
Is an undergraduate degree a bachelor’s? The answer is a resounding yes! In the realm of higher education, these terms often intertwine, yet subtle distinctions exist. Understanding these differences is crucial for navigating the academic landscape and making informed decisions about your educational journey.
An undergraduate degree, a foundational step in higher education, encompasses a broad range of programs designed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of a chosen field. The most common type of undergraduate degree is the bachelor’s degree, a testament to a student’s successful completion of a structured curriculum and the acquisition of specialized knowledge and skills. While other undergraduate degrees exist, the bachelor’s degree stands as the cornerstone of many academic and professional pursuits.
Understanding the Terminology
Navigating the world of higher education can be confusing, especially when it comes to understanding the different types of degrees available. Two terms that often get used interchangeably are “undergraduate degree” and “bachelor’s degree.” While they are closely related, there are subtle differences that are important to understand.
Undergraduate Degree
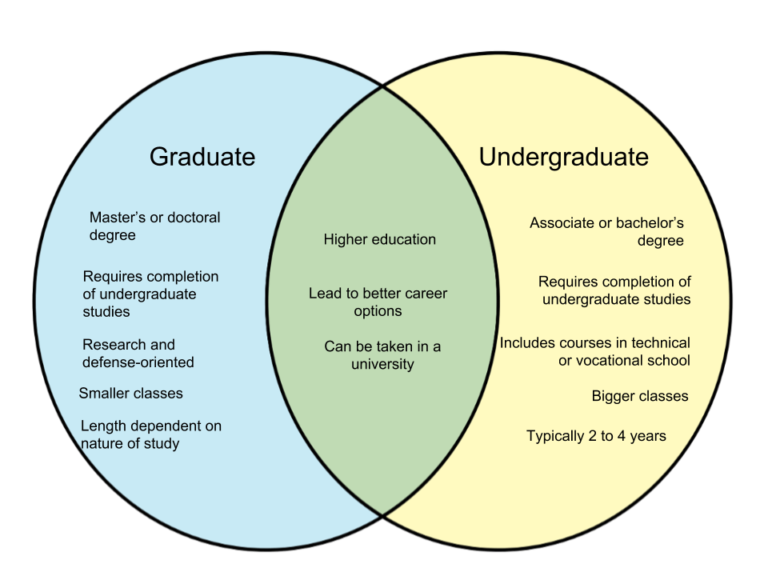
An undergraduate degree is a broad term that encompasses any degree earned by a student before they pursue a graduate degree. It typically represents the first level of higher education after secondary school. Undergraduate degrees are generally designed to provide students with a foundational knowledge in a specific field of study. This foundation can then be used as a springboard for further specialized study or for entering the workforce.
Bachelor’s Degree
A bachelor’s degree is a specific type of undergraduate degree. It is the most common type of undergraduate degree awarded in the United States and many other countries. A bachelor’s degree typically requires four years of full-time study and culminates in the completion of a specific curriculum. A bachelor’s degree is generally considered the minimum requirement for many entry-level professional positions, and it can also serve as a prerequisite for admission to graduate programs.
Comparison of Undergraduate and Bachelor’s Degrees
The terms “undergraduate degree” and “bachelor’s degree” are often used interchangeably, but it is important to understand their subtle differences.
An undergraduate degree is a broad category that encompasses all degrees earned before a graduate degree, while a bachelor’s degree is a specific type of undergraduate degree that is typically the most common.
While all bachelor’s degrees are undergraduate degrees, not all undergraduate degrees are bachelor’s degrees. Other types of undergraduate degrees include associate degrees and certificates.
The Structure of an Undergraduate Degree

An undergraduate degree is a foundational academic qualification that marks the completion of a structured program of study at a university or college. It’s typically the first step in a higher education journey, and it lays the groundwork for future career aspirations and advanced studies.
The structure of an undergraduate degree program is designed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of a chosen field while equipping them with essential skills and knowledge. Here’s a breakdown of the typical components and requirements:
Duration and Credit Requirements
The duration of an undergraduate degree program varies depending on the institution and the specific program. In most cases, a bachelor’s degree requires four years of full-time study, leading to the accumulation of a certain number of credits. These credits represent the successful completion of individual courses and are used to determine the overall progress towards graduation.
