
- Introduction to Forex Trading
- Understanding Currency Pairs: Online Currency Trading Forex
- Forex Trading Platforms and Tools
- Fundamental Analysis in Forex Trading
- Technical Analysis in Forex Trading
- Forex Trading Strategies
- Risk Management in Forex Trading
- The Future of Forex Trading
- Last Recap
- Quick FAQs
Online currency trading forex, also known as foreign exchange trading, is a dynamic and exciting market where individuals and institutions trade currencies around the world. It is the largest and most liquid financial market globally, with trillions of dollars exchanged daily. This vast market offers both opportunities and risks, making it essential for traders to have a comprehensive understanding of the fundamentals and strategies involved.
Forex trading allows participants to speculate on the price movements of different currency pairs, profiting from the fluctuations in exchange rates. The market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, offering flexibility and accessibility to traders worldwide. However, the fast-paced nature of forex trading requires discipline, risk management, and a solid understanding of market dynamics to succeed.
Introduction to Forex Trading
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the simultaneous buying of one currency and selling of another. It is the largest and most liquid financial market globally, with trillions of dollars exchanged daily. Forex trading plays a crucial role in facilitating international trade, investment, and tourism by enabling businesses and individuals to convert currencies for various purposes.
Key Characteristics of Forex Trading
Forex trading possesses several unique characteristics that distinguish it from other financial markets. These characteristics make Forex trading attractive to both experienced and novice investors.
- High Liquidity: The Forex market is highly liquid, meaning that currencies can be bought and sold quickly and easily at any time. This is due to the massive volume of transactions that occur daily, ensuring that there are always buyers and sellers available. This high liquidity makes it easier for traders to enter and exit positions without significantly impacting the market price.
- 24/5 Availability: Unlike stock markets that operate during specific hours, the Forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week. This global nature of the market is due to the involvement of traders from various time zones around the world. The continuous trading allows traders to take advantage of market opportunities at any time, regardless of their location.
- Leverage: Forex trading offers leverage, which allows traders to control a larger position in the market with a smaller amount of capital. Leverage magnifies both potential profits and losses, making it a powerful tool for experienced traders but also a risky one for beginners. It is essential to understand the risks associated with leverage and use it responsibly.
History of Forex Trading
The history of Forex trading dates back to the early days of international trade. In the past, currencies were exchanged through a network of banks and brokers, which facilitated the conversion of currencies for merchants and travelers. The development of electronic trading platforms in the late 20th century revolutionized Forex trading, making it more accessible to individuals and institutions worldwide.
The growth of Forex trading has been driven by several factors, including:
- Globalization: The increasing interconnectedness of the global economy has led to a rise in international trade and investment, driving the demand for foreign exchange services.
- Technological Advancements: The development of electronic trading platforms and internet access has made Forex trading more accessible and efficient, allowing traders to participate in the market from anywhere in the world.
- Increased Volatility: The global financial crisis of 2008 and other economic events have led to increased volatility in currency markets, attracting more traders seeking to profit from price fluctuations.
Understanding Currency Pairs: Online Currency Trading Forex
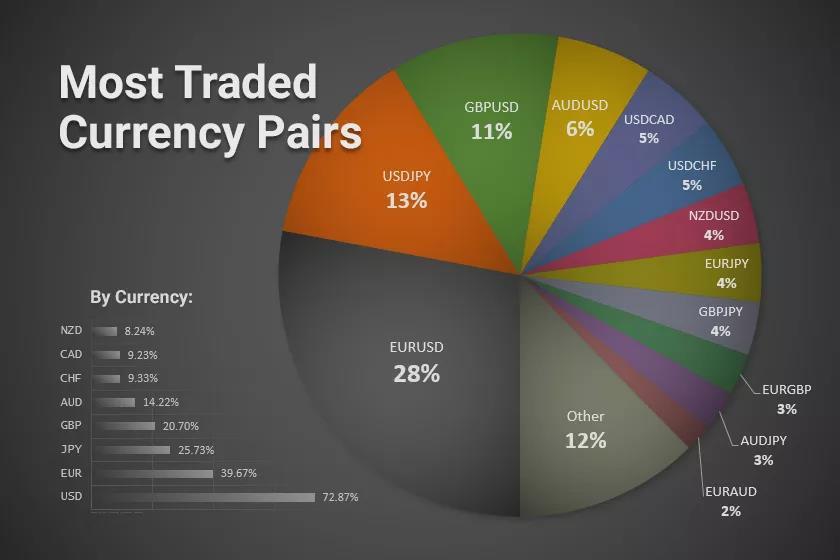
The foundation of Forex trading lies in understanding currency pairs. A currency pair represents the value of one currency against another. It’s the basis for all Forex transactions, determining the price at which one currency can be exchanged for another.
