
Is bachelor degree an undergraduate – Is a bachelor’s degree an undergraduate degree? The answer is a resounding yes! A bachelor’s degree is the cornerstone of undergraduate education, marking the completion of a four-year program of study. This degree signifies a significant milestone in a student’s academic journey, opening doors to diverse career paths and advanced learning opportunities.
The bachelor’s degree has a rich history, evolving from its medieval origins to become the standard qualification for entry-level positions in numerous fields. From the humanities and social sciences to STEM disciplines and business, bachelor’s degrees provide students with a comprehensive foundation in their chosen areas of study, equipping them with essential knowledge, skills, and critical thinking abilities.
Definition and Meaning
.jpg)
A bachelor’s degree is a foundational academic qualification awarded by universities and colleges upon successful completion of an undergraduate program. It signifies that the recipient has acquired a broad and in-depth understanding of a specific field of study.
The bachelor’s degree is a cornerstone of higher education, providing a comprehensive knowledge base and a set of transferable skills that are highly valued in the job market. It serves as a stepping stone for further academic pursuits, such as master’s or doctoral degrees, or as a qualification for entry-level positions in various industries.
Historical Evolution of the Bachelor’s Degree
The origins of the bachelor’s degree can be traced back to medieval Europe, where it was initially awarded to students who had completed a course of study in theology, law, or medicine. The term “bachelor” itself originated from the Latin word “baccalaureus,” which referred to a young knight or warrior who was still under training.
Over time, the bachelor’s degree evolved to encompass a wider range of academic disciplines, and its significance as a mark of academic achievement became more firmly established. In the 19th and 20th centuries, the development of universities and the expansion of higher education led to the proliferation of bachelor’s degree programs across a vast spectrum of fields.
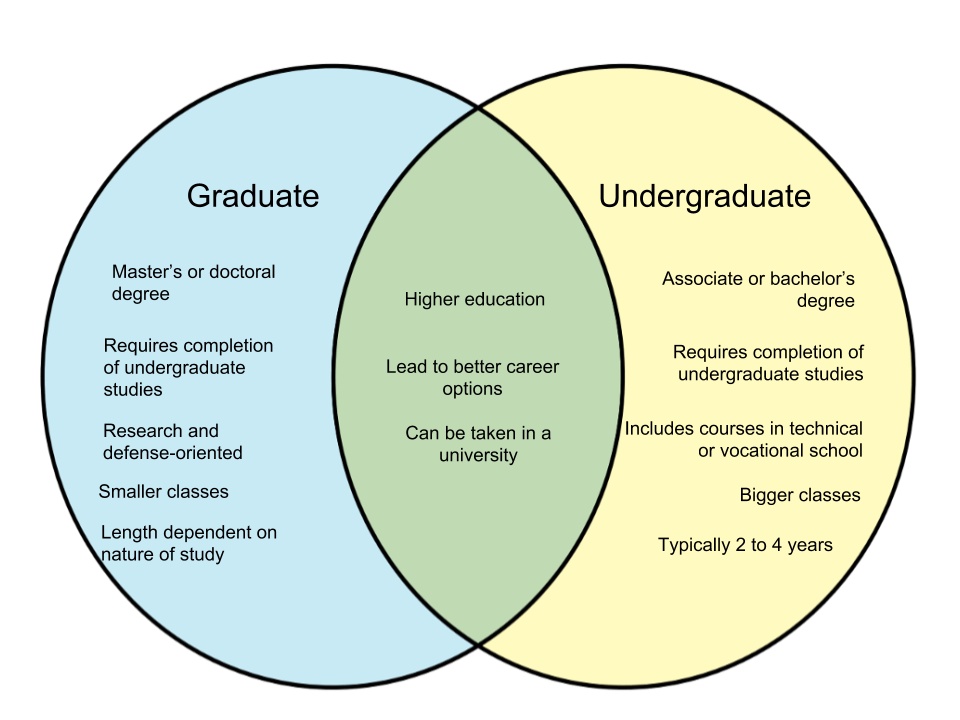
Comparison with Other Academic Qualifications
The bachelor’s degree is one of many academic qualifications offered by universities and colleges. It is typically a four-year program, although the duration may vary depending on the specific program and institution.
Associate Degrees
An associate degree is a two-year program that provides a more focused and specialized education in a particular field. It is often considered a stepping stone to a bachelor’s degree or a qualification for entry-level positions in certain industries.
Master’s Degrees
A master’s degree is a postgraduate qualification that builds upon the knowledge and skills acquired during a bachelor’s degree program. It is typically a one- or two-year program that involves advanced coursework, research, or practical experience.