For instance, a typical undergraduate degree program might require students to earn 120-130 credits, which translates to approximately 30-35 credits per year. These credits are awarded based on the successful completion of courses, which are typically divided into semesters or quarters.
Course Components
Undergraduate degree programs consist of a variety of courses that are strategically designed to provide a balanced and comprehensive educational experience. These courses can be categorized into several key components:
- Core Courses: These courses are fundamental to the chosen major and provide a strong foundation in the core principles and concepts of the field. They cover essential topics that are considered necessary for a comprehensive understanding of the discipline.
- Major Courses: These courses delve deeper into specialized areas within the chosen major, allowing students to develop expertise and build a strong foundation in their chosen field. They often include advanced topics and research methodologies.
- Electives: Electives offer students the opportunity to explore other areas of interest, broaden their horizons, and gain valuable skills outside their major. They can range from related fields to completely different disciplines, fostering intellectual curiosity and well-roundedness.
- General Education Courses: These courses are designed to provide students with a broad foundation in various disciplines, including humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences. They foster critical thinking, communication skills, and a well-rounded understanding of the world.
Types of Bachelor’s Degrees
While the core structure of an undergraduate degree program is generally consistent, there are various types of bachelor’s degrees that cater to different academic and career aspirations. Here are some of the most common types:
- Bachelor of Arts (BA): A BA degree typically focuses on humanities and social sciences, emphasizing critical thinking, analytical skills, and communication. It prepares students for careers in fields such as writing, journalism, history, social work, and education.
- Bachelor of Science (BS): A BS degree emphasizes scientific and technical fields, focusing on problem-solving, analytical skills, and practical applications. It prepares students for careers in STEM fields such as engineering, computer science, biology, and chemistry.
- Specialized Degrees: Many universities offer specialized bachelor’s degrees in specific areas, such as Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA) for art and design, Bachelor of Music (BM) for music, and Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) for business. These degrees provide in-depth training and prepare students for specific career paths.
Examples of Common Undergraduate Degree Programs
Here are examples of common undergraduate degree programs across various academic disciplines, highlighting their unique curriculum and career paths:
- Business Administration: This program focuses on principles of management, finance, marketing, and accounting. It prepares students for careers in various business sectors, such as management, consulting, finance, and marketing.
- Computer Science: This program focuses on the design, development, and analysis of software and computer systems. It prepares students for careers in software development, data science, cybersecurity, and web development.
- Education: This program focuses on teaching methods, curriculum development, and educational psychology. It prepares students for careers as teachers, educational administrators, and curriculum specialists.
- Engineering: This program focuses on applying scientific principles to design, build, and operate machines, structures, and systems. It prepares students for careers in various engineering disciplines, such as civil, mechanical, electrical, and chemical engineering.
- Nursing: This program focuses on providing healthcare services, including patient care, medication administration, and health education. It prepares students for careers as registered nurses, advanced practice nurses, and nurse educators.
- Psychology: This program focuses on the study of human behavior, cognition, and mental processes. It prepares students for careers in research, clinical psychology, counseling, and human resources.
The Benefits of an Undergraduate Degree

An undergraduate degree, typically a bachelor’s degree, is a valuable investment in your future. It opens doors to a wider range of opportunities, enhancing your earning potential, job prospects, and personal growth.
Increased Earning Potential
A bachelor’s degree is often a prerequisite for many high-paying jobs. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, workers with a bachelor’s degree earn significantly more than those with only a high school diploma. For example, in 2021, the median annual wage for workers with a bachelor’s degree was $77,000, compared to $41,000 for those with a high school diploma. This disparity highlights the substantial financial advantage of pursuing a bachelor’s degree.
Improved Job Prospects
The job market is increasingly competitive, and a bachelor’s degree can give you a significant edge. Employers often prefer candidates with a college degree, as it demonstrates a commitment to learning, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. A bachelor’s degree can also open doors to specialized fields that require a specific set of knowledge and skills.