Types of Currency Pairs
Currency pairs are categorized into different types based on their popularity, trading volume, and volatility.
- Major Pairs: These are the most actively traded currency pairs in the Forex market. They typically involve the US dollar (USD) against other major global currencies. Examples include:
- EUR/USD (Euro against US Dollar)
- USD/JPY (US Dollar against Japanese Yen)
- GBP/USD (British Pound against US Dollar)
- USD/CHF (US Dollar against Swiss Franc)
- AUD/USD (Australian Dollar against US Dollar)
- Minor Pairs: These pairs involve two major currencies, but one of them is not the US dollar. They are generally less volatile than major pairs and have lower trading volumes. Examples include:
- EUR/GBP (Euro against British Pound)
- GBP/JPY (British Pound against Japanese Yen)
- AUD/JPY (Australian Dollar against Japanese Yen)
- Exotic Pairs: These pairs involve a major currency and a currency from a developing or emerging market. They tend to be more volatile and have lower liquidity than major or minor pairs. Examples include:
- USD/TRY (US Dollar against Turkish Lira)
- EUR/ZAR (Euro against South African Rand)
- USD/MXN (US Dollar against Mexican Peso)
Forex Trading Platforms and Tools

Forex trading platforms are the software interfaces that traders use to access the foreign exchange market. They provide tools and features that allow traders to place orders, monitor market movements, and analyze trading opportunities. The choice of platform can significantly impact a trader’s experience and success.
Types of Forex Trading Platforms
The availability of a wide range of forex trading platforms gives traders the flexibility to choose a platform that best suits their trading style, experience level, and specific needs.
- Desktop Platforms: These are traditional platforms that are downloaded and installed on a computer. They typically offer more advanced features and functionalities than web-based platforms. Examples include MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), and cTrader.
- Web-based Platforms: These platforms are accessible through a web browser and do not require any downloads. They are convenient for traders who want to access their accounts from any device with an internet connection. Examples include ThinkMarkets, Forex.com, and FXTM.
- Mobile Platforms: These platforms are designed for mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. They provide traders with on-the-go access to their accounts and market information. Examples include MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), and TradingView.
Essential Trading Tools
These tools are crucial for analyzing market trends, identifying trading opportunities, and managing risk.
- Charting Software: Charting software allows traders to visualize price movements over time and identify patterns and trends. Most trading platforms include built-in charting software, while others offer third-party charting tools like TradingView. Popular chart types include line charts, bar charts, candlestick charts, and point and figure charts.
- Technical Indicators: Technical indicators are mathematical calculations that analyze historical price data to identify potential trading signals. Common technical indicators include moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), MACD, Bollinger Bands, and stochastic oscillators.
- Economic Calendars: Economic calendars provide traders with information on upcoming economic events that can impact currency movements. These events include interest rate decisions, inflation reports, and employment data. Traders can use economic calendars to anticipate potential market volatility and adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
Fundamental Analysis in Forex Trading
Fundamental analysis is a crucial aspect of Forex trading that involves evaluating the economic factors that influence currency exchange rates. It examines the economic health of countries and their potential impact on the value of their currencies. By understanding the fundamental forces driving currency movements, traders can make informed decisions about buying or selling currencies.
Key Economic Indicators
Economic indicators provide valuable insights into the health of a country’s economy and can influence currency movements. These indicators can be categorized into various types, each offering a different perspective on economic performance.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): GDP measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders. A strong GDP growth rate suggests a healthy economy and can lead to a stronger currency.
- Inflation: Inflation refers to the rate at which prices for goods and services increase over time. High inflation can erode the purchasing power of a currency and weaken its value.
- Interest Rates: Central banks adjust interest rates to control inflation and economic growth. Higher interest rates attract foreign investment, boosting demand for the currency and strengthening its value.
- Unemployment Rate: The unemployment rate indicates the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed. A low unemployment rate suggests a strong economy and can support a currency’s value.
- Trade Balance: The trade balance reflects the difference between a country’s exports and imports. A trade surplus (exports exceeding imports) can strengthen a currency, while a trade deficit (imports exceeding exports) can weaken it.
- Government Debt: High levels of government debt can indicate financial instability and may lead to a decline in currency value.
Technical Analysis in Forex Trading
Technical analysis is a method used by traders to predict future price movements by studying past price and volume data. It relies on the idea that market history tends to repeat itself and that patterns in price charts can provide insights into future trends. Technical analysts use a variety of tools and techniques, including indicators, chart patterns, and volume analysis, to identify trading opportunities.
Popular Technical Indicators
Technical indicators are mathematical calculations based on price and volume data that help traders identify trends, momentum, and overbought or oversold conditions. These indicators can be used to generate buy or sell signals, confirm existing trends, or identify potential reversals.
