploring the security implications of pre-authorization in online transactions and the ever-present threat of fraud. Finally, we’ll touch upon the legal and regulatory frameworks governing pre-authorization, and explore how technology is shaping its future.
Definition and Scope of Pre-Authorization
Pre-authorization, a critical process across numerous sectors, involves obtaining prior approval for a service or transaction before it’s executed. This proactive approach aims to verify eligibility, ensure coverage, and manage costs effectively. The specific procedures and requirements vary considerably depending on the context.
Pre-Authorization in Different Contexts
Pre-authorization manifests differently across various industries. In healthcare, it typically involves a provider contacting an insurance company to confirm coverage for a specific procedure or medication before treatment begins. This prevents patients from incurring unexpected out-of-pocket expenses. In the finance sector, pre-authorization might refer to a merchant obtaining approval from a card issuer for a large transaction, minimizing the risk of fraudulent activity or exceeding credit limits. Similarly, travel agencies often pre-authorize funds on credit cards to secure bookings for flights or accommodations. The common thread is the upfront verification to mitigate risk and ensure compliance with established guidelines.
Examples of Pre-Authorization Processes
A healthcare provider seeking pre-authorization for a patient’s knee replacement surgery would submit a detailed request to the insurance company, including medical records and procedure codes. The insurer then reviews the request to determine medical necessity and coverage. In contrast, a retailer processing a large online purchase might use a pre-authorization service to verify the cardholder’s available credit before completing the sale. A travel agency, booking a luxury vacation package, might pre-authorize a significant amount on the client’s card to guarantee the reservation. These examples highlight the diverse applications and varying complexities of pre-authorization across different sectors.
Objectives of Pre-Authorization Procedures
The primary objectives of pre-authorization are threefold: cost control, fraud prevention, and ensuring compliance. Cost control is achieved by verifying coverage and preventing unnecessary or unapproved procedures or transactions. Fraud prevention is addressed by validating the legitimacy of requests and preventing unauthorized access or usage. Compliance ensures adherence to regulatory requirements and internal policies, protecting both the provider and the customer.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Pre-Authorization Systems
Implementing pre-authorization systems offers several advantages, including reduced financial risk, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction through clearer expectations regarding costs and coverage. However, drawbacks exist, such as increased administrative burden, potential delays in service delivery, and the possibility of rejected requests leading to frustration for both providers and customers. The balance between benefits and drawbacks depends heavily on the specific implementation and the industry context.
Comparison of Pre-Authorization with Other Authorization Methods
| Feature | Pre-Authorization | Real-time Authorization | Post-Authorization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Timing | Before service/transaction | During service/transaction | After service/transaction |
| Risk | Low risk of unauthorized spending | Medium risk of unauthorized spending | High risk of unauthorized spending |
| Efficiency | Can improve efficiency by preventing unnecessary work | Efficient for immediate transactions | Least efficient, may involve disputes |
| Cost | May involve upfront administrative costs | Generally lower administrative costs | Potentially high costs due to disputes and reversals |
Pre-Authorization in Healthcare
Pre-authorization in healthcare is a crucial process that plays a significant role in managing healthcare costs and ensuring the appropriate use of resources. It involves obtaining approval from a health insurance provider before a medical procedure or service is performed. This process helps to control expenses by verifying the medical necessity of the procedure and confirming coverage under the patient’s insurance plan.
The Role of Pre-Authorization in Managing Healthcare Costs
Pre-authorization helps manage healthcare costs by several mechanisms. Firstly, it ensures that only medically necessary procedures are performed, reducing unnecessary spending on treatments that may not provide significant clinical benefit. Secondly, it allows insurers to negotiate prices with healthcare providers beforehand, leading to potentially lower costs. Finally, it helps to identify and prevent fraudulent or abusive billing practices. By streamlining the approval process and verifying coverage upfront, pre-authorization minimizes the risk of patients receiving unexpected bills for services not covered by their insurance.
The Process of Obtaining Pre-Authorization for Medical Procedures
The process of obtaining pre-authorization typically begins with the healthcare provider submitting a request to the patient’s insurance company. This request usually includes details about the patient, the proposed procedure, its medical necessity, and supporting medical documentation. The insurance company then reviews the request, assessing factors such as the patient’s medical history, the appropriateness of the procedure, and its alignment with accepted medical guidelines. Following the review, the insurer either approves or denies the request, informing both the provider and the patient of the decision. If approved, the pre-authorization grants permission to proceed with the procedure.