Enhanced Knowledge and Skills
A bachelor’s degree provides a structured and rigorous curriculum that develops a wide range of knowledge and skills. You will learn about different subjects, develop critical thinking abilities, improve your communication skills, and gain valuable research and analytical skills. These skills are highly transferable and applicable to various industries and career paths.
Personal and Professional Growth
Pursuing a bachelor’s degree is not just about acquiring knowledge; it’s also about personal and professional growth. You will develop your independence, time management skills, and ability to work independently and collaboratively. The college experience exposes you to diverse perspectives, encourages intellectual curiosity, and fosters a sense of community.
Advancement and Leadership Opportunities
A bachelor’s degree can unlock advancement and leadership opportunities. Many organizations require a bachelor’s degree for management and leadership roles. The knowledge and skills gained through a bachelor’s degree can equip you to take on greater responsibilities, lead teams, and make informed decisions.
The Role of an Undergraduate Degree in Today’s World
The landscape of higher education is rapidly evolving, and the role of undergraduate degrees in the 21st century is undergoing a significant transformation. As technology continues to advance and the global economy becomes increasingly interconnected, the demand for individuals with specialized skills and knowledge is growing. This shift is influencing the way undergraduate degrees are designed and delivered, with institutions adapting their programs to meet the needs of emerging industries and the workforce of the future.
The Growing Importance of Specialized Skills
The traditional model of higher education, where students pursued a broad liberal arts education, is being challenged by the need for specialized skills in a rapidly changing job market. Employers are increasingly seeking candidates with specific technical skills and practical experience relevant to their industries. This trend is driving the development of specialized undergraduate degrees that focus on specific fields, such as data science, cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and digital marketing. These programs are designed to equip students with the technical knowledge and practical skills necessary to succeed in these emerging fields.
Adapting Undergraduate Degrees to Meet Emerging Needs, Is an undergraduate degree a bachelor’s
Higher education institutions are responding to the evolving needs of the workforce by adapting their undergraduate programs to meet the demands of emerging industries. This includes:
- Introducing new programs and specializations: Universities are developing new programs and specializations in fields like data science, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence, which are in high demand in the technology sector.
- Integrating technology into existing programs: Traditional programs are being updated to incorporate technology-based learning experiences, such as online courses, simulations, and virtual labs, to enhance students’ technical skills.
- Promoting interdisciplinary learning: Universities are encouraging students to pursue interdisciplinary degrees that combine knowledge from different fields, such as computer science and business, or engineering and design. This approach prepares graduates with a broader range of skills and knowledge, making them more adaptable to a changing job market.
- Emphasizing practical skills and experience: Universities are placing greater emphasis on practical skills and experience, offering internships, apprenticeships, and project-based learning opportunities to prepare students for the workforce.
Outcome Summary: Is An Undergraduate Degree A Bachelor’s
In conclusion, the term “undergraduate degree” encompasses a spectrum of academic programs, with the bachelor’s degree serving as the most prevalent and recognized. Whether you’re pursuing a Bachelor of Arts, a Bachelor of Science, or a specialized degree, the value of an undergraduate education remains undeniable. It equips individuals with the knowledge, skills, and credentials necessary to excel in a competitive job market and contribute meaningfully to society. As you embark on your academic journey, consider the diverse options available within the realm of undergraduate degrees and choose a path that aligns with your aspirations and passions.
Top FAQs
What are some examples of undergraduate degrees?
Common undergraduate degrees include Bachelor of Arts (BA), Bachelor of Science (BS), Bachelor of Engineering (BEng), Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA), and many more specialized degrees.
How long does it take to earn an undergraduate degree?
A typical undergraduate degree program in the United States takes four years to complete, though some programs may be shorter or longer depending on the institution and the chosen field of study.
What are the benefits of earning an undergraduate degree?
Benefits include increased earning potential, improved job prospects, enhanced knowledge and skills, personal and professional growth, and access to advanced education and career opportunities.
Are there any alternative paths to a bachelor’s degree?
Yes, there are alternative paths, such as associate degrees or online programs, that can lead to a bachelor’s degree. These options offer flexibility and accessibility for individuals with diverse backgrounds and learning styles.