- Moving Averages (MA): MAs smooth out price fluctuations and help identify trends. Common types include simple moving average (SMA), exponential moving average (EMA), and weighted moving average (WMA).
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): RSI measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. Values above 70 suggest an overbought market, while values below 30 indicate an oversold market.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages. Crossovers and divergences can signal buy or sell opportunities.
- Stochastic Oscillator: This indicator compares a security’s closing price to its price range over a given period. It helps identify overbought or oversold conditions and potential reversals.
Chart Patterns, Online currency trading forex
Chart patterns are recognizable formations in price charts that suggest potential price movements. These patterns can be bullish, bearish, or neutral, and they are often used to confirm or refute existing trends.
- Head and Shoulders: This bearish pattern suggests a reversal of an uptrend. It consists of three peaks, with the middle peak (the head) being the highest.
- Double Top/Bottom: These patterns indicate a potential reversal of the current trend. A double top occurs when a price reaches a resistance level twice, while a double bottom occurs when a price reaches a support level twice.
- Triangles: Triangles are consolidation patterns that suggest a breakout in the direction of the existing trend. There are different types of triangles, including symmetrical, ascending, and descending.
- Flags and Pennants: These patterns indicate a continuation of the existing trend. They are characterized by a brief consolidation period followed by a breakout in the direction of the trend.
Forex Trading Strategies
Forex trading strategies are essential for navigating the dynamic currency market. These strategies offer a framework for making informed decisions and managing risk. They can be broadly categorized into four main types: scalping, day trading, swing trading, and trend trading.
Scalping
Scalping is a high-frequency trading strategy that aims to profit from small price fluctuations in the market. Scalpers typically open and close trades within a short timeframe, often within minutes or even seconds. This strategy requires a high level of technical analysis skills, as scalpers rely on charts and indicators to identify short-term price movements.
Advantages of Scalping
- Potential for high profits: Scalping can generate significant profits when executed correctly, as even small price changes can be amplified due to the high volume of trades.
- Flexibility: Scalping can be implemented during any market condition, as long as there is sufficient volatility.
Disadvantages of Scalping
- High risk: Scalping involves a high level of risk, as even minor errors in analysis or execution can lead to substantial losses.
- High trading costs: Frequent trading can result in significant brokerage fees and slippage, reducing potential profits.
- Stressful: Scalping requires constant monitoring of the market, which can be mentally demanding and stressful.
Example of Scalping
A scalper might identify a small upward price movement in the EUR/USD currency pair. They would then open a buy order at the current market price, aiming to close the trade once the price reaches a predetermined profit target, which could be just a few pips higher. If the price moves against the scalper, they would close the trade at a predetermined stop-loss level to limit potential losses.
Day Trading
Day trading involves opening and closing trades within the same trading day, aiming to profit from intraday price fluctuations. Day traders typically focus on short-term trends and market news, using technical analysis tools to identify trading opportunities.
Advantages of Day Trading
- Greater flexibility: Day traders have more flexibility than swing traders, as they can adapt to changing market conditions throughout the day.
- Lower risk: Day trading generally involves lower risk than swing trading, as positions are held for shorter periods.
Disadvantages of Day Trading
- Requires constant monitoring: Day trading requires traders to be constantly monitoring the market and making decisions, which can be demanding.
- Higher trading costs: Frequent trading can result in higher brokerage fees and slippage.
- Difficult to predict: Day trading relies on short-term price movements, which can be difficult to predict accurately.
Example of Day Trading
A day trader might notice a bullish breakout pattern in the GBP/USD currency pair. They would then open a buy order at the breakout point, aiming to close the trade at a predetermined profit target later in the day. If the price moves against the day trader, they would close the trade at a predetermined stop-loss level to limit potential losses.
Swing Trading
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days or weeks, aiming to profit from larger price swings in the market. Swing traders typically use technical and fundamental analysis to identify potential trading opportunities.
Advantages of Swing Trading
- Lower trading costs: Holding positions for longer periods reduces trading costs, as fewer trades are executed.
- Less demanding: Swing trading requires less constant monitoring than day trading, as positions are held for longer periods.
Disadvantages of Swing Trading
- Higher risk: Holding positions for longer periods exposes traders to greater risk of market fluctuations.
- Requires patience: Swing trading requires patience, as profits may not materialize immediately.
- More challenging to predict: Predicting longer-term price movements can be more challenging than predicting short-term movements.
Example of Swing Trading
A swing trader might identify a strong uptrend in the USD/JPY currency pair, supported by positive economic data and a weakening Japanese yen. They would then open a buy order, aiming to hold the position for several weeks, hoping to profit from the ongoing uptrend. If the price moves against the swing trader, they would close the trade at a predetermined stop-loss level to limit potential losses.
Trend Trading
Trend trading involves identifying and following major price trends in the market. Trend traders typically use technical analysis tools to identify trend lines and support and resistance levels, aiming to profit from the continuation of established trends.