Common Reasons for Pre-Authorization Denials in Healthcare
Pre-authorization denials can stem from several factors. These include insufficient or inadequate medical documentation justifying the necessity of the procedure, the procedure not being covered under the patient’s specific insurance plan, the procedure not being considered medically necessary according to the insurer’s guidelines, or the patient not meeting the plan’s criteria for coverage. Another common reason is errors in the pre-authorization request itself, such as incorrect patient information or missing required documentation.
Best Practices for Healthcare Providers to Navigate Pre-Authorization Requirements
Effective navigation of pre-authorization requires proactive measures. Healthcare providers should maintain up-to-date knowledge of their payer’s specific pre-authorization requirements. This includes understanding the necessary documentation, the timelines for submission, and the specific criteria for approval. Accurate and comprehensive documentation is critical. Submitting requests well in advance of the scheduled procedure minimizes delays. Furthermore, establishing clear communication channels with insurance companies helps resolve any ambiguities or issues promptly. Finally, implementing a robust system for tracking pre-authorization requests and their status ensures efficient management of the process.
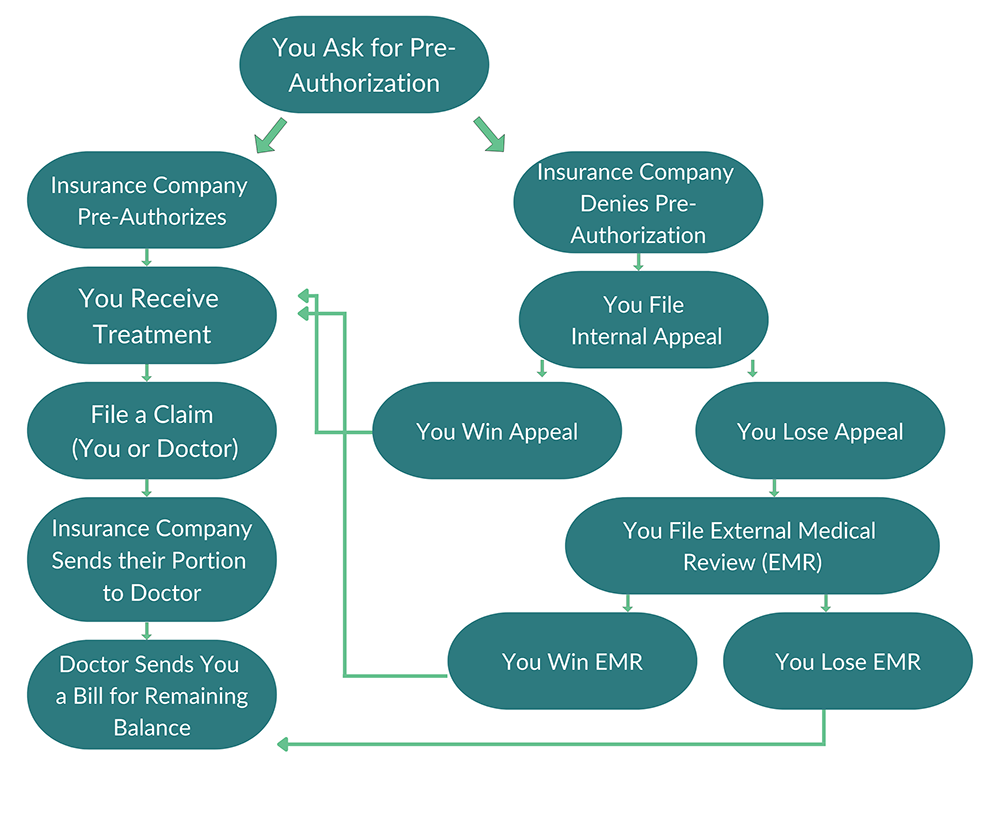
A Typical Healthcare Pre-Authorization Process Flowchart
A typical healthcare pre-authorization process can be visualized as follows:
[Descriptive Flowchart]
The flowchart would begin with a box labeled “Patient requests medical procedure”. An arrow would lead to a box labeled “Provider submits pre-authorization request to insurer,” which contains details such as the patient’s information, procedure details, and medical necessity documentation. An arrow would then lead to a decision diamond labeled “Insurer reviews request”. From the diamond, one arrow would lead to a box labeled “Request Approved – Proceed with procedure”, while another arrow leads to a box labeled “Request Denied – Reasons for denial provided”. A final arrow from both boxes would lead to a box labeled “Provider and patient notified of decision”. This illustrates the sequential steps involved, from initial request to final notification.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects of Pre-Authorization
Pre-authorization, while streamlining healthcare processes and potentially reducing costs, operates within a complex legal and regulatory framework that varies significantly across jurisdictions. Understanding these legal aspects is crucial for both healthcare providers and payers to ensure compliance and avoid potential liabilities. This section will explore the relevant laws, potential consequences of non-compliance, ethical considerations, and illustrative legal cases.
