
Most volatile pairs in forex are the heart-pounding thrill of the currency market, where dramatic price swings can lead to both substantial profits and significant losses. These pairs, characterized by their rapid and unpredictable movements, are a magnet for traders seeking high-risk, high-reward opportunities. Understanding the factors driving volatility, identifying these pairs, and mastering the art of risk management are crucial for navigating the treacherous waters of volatile forex trading.
From the explosive rallies of emerging market currencies to the sudden reversals of major economies, volatile pairs present a unique set of challenges and rewards. Traders must possess a keen understanding of economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market sentiment to capitalize on these opportunities. The ability to predict and react to rapid price changes is paramount, requiring a blend of technical analysis, fundamental knowledge, and disciplined risk management.
Understanding Volatility in Forex: Most Volatile Pairs In Forex
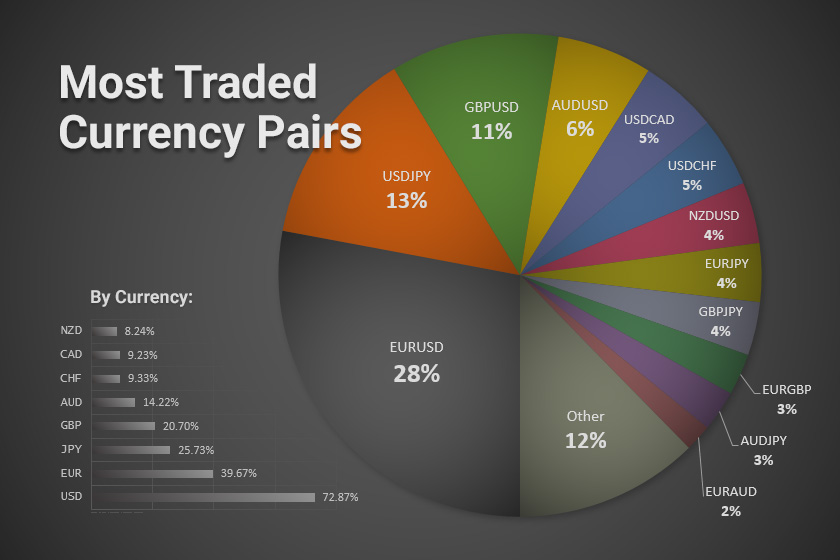
Volatility is a crucial concept in Forex trading, influencing risk and potential profit. Understanding volatility helps traders make informed decisions about which currency pairs to trade, the strategies to employ, and the risk management techniques to use.
Factors Contributing to Volatility in Forex Pairs
Volatility in Forex pairs is driven by a combination of economic, political, and social factors. Understanding these factors helps traders anticipate potential price fluctuations and adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
- Economic Indicators: Key economic releases, such as interest rate decisions, inflation data, and employment figures, can significantly impact currency values. When an economic indicator surprises the market, it can lead to sharp price movements. For example, a stronger-than-expected GDP report may boost a currency’s value, while a disappointing unemployment report may weaken it.
- Political Events: Political events, such as elections, policy changes, and geopolitical tensions, can also influence currency volatility. Political instability or uncertainty can lead to increased risk aversion, causing investors to sell riskier assets, including currencies, and seek safe havens like the US dollar.
- Central Bank Actions: Central banks play a crucial role in managing inflation and economic growth. Their monetary policy decisions, such as interest rate changes or quantitative easing, can significantly impact currency values. For instance, a central bank raising interest rates may attract foreign investment, strengthening the currency.
- Global Events: Global events, such as natural disasters, pandemics, or trade wars, can have a ripple effect on the Forex market. These events can create uncertainty and volatility, affecting investor sentiment and currency values.
- Market Sentiment: Investor sentiment, or the overall mood of the market, can influence currency prices. Positive sentiment can lead to higher demand for a currency, pushing its value up, while negative sentiment can lead to a decline in demand and a weakening of the currency.