Advantages of Trend Trading
- Higher probability of success: Trend trading follows established trends, which generally have a higher probability of continuing than short-term price fluctuations.
- Lower risk: Trend trading typically involves lower risk than other strategies, as positions are held for longer periods, allowing for more time to manage risk.
Disadvantages of Trend Trading
- Requires patience: Trend trading requires patience, as profits may not materialize immediately.
- Less frequent trading opportunities: Trend trading opportunities are less frequent than other strategies, as it focuses on long-term trends.
Example of Trend Trading
A trend trader might identify a strong uptrend in the AUD/USD currency pair, supported by a series of higher highs and higher lows. They would then open a buy order, aiming to hold the position for several weeks or months, hoping to profit from the continuation of the uptrend. If the price moves against the trend trader, they would close the trade at a predetermined stop-loss level to limit potential losses.
Risk Management in Forex Trading
Risk management is an essential aspect of forex trading, as it helps traders protect their capital and prevent significant losses. It involves a set of strategies and techniques that aim to mitigate potential risks associated with forex trading. By implementing effective risk management practices, traders can enhance their trading experience and increase their chances of long-term success.
Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are crucial tools in risk management. They are pre-set instructions that automatically close a trade when the price reaches a specific level. This predetermined level is set below the entry price for a long position or above the entry price for a short position. When the price hits the stop-loss level, the order is triggered, limiting potential losses.
Position Sizing
Position sizing is the process of determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to each trade. It is crucial to avoid risking too much capital on a single trade. A common rule of thumb is to risk no more than 1-2% of the total trading capital per trade. This ensures that even if a trade goes against the trader, the overall portfolio is not significantly impacted.
Diversification
Diversification is the practice of spreading investments across different asset classes or trading instruments. In forex trading, diversification can involve trading multiple currency pairs or trading other financial instruments, such as stocks or bonds. This strategy helps reduce overall risk by minimizing the impact of any single investment on the portfolio.
Psychological Aspects of Trading
Managing emotions is a critical aspect of risk management in forex trading. Fear, greed, and overconfidence can lead to impulsive decisions and poor trading outcomes. Traders should strive to maintain a disciplined and objective approach to trading, avoiding emotional biases. This can be achieved through techniques like journaling, self-reflection, and seeking guidance from experienced traders.
The Future of Forex Trading
The foreign exchange market is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing regulatory landscapes, and the ever-shifting global economic landscape. This dynamic environment presents both opportunities and challenges for Forex traders. Understanding these trends is crucial for navigating the future of Forex trading successfully.
Technological Advancements Shaping the Forex Landscape
Technological advancements are fundamentally transforming the Forex trading landscape, empowering traders with new tools and strategies.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms are increasingly used in Forex trading to analyze vast datasets, identify patterns, and make trading decisions with greater speed and accuracy. These technologies can automate trading processes, improve risk management, and provide personalized trading insights.
- High-Frequency Trading (HFT): HFT algorithms execute trades at lightning speed, leveraging milliseconds to capitalize on fleeting market opportunities. This trend has increased market liquidity and volatility, requiring traders to adapt their strategies to compete with HFT algorithms.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology is transforming the financial industry by enabling secure and transparent transactions. Its potential applications in Forex trading include streamlining settlement processes, reducing counterparty risk, and enhancing transparency in the market.
Last Recap

Navigating the world of online currency trading forex requires a blend of knowledge, strategy, and discipline. By understanding the fundamental principles, utilizing technical analysis, and implementing effective risk management techniques, traders can position themselves for success in this dynamic and ever-evolving market. While forex trading presents opportunities for profit, it’s crucial to remember that risk is inherent in any financial endeavor. By approaching forex trading with a well-defined strategy and a commitment to continuous learning, individuals can enhance their chances of achieving their financial goals.
Quick FAQs
What is the minimum amount I need to start forex trading?
The minimum amount required to start forex trading varies depending on the broker and account type. Some brokers offer micro-accounts with as little as $5 or $10, while others may require a higher minimum deposit. It’s essential to choose a broker that aligns with your trading goals and financial resources.
Is forex trading legal?
Forex trading is legal in most countries, but it’s crucial to ensure that you are trading with a regulated and reputable broker. Look for brokers licensed by reputable financial authorities like the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK or the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the US.
What are the risks associated with forex trading?
Forex trading involves inherent risks, including the potential for significant financial losses. Currency values can fluctuate rapidly, and leverage can amplify both profits and losses. It’s essential to manage risk effectively by using stop-loss orders, position sizing, and diversifying your portfolio.
How can I learn more about forex trading?
There are numerous resources available to learn about forex trading, including online courses, books, articles, and educational websites. Consider starting with reputable sources and seeking guidance from experienced traders or financial advisors.