Relevant Laws and Regulations Governing Pre-Authorization
The legal landscape surrounding pre-authorization is multifaceted and depends heavily on the specific country, state, or region. In the United States, for example, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) indirectly influences pre-authorization practices by promoting managed care and cost-containment strategies. State-level regulations may also dictate specific requirements for pre-authorization processes within certain healthcare settings or for particular services. Similarly, in the European Union, member states have varying regulations concerning healthcare financing and access, which impact how pre-authorization is implemented. Canada’s provincial healthcare systems each have their own rules and guidelines related to pre-authorization, often embedded within broader healthcare funding agreements. International organizations like the WHO also provide guidance on healthcare access and quality, which can inform best practices for pre-authorization but don’t constitute legally binding regulations in themselves. Therefore, a thorough understanding of the specific jurisdictional regulations is paramount.
Implications of Non-Compliance with Pre-Authorization Requirements
Failure to comply with pre-authorization requirements can result in a range of serious consequences. Healthcare providers may face denial of claims, resulting in significant financial losses. In some cases, non-compliance can lead to penalties, fines, or even legal action from regulatory bodies. Furthermore, reputational damage can occur, impacting patient trust and referrals. For payers, non-compliance might lead to increased healthcare expenditures due to unauthorized services and inefficient resource allocation. The severity of the consequences varies depending on the specific regulations violated and the jurisdiction involved. For instance, a single instance of non-compliance might result in a warning, while repeated violations could lead to more substantial penalties.
Ethical Considerations Related to Pre-Authorization Practices
Ethical considerations in pre-authorization revolve around ensuring patient access to necessary care while maintaining responsible resource allocation. A key concern is the potential for delays in treatment due to bureaucratic hurdles in the pre-authorization process. This can have serious implications for patients with time-sensitive conditions. Transparency and clear communication with patients regarding the pre-authorization process are essential to mitigate ethical concerns. Moreover, there are potential biases embedded within pre-authorization criteria, potentially leading to inequitable access to care based on factors such as socioeconomic status or geographic location. Striking a balance between cost-containment and patient well-being is a central ethical challenge in the implementation of pre-authorization systems.
Examples of Legal Cases Involving Disputes Over Pre-Authorization
While specific details of legal cases are often confidential or not publicly available, the general nature of disputes frequently revolves around denials of pre-authorization for medically necessary procedures or treatments. Cases may involve patients challenging the payer’s decision based on arguments of medical necessity or procedural errors in the pre-authorization process. Healthcare providers may also be involved in legal disputes, particularly if they performed services without proper pre-authorization and subsequently faced payment denials. These cases often highlight the complexities and ambiguities inherent in pre-authorization guidelines and the potential for significant financial and emotional consequences for all parties involved. Many such cases are settled outside of court, preventing public access to details.
Key Legal Considerations for Businesses Using Pre-Authorization
- Thorough understanding and compliance with all applicable federal, state, and local regulations.
- Establishment of clear and transparent internal policies and procedures for handling pre-authorization requests.
- Implementation of robust documentation systems to track pre-authorization requests and approvals.
- Maintenance of accurate and up-to-date records of all communications with payers and patients regarding pre-authorization.
- Development of processes to address and resolve disputes efficiently and fairly.
- Provision of adequate training to staff on pre-authorization procedures and relevant regulations.