Examples of High and Low Volatility Forex Pairs
- High Volatility Pairs: These pairs are known for their significant price fluctuations and are often favored by traders seeking higher potential profits but also facing higher risk. Examples include:
- GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar): The British Pound is often considered a riskier currency due to the UK’s political and economic uncertainties. The GBP/USD pair is known for its volatility, particularly during times of economic or political instability.
- EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar): The Euro is influenced by the economic performance of the Eurozone, which comprises 19 countries. The EUR/USD pair can exhibit significant volatility due to the diverse economic and political landscapes of the Eurozone members.
- AUD/USD (Australian Dollar/US Dollar): The Australian Dollar is closely tied to commodity prices, particularly those of gold and iron ore. As commodity prices fluctuate, so too does the AUD/USD pair, making it a relatively volatile currency pair.
- Low Volatility Pairs: These pairs tend to have smaller price movements and are often preferred by traders seeking lower risk and more stable returns. Examples include:
- USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen): The Japanese Yen is often considered a safe-haven currency, meaning investors seek it out during times of global uncertainty. The USD/JPY pair tends to be less volatile compared to other major currency pairs.
- USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc): The Swiss Franc is also considered a safe-haven currency, and the USD/CHF pair generally exhibits lower volatility than other major currency pairs.
- Historical Volatility Analysis: Analyzing past price data is a common approach. By examining the standard deviation of price movements over a specific period, traders can identify pairs with historically high volatility. For example, the average daily price range of the USD/JPY pair over the past year can be compared to other pairs to determine its relative volatility.
- Economic Calendar Monitoring: Economic events such as interest rate announcements, inflation reports, and employment data can significantly impact currency values. Monitoring the economic calendar helps traders identify pairs likely to experience increased volatility during these events. For instance, the release of the US Non-Farm Payrolls report often leads to significant volatility in USD-related pairs.
- News and Market Sentiment Analysis: News headlines, political events, and market sentiment can influence currency valuations. Traders often use news sources and sentiment indicators to gauge the overall market mood and identify pairs that might be particularly sensitive to current events. For example, a sudden geopolitical crisis could lead to a sharp increase in volatility in pairs involving the currencies of the countries involved.
- Technical Analysis Indicators: Technical indicators like the Average True Range (ATR) and Bollinger Bands can be used to assess volatility levels. The ATR measures the average price range over a specified period, while Bollinger Bands provide a visual representation of price volatility. Traders can compare these indicators across different pairs to identify those with higher volatility levels.
- USD/JPY: The USD/JPY pair is often considered one of the most volatile pairs due to its sensitivity to global economic conditions and Japanese monetary policy. Its volatility is particularly pronounced during periods of economic uncertainty or when the Bank of Japan intervenes in the currency market.
- GBP/USD: The GBP/USD pair is known for its volatility due to the UK’s economic performance, Brexit-related uncertainties, and the Bank of England’s monetary policy decisions. Its volatility can fluctuate significantly depending on the political and economic climate.
- AUD/USD: The AUD/USD pair is influenced by Australia’s commodity prices, particularly iron ore and gold. The pair’s volatility is often tied to global demand for commodities and the Australian Reserve Bank’s interest rate decisions.
- Interest Rate Announcements: Central bank interest rate announcements can significantly impact currency values and volatility. When a central bank raises interest rates, it typically strengthens the currency, leading to increased volatility in pairs involving that currency. Conversely, interest rate cuts often weaken the currency, resulting in higher volatility.
- Economic Data Releases: Major economic data releases, such as GDP growth, inflation figures, and employment reports, can also cause volatility in Forex pairs. Positive economic data tends to strengthen a currency, while negative data weakens it, leading to price fluctuations.
- Political Events: Political events, such as elections, referendums, or changes in government, can significantly influence currency values and volatility. Uncertain political situations often lead to increased volatility in pairs involving the currencies of the affected countries.