The bachelor’s degree is a versatile qualification that can open doors to a wide range of opportunities, both academically and professionally.
Undergraduate Education: Is Bachelor Degree An Undergraduate
Undergraduate education is the first stage of higher education, typically pursued after completing secondary school (high school). It provides students with a foundation in a chosen field of study, preparing them for careers or further academic pursuits.
Duration of a Bachelor’s Degree Program
The typical duration of a bachelor’s degree program is four years, although it can vary depending on the institution and the specific program of study. Some programs, such as accelerated programs or those offered online, may be completed in less time. Others, such as those in fields like medicine or law, may require more than four years of study.
Types of Bachelor’s Degree Programs
Bachelor’s degree programs are offered in a wide range of disciplines, encompassing various fields of study. Some common types of bachelor’s degree programs include:
- Arts and Humanities: These programs focus on critical thinking, communication, and cultural understanding. Examples include Bachelor of Arts (BA) in English Literature, History, Philosophy, or Music.
- Social Sciences: These programs explore human behavior, social structures, and interactions. Examples include Bachelor of Arts (BA) in Psychology, Sociology, Political Science, or Economics.
- Sciences: These programs delve into the natural world, including biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics. Examples include Bachelor of Science (BS) in Biology, Chemistry, Physics, or Mathematics.
- Engineering: These programs focus on applying scientific principles to solve technical problems. Examples include Bachelor of Science (BS) in Mechanical Engineering, Electrical Engineering, Civil Engineering, or Chemical Engineering.
- Business: These programs equip students with skills in management, finance, marketing, and accounting. Examples include Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) in Management, Finance, Marketing, or Accounting.
- Computer Science: These programs focus on the design, development, and application of software and computer systems. Examples include Bachelor of Science (BS) in Computer Science, Software Engineering, or Information Technology.
Benefits of a Bachelor’s Degree
A bachelor’s degree is a valuable investment that opens doors to a wide range of opportunities. It provides a strong foundation for personal and professional growth, leading to enhanced career prospects, higher earning potential, and a fulfilling life.
Career Prospects and Earning Potential, Is bachelor degree an undergraduate
A bachelor’s degree significantly improves career prospects and earning potential. Individuals with a bachelor’s degree are more likely to secure employment in competitive job markets and progress in their careers.
- Higher Salary: Studies consistently show that individuals with a bachelor’s degree earn significantly more than those with only a high school diploma. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, workers with a bachelor’s degree earn an average of 67% more than those with only a high school diploma.
- Greater Job Security: A bachelor’s degree equips individuals with the knowledge, skills, and credentials that are highly sought after by employers. This translates to greater job security, as individuals with a bachelor’s degree are less likely to be affected by economic downturns or layoffs.
- Career Advancement: Many industries and professions require a bachelor’s degree for entry-level positions and advancement opportunities. A bachelor’s degree provides the necessary foundation for individuals to progress in their careers, taking on more challenging roles and responsibilities.
Value Across Different Industries and Professions
The value of a bachelor’s degree varies across different industries and professions. However, it remains a valuable asset in most fields, providing individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to succeed.
- STEM Fields: Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields typically require a bachelor’s degree, and often a master’s or doctorate degree, for entry-level positions and research opportunities. The demand for skilled professionals in STEM fields is high, leading to competitive salaries and career advancement opportunities.
- Business and Finance: A bachelor’s degree in business or finance is highly valued in the corporate world. It provides individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to succeed in roles such as financial analysts, accountants, and marketing managers.
- Healthcare: A bachelor’s degree is essential for many healthcare professions, such as nursing, pharmacy, and physical therapy. It provides the necessary foundation for individuals to provide quality patient care and contribute to the healthcare system.
Pathways to a Bachelor’s Degree

A bachelor’s degree can be obtained through various pathways, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right pathway depends on individual circumstances, goals, and learning preferences.
Traditional University Programs
Traditional university programs involve full-time enrollment at a brick-and-mortar institution, typically spanning four years.
- Advantages:
- Immersive learning environment with access to professors, libraries, and student resources.
- Strong alumni network and potential for career connections.
- Structured curriculum and established academic rigor.
- Disadvantages:
- High tuition costs and potential student loan debt.
- Limited flexibility in scheduling and course selection.
- May require relocation for students who live far from the university.
Online Learning
Online learning programs allow students to pursue a bachelor’s degree remotely, accessing courses and resources through the internet.
- Advantages:
- Flexibility and convenience to study from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Wide range of program options and specialization areas.