- Regular review and update of policies and procedures to ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
Technological Aspects of Pre-Authorization
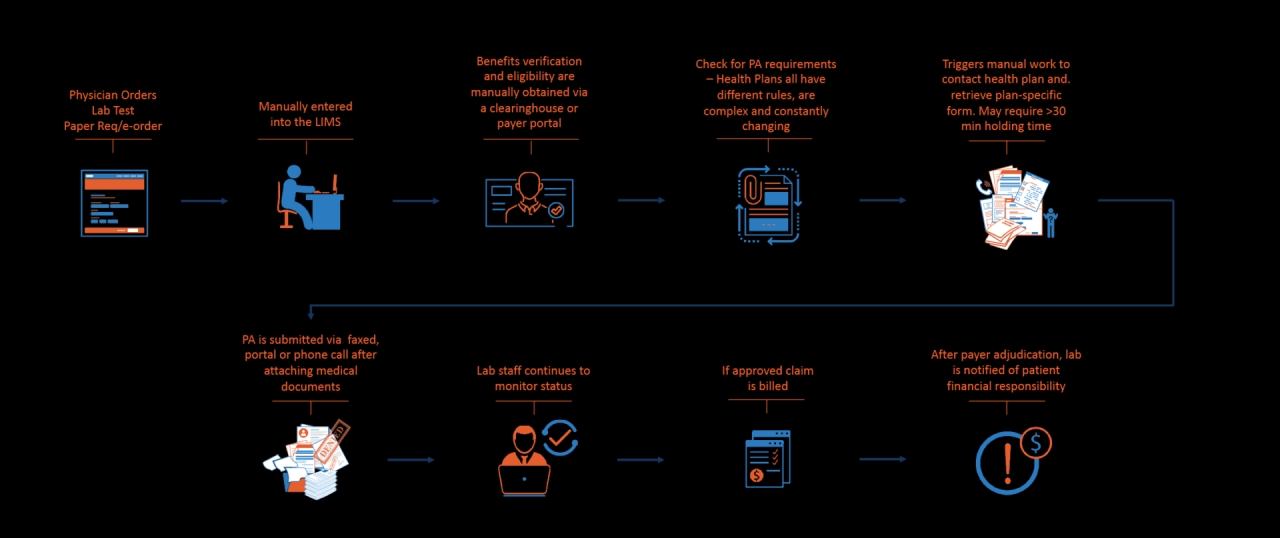
The increasing complexity and volume of healthcare claims necessitate efficient pre-authorization processes. Technology plays a crucial role in streamlining these processes, improving accuracy, and reducing administrative burdens for both providers and payers. Automation, sophisticated software, and seamless integration with existing systems are key components of modern pre-authorization management.
Automation of Pre-Authorization Processes
Technology significantly automates various stages of pre-authorization, from initial request submission to final approval or denial. This automation reduces manual data entry, minimizes human error, and accelerates the overall process. For instance, systems can automatically verify patient eligibility, check for prior authorizations, and compare requested services against the patient’s coverage. This automated validation reduces delays and improves the overall efficiency of the process.
Software and Systems for Pre-Authorization Management
Several software solutions and systems are specifically designed for pre-authorization management. These range from standalone applications to integrated platforms that connect with electronic health records (EHRs) and other healthcare information systems. Examples include specialized pre-authorization software offered by companies such as Availity, Change Healthcare, and ZirMed. These systems often incorporate features such as automated claim submission, real-time eligibility verification, and comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities. They can also facilitate communication between providers and payers, providing a centralized platform for managing the entire pre-authorization workflow.
Integration with Other Business Systems
Effective pre-authorization systems integrate seamlessly with other business systems within a healthcare organization or payer network. This integration ensures data consistency and reduces the need for manual data transfer. For example, integration with EHR systems allows for automatic retrieval of patient information and medical records, eliminating the need for manual data entry. Integration with billing systems allows for streamlined claim processing and reduces the risk of payment delays. Similarly, integration with provider portals enables real-time status updates and facilitates efficient communication.
Benefits and Challenges of Automated Pre-Authorization Systems
Implementing automated pre-authorization systems offers numerous benefits, including reduced processing times, improved accuracy, lower administrative costs, and enhanced patient satisfaction. However, challenges exist. These include the initial investment costs associated with software acquisition and implementation, the need for comprehensive staff training, and the potential for system integration complexities. Data security and compliance with relevant regulations are also critical considerations. For example, a large hospital system might experience significant cost savings from reduced administrative staff and faster claim processing, but needs to account for the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs.
Use of APIs and Other Technologies in Streamlining Workflows
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) play a vital role in streamlining pre-authorization workflows by enabling seamless data exchange between different systems. APIs allow for real-time communication between provider systems, payer systems, and other relevant platforms. For example, an API can facilitate the automatic transmission of pre-authorization requests, reducing the need for manual submissions. Other technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA) can further automate repetitive tasks, improving efficiency and reducing human error. The use of cloud-based solutions also enhances accessibility and scalability, enabling healthcare organizations to adapt to changing needs and volumes.