- Opportunities:
- Potential for Higher Profits: Rapid price movements allow traders to capitalize on large price swings, potentially generating substantial profits in a short timeframe.
- Faster Trade Execution: With frequent price fluctuations, traders can enter and exit trades quickly, taking advantage of short-term trends and market momentum.
- Risks:
- Increased Risk of Losses: Large price swings can quickly erode trading capital, leading to significant losses if trades are not managed effectively.
- Difficulty in Predicting Market Direction: The unpredictable nature of volatile pairs makes it challenging to accurately predict future price movements, increasing the risk of wrong entries and exits.
- Wider Stop-Loss Levels: Traders often need to set wider stop-loss orders to mitigate potential losses in volatile markets, which can lead to premature exits and missed opportunities.
- Scalping: This strategy involves entering and exiting trades quickly, profiting from small price movements. Scalpers rely on high trading frequency and tight stop-loss orders to manage risk.
- News Trading: This strategy involves capitalizing on market reactions to economic news releases and events. Traders often use technical indicators to identify potential entry and exit points, anticipating market volatility around news announcements.
- Breakout Trading: This strategy focuses on identifying and trading breakouts from established price ranges. Traders use technical indicators like moving averages and Bollinger Bands to identify potential breakout points.
- Range Trading: While seemingly counterintuitive, range trading can be effective in volatile markets. By identifying support and resistance levels, traders can enter trades when the price bounces off these levels, expecting a reversal within the established range.
- Stable Forex Pairs: Stable pairs, like EUR/USD or USD/JPY, are characterized by relatively small price fluctuations. Traders often employ longer-term strategies, focusing on fundamental analysis and trend identification.
- Volatile Forex Pairs: Volatile pairs, like GBP/USD or AUD/USD, experience frequent and large price swings. Traders typically utilize short-term strategies, emphasizing technical analysis and rapid trade execution.
- Position Sizing: This strategy involves determining the appropriate size of trades based on the trader’s risk tolerance and account balance.
- Stop-Loss Orders: These orders automatically close a position when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.
- Take-Profit Orders: These orders automatically close a position when the price reaches a predetermined profit target, securing gains.
- Trailing Stop-Loss Orders: These orders adjust the stop-loss level based on price movements, allowing for greater profit potential while still limiting losses.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: This ratio measures the potential profit compared to the potential loss for a trade. It is a key factor in determining the profitability of a trading strategy.
Identifying the Most Volatile Forex Pairs
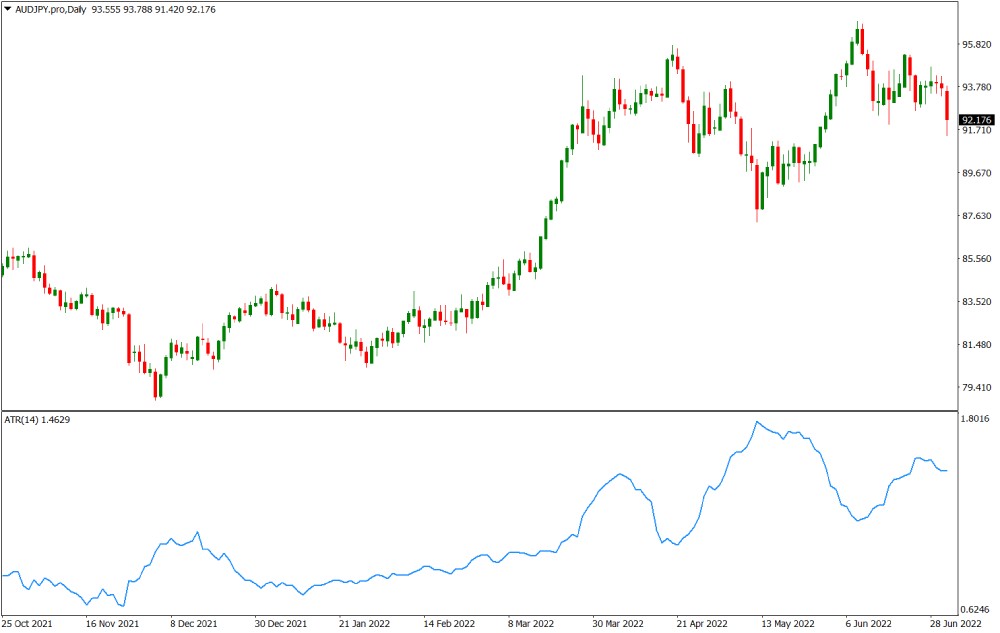
Identifying the most volatile Forex pairs is a crucial aspect of Forex trading, as volatility can present both opportunities and risks. Volatility refers to the rate and magnitude of price fluctuations in a currency pair, and understanding it allows traders to make informed decisions about their trading strategies.