- Potential cost savings compared to traditional programs.
- Disadvantages:
- Potential for distractions and lack of in-person interaction with peers and professors.
- Limited access to campus resources and facilities.
- Self-discipline and time management skills are crucial for success.
Accelerated Programs
Accelerated programs allow students to complete a bachelor’s degree in a shorter timeframe, typically within three years or less.
- Advantages:
- Faster completion of degree, leading to quicker career advancement.
- Potential cost savings by reducing the overall time spent in college.
- Intense and focused learning experience.
- Disadvantages:
- More demanding course load and time commitment.
- May require higher levels of self-motivation and discipline.
- Limited time for extracurricular activities and personal commitments.
Transfer Credits
Transfer credits allow students to apply previously earned credits from other institutions towards their bachelor’s degree.
- Role in Achieving a Bachelor’s Degree:
- Transfer credits can shorten the time and cost of completing a degree.
- Students can leverage credits earned at community colleges, technical schools, or other universities.
- The transferability of credits depends on the receiving institution’s policies and the courses taken.
Importance of Choosing the Right Bachelor’s Degree
Your bachelor’s degree is a significant investment of time, effort, and financial resources. It’s crucial to choose a program that aligns with your career aspirations and personal goals. A well-chosen degree can open doors to rewarding career paths and intellectual growth.
Researching and Evaluating Degree Programs
It’s essential to research and evaluate different degree programs to find the best fit. Here’s a framework to guide your research:
* Define your career goals: What kind of work do you envision yourself doing? What industries are you interested in? What are the typical educational requirements for those roles?
* Explore different degree programs: Research programs related to your career goals. Consider the curriculum, faculty, facilities, and career services offered by different institutions.
* Consider your interests and strengths: Choose a program that aligns with your natural talents and interests. This will make your studies more enjoyable and increase your chances of success.
* Evaluate job market demand: Research the job market for graduates with the degree you are considering. Consider factors like salary potential, job availability, and industry growth.
* Network with professionals: Connect with professionals in your field of interest. Ask them about their educational backgrounds and career paths.
* Visit college campuses: If possible, visit campuses to get a firsthand look at the learning environment. Talk to students and faculty to get their perspectives.
Potential Consequences of Choosing a Misaligned Degree Program
Choosing a degree program that doesn’t match your career aspirations can have significant consequences. Here are some potential outcomes:
* Limited career options: You may find yourself with limited career options after graduation, as your degree may not be directly relevant to the jobs you are interested in.
* Difficulty finding employment: Employers may not see your degree as valuable if it doesn’t align with the skills and knowledge they require.
* Career dissatisfaction: You may find yourself in a job that doesn’t fulfill you or utilize your skills and knowledge, leading to career dissatisfaction.
* Financial strain: You may have invested time and money in a degree that doesn’t lead to a fulfilling career, which can be financially straining.
Closure
In conclusion, a bachelor’s degree is an invaluable investment in your future. It unlocks a world of possibilities, enhancing your career prospects, earning potential, and personal growth. Whether you aspire to become a doctor, an engineer, a teacher, or a business leader, a bachelor’s degree serves as a fundamental stepping stone on your path to success. As you embark on your academic journey, carefully consider your career goals and choose a degree program that aligns with your aspirations. The right bachelor’s degree can be a powerful catalyst for achieving your dreams and making a meaningful contribution to society.
FAQ Guide
What is the difference between a bachelor’s degree and a master’s degree?
A bachelor’s degree is an undergraduate degree, while a master’s degree is a postgraduate degree. A bachelor’s degree is typically required for entry-level positions, while a master’s degree can lead to more specialized roles or advanced research opportunities.
Is a bachelor’s degree required for all jobs?
While a bachelor’s degree is becoming increasingly common, it’s not a requirement for every job. Some fields, such as trades or certain technical roles, may accept work experience or vocational training as alternatives. However, a bachelor’s degree often opens up more career options and higher earning potential.
How long does it take to earn a bachelor’s degree?
A traditional four-year bachelor’s degree program typically takes four years to complete, although some programs may be accelerated or require more time depending on the chosen major and course load.
What are some examples of bachelor’s degree programs?
There are numerous bachelor’s degree programs available, covering a wide range of disciplines, including:
- Arts and Humanities (e.g., English, History, Philosophy)
- Social Sciences (e.g., Psychology, Sociology, Economics)
- STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics)
- Business (e.g., Finance, Marketing, Management)
- Health Sciences (e.g., Nursing, Medicine, Pharmacy)