Future Trends in Pre-Authorization

Pre-authorization, while currently a necessary but often cumbersome process, is poised for significant transformation. The convergence of technological advancements and evolving healthcare landscapes is driving a shift towards more streamlined, efficient, and patient-centric systems. This section explores the emerging trends shaping the future of pre-authorization across various industries.
Emerging Trends in Pre-Authorization Technology and Processes
Several technological advancements are streamlining pre-authorization. Real-time eligibility verification systems, integrated with electronic health records (EHRs), are reducing delays and administrative burdens. The rise of APIs and data exchange platforms allows for seamless information flow between payers, providers, and patients. Blockchain technology offers the potential for enhanced security and transparency in the authorization process, ensuring data integrity and reducing the risk of fraud. Furthermore, the development of user-friendly interfaces and mobile applications is making the process more accessible and convenient for all stakeholders.
Challenges and Opportunities in Pre-Authorization
The future of pre-authorization presents both challenges and opportunities. One key challenge lies in ensuring data interoperability across disparate systems. Differences in data formats and standards can hinder seamless information exchange. Another challenge involves addressing security concerns related to sensitive patient data. Robust security measures are crucial to prevent data breaches and protect patient privacy. Opportunities exist in leveraging advanced analytics to identify patterns of utilization and predict potential denials, allowing for proactive intervention and improved efficiency. The development of intelligent automation can further streamline processes and reduce manual effort.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning on Pre-Authorization
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming pre-authorization by automating tasks, improving accuracy, and enhancing decision-making. AI-powered systems can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns, predict denials, and personalize the authorization process. ML algorithms can learn from past data to optimize authorization workflows and reduce processing times. For example, an AI system could analyze claims data to identify high-risk cases requiring closer scrutiny, freeing up human reviewers to focus on complex situations. This leads to faster turnaround times and improved accuracy in authorization decisions. Furthermore, AI can personalize the pre-authorization experience by tailoring communication and support based on individual patient needs.
Predictions for the Evolution of Pre-Authorization in Different Industries
In healthcare, we can anticipate a move towards fully automated pre-authorization for routine procedures, with AI handling the majority of straightforward cases. The focus will shift towards managing complex cases requiring human intervention. In the insurance industry, AI-driven fraud detection systems will play a crucial role in minimizing fraudulent claims. In the travel industry, pre-authorization systems may become more integrated with booking platforms, streamlining the process for customers. The financial services sector might see AI-powered systems analyzing transaction data to automate pre-authorization for payments and credit approvals.
Scenario: Impact of a Significant Technological Advancement
Imagine a future where a sophisticated AI system, leveraging advanced natural language processing and predictive analytics, is integrated into the pre-authorization process. This system can instantly analyze a patient’s medical history, procedure details, and insurance coverage to determine eligibility and generate an authorization in real-time. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and reduces processing times from days to seconds. The system could also proactively identify potential issues and alert providers to necessary documentation, preventing denials and ensuring smooth patient care. This scenario highlights the potential for significantly reduced administrative burden, improved patient experience, and cost savings for healthcare providers and payers.
Final Review
Pre-authorization, while often perceived as a mere formality, plays a critical role in safeguarding resources and mitigating risks across various sectors. Its evolution, driven by technological advancements and regulatory changes, continues to shape how businesses operate and individuals access services. Understanding its intricacies is key to navigating the complexities of modern transactions and ensuring smooth, secure processes. The future of pre-authorization promises greater efficiency and security, further solidifying its importance in the digital age.
Commonly Asked Questions
What happens if my pre-authorization is denied?
A denial typically requires you to appeal the decision, providing additional information or exploring alternative options. The specific process varies depending on the industry and provider.
How long does pre-authorization usually take?
Processing times vary widely depending on the complexity of the request and the provider’s workload. Some requests may be processed within hours, while others can take several days or even weeks.
Is pre-authorization required for all medical procedures?
No, not all medical procedures require pre-authorization. The necessity depends on factors like the type of procedure, insurance coverage, and the provider’s policies.
Can I pre-authorize a transaction without a credit card?
Some systems allow pre-authorization using alternative payment methods, but this depends on the specific merchant and payment processor.