Methods for Identifying Volatile Forex Pairs, Most volatile pairs in forex
Traders use various methods to identify volatile Forex pairs.
Historical Data on Forex Pair Volatility
Correlation between Economic Events and Forex Pair Volatility
The Impact of Volatility on Trading Strategies
Volatility is a double-edged sword in Forex trading. While it can present lucrative opportunities for quick profits, it also carries significant risks that can lead to substantial losses. Understanding the interplay between volatility and trading strategies is crucial for navigating the dynamic Forex market.
Risks and Opportunities of Trading Volatile Forex Pairs
Volatile Forex pairs, characterized by frequent and large price fluctuations, offer both exciting opportunities and significant risks for traders.
Trading Strategies for High Volatility Forex Pairs
Trading volatile Forex pairs requires a different approach than trading stable pairs. Here are some strategies designed for high volatility environments:
Trading Volatile vs. Stable Forex Pairs
Managing Risk in Volatile Markets
Volatility in the forex market presents unique challenges for traders. It can lead to substantial profits, but also to significant losses if not managed effectively. Risk management strategies are crucial for navigating these turbulent waters and preserving capital.
Common Risk Management Strategies
Risk management strategies aim to mitigate potential losses and protect trading capital. These strategies can be categorized into two main types:
Implementing Risk Management Strategies
Implementing effective risk management strategies requires a structured approach:
- Define Risk Tolerance: Determine the maximum amount of capital you are willing to risk on a single trade or a series of trades.
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: Place stop-loss orders at a level that aligns with your risk tolerance and the market’s volatility.
- Use Take-Profit Orders: Implement take-profit orders to lock in gains and protect profits.
- Monitor Positions Regularly: Keep a close eye on your open positions and adjust stop-loss levels as needed.
- Review Performance: Regularly review your trading performance and identify areas for improvement in your risk management strategy.
Adjusting Trading Strategies
Market volatility levels can significantly impact trading strategies.
- High Volatility: In highly volatile markets, traders may prefer to use smaller position sizes, tighter stop-loss orders, and shorter trading timeframes. This approach helps to minimize potential losses and capitalize on short-term price swings.
- Low Volatility: In low volatility markets, traders may opt for larger position sizes, wider stop-loss orders, and longer trading timeframes. This approach allows for greater potential profits but requires patience and discipline.
The Role of Fundamental and Technical Analysis
Fundamental and technical analysis are two essential tools for traders in the volatile world of Forex. While fundamental analysis focuses on the economic factors that influence currency values, technical analysis relies on price charts and indicators to predict future price movements. By understanding the role of each approach, traders can develop a comprehensive strategy for navigating volatile Forex pairs.
Fundamental Analysis for Volatile Forex Pairs
Fundamental analysis helps traders identify volatile Forex pairs by examining the economic health and political stability of the countries whose currencies are being traded. Key economic indicators, such as interest rates, inflation, GDP growth, and unemployment rates, can provide insights into a country’s economic strength and its potential impact on currency values. For example, a country with a strong economy and high interest rates is likely to attract foreign investment, leading to an increase in demand for its currency and potentially higher volatility.
- Interest Rate Differentials: When a country’s central bank raises interest rates, it attracts foreign investors seeking higher returns, increasing demand for its currency. This can lead to a stronger currency and potentially higher volatility. Conversely, a decrease in interest rates can weaken the currency and increase volatility.
- Economic Growth: A country with a robust economy and strong GDP growth is likely to attract foreign investment, boosting demand for its currency and increasing volatility.
- Political Stability: Political instability or uncertainty can negatively impact a country’s currency, leading to increased volatility. For instance, a country experiencing political turmoil or a change in government may see its currency depreciate as investors become wary of the potential for economic disruption.
Technical Analysis for Volatility Trends
Technical analysis uses price charts and indicators to identify trends and patterns in currency movements, which can help traders understand volatility. By studying historical price data, traders can identify areas of support and resistance, as well as trend lines and momentum indicators that suggest potential price reversals or breakouts.
- Moving Averages: Moving averages are trend-following indicators that smooth out price fluctuations and can help identify potential support and resistance levels. A breakout above a long-term moving average could indicate a strong upward trend, potentially leading to increased volatility.
- Bollinger Bands: Bollinger Bands are volatility indicators that measure price fluctuations around a moving average. Wider bands suggest higher volatility, while narrower bands indicate lower volatility.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. A high RSI reading (above 70) suggests a potential for a price reversal, while a low reading (below 30) indicates a possible oversold condition.
Combining Fundamental and Technical Analysis
Combining fundamental and technical analysis provides a comprehensive approach to trading volatile Forex pairs. Fundamental analysis helps traders understand the underlying economic and political factors that drive currency movements, while technical analysis provides insights into price trends and potential price reversals. By integrating both approaches, traders can develop a well-informed trading strategy that considers both the macro-economic environment and the technical signals.
- Identifying Potential Volatility: Fundamental analysis can identify volatile Forex pairs by examining economic indicators and political events. Once a volatile pair is identified, technical analysis can be used to pinpoint entry and exit points based on price trends and indicators.
- Confirming Trading Signals: Technical analysis can confirm trading signals identified through fundamental analysis. For instance, if a country’s interest rates are expected to rise, leading to a stronger currency, technical indicators such as a breakout above a long-term moving average could provide a confirmation signal for a long position.
- Managing Risk: Combining both approaches helps traders manage risk by understanding the underlying factors driving volatility and identifying potential price reversals. This can help traders set appropriate stop-loss orders and manage their positions effectively.
Closing Notes
Trading volatile forex pairs is a high-stakes game, demanding a blend of knowledge, discipline, and a healthy dose of risk tolerance. While the potential for substantial profits is enticing, the risks of significant losses are equally real. By carefully selecting pairs, employing sound risk management strategies, and staying informed about market dynamics, traders can navigate the turbulent waters of volatility and potentially emerge with impressive returns. However, it’s crucial to remember that volatility is a double-edged sword, and a deep understanding of the market is essential for success.
FAQ
What are the most volatile Forex pairs?
Some of the most volatile Forex pairs include GBP/USD, USD/JPY, AUD/USD, and NZD/USD. However, volatility can fluctuate based on economic events and market conditions.
How can I use volatility to my advantage?
Traders can use volatility to their advantage by employing strategies that capitalize on rapid price movements. This might involve using scalping techniques, trading breakouts, or employing volatility-based indicators.
What are the risks of trading volatile pairs?
The risks of trading volatile pairs include the possibility of significant losses due to rapid price swings. It’s crucial to manage risk effectively to mitigate potential losses.
How can I manage risk when trading volatile pairs?
Risk management strategies for volatile pairs include using stop-loss orders, limiting position sizes, and diversifying your portfolio.




