
- General Overview of Bachelor’s Degree Requirements
- Factors Influencing Credit Hour Requirements
- Course Load and Credit Hour Accumulation
- Graduation Requirements and Credit Hour Completion: How Many Credit Hours For Bachelor’s Degree
- Credit Hour Variations and Considerations
- Resources for Understanding Credit Hour Requirements
- Last Recap
- FAQ Compilation
How many credit hours for bachelor’s degree – How many credit hours for a bachelor’s degree? This question often arises for aspiring college students, as understanding the path to graduation is crucial. A bachelor’s degree typically requires a set number of credit hours, reflecting the accumulated knowledge and skills acquired through coursework. The credit hour requirement can vary depending on the chosen field of study, the institution, and even the specific program.
The journey to a bachelor’s degree involves navigating a structured curriculum, with each course contributing to the overall credit hour accumulation. This journey is not only about acquiring knowledge but also about developing critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills. The credit hour system provides a standardized measure of academic progress, allowing institutions and students to track the completion of degree requirements.
General Overview of Bachelor’s Degree Requirements
A bachelor’s degree is a standard undergraduate degree offered by universities and colleges in the United States. It is a significant academic achievement that signifies completion of a specific program of study. The requirements for obtaining a bachelor’s degree vary depending on the institution and the chosen field of study. However, there are some common elements that are consistent across most programs.
The number of credit hours required to earn a bachelor’s degree is one of the key factors to consider.
Standard Credit Hour Requirement
The standard credit hour requirement for a bachelor’s degree in the United States is 120 credit hours. This number represents the total amount of coursework that a student must complete to fulfill the degree requirements.
Credit Hour Requirements Across Academic Fields
The credit hour requirement can vary slightly depending on the chosen field of study. For example, some fields, such as engineering or medicine, may require more than 120 credit hours due to the intensive nature of their coursework. Conversely, some fields, such as liberal arts or social sciences, may require fewer credit hours. Here are some examples:
- Engineering: 128-132 credit hours
- Medicine: 128-132 credit hours
- Business: 120-124 credit hours
- Liberal Arts: 120-124 credit hours
- Social Sciences: 120-124 credit hours
Impact of Transfer Credits
Transfer credits are earned at another institution and can be applied toward the completion of a bachelor’s degree at a different institution. The number of transfer credits accepted varies depending on the institution and the specific courses taken. Students who have earned transfer credits may have a reduced credit hour requirement for their bachelor’s degree. For example, a student who has earned 30 transfer credits may only need to complete 90 additional credit hours at their new institution.
Factors Influencing Credit Hour Requirements

The number of credit hours required for a bachelor’s degree can vary significantly depending on a range of factors. These factors are designed to ensure students acquire the necessary knowledge and skills for their chosen field.
Course Intensity and Workload, How many credit hours for bachelor’s degree
The intensity and workload of courses are key factors in determining credit hour requirements. A course that meets for three hours per week may carry three credit hours, while a course that meets for five hours per week might be assigned four or five credit hours. This reflects the increased time commitment and academic rigor associated with the course.
University and Institutional Policies
Universities and institutions have varying credit hour requirements, often based on their academic traditions, program structures, and accreditation standards. Some institutions may follow a standard model where most programs require 120 credit hours for graduation, while others may have more flexible or specialized requirements.
For example, a university emphasizing liberal arts education may require a broader range of courses, leading to a higher credit hour requirement compared to a university with a more focused professional program.
Course Load and Credit Hour Accumulation
To earn a bachelor’s degree, students typically enroll in a set number of credit hours each semester. This course load determines how quickly they progress toward graduation. Understanding the typical course load and the different ways to accumulate credit hours can help students plan their academic journey effectively.
Typical Course Load for Full-Time Students
Full-time undergraduate students typically take a course load of 12 to 18 credit hours per semester. This translates to 3 to 4 courses, depending on the credit hour value of each course. A 12-credit hour course load is considered the minimum for full-time status, while a 15-credit hour load is more common. Students aiming to graduate in four years often take a heavier course load of 16 to 18 credit hours.
Accumulating Credit Hours
Students can accumulate credit hours in various ways:
- Traditional Courses: The majority of credit hours are earned through traditional courses taken during the fall and spring semesters. These courses are typically offered in a lecture format with assigned readings, homework, and exams.
- Summer Courses: Many universities offer summer courses that allow students to accelerate their degree progress. These courses are often shorter and more condensed, covering the same material as a regular semester course. Taking summer courses can help students graduate early or free up their schedule during the regular academic year.
- Internships: Some universities offer internship programs that can provide students with valuable work experience and earn them college credit. These internships are typically supervised by faculty members and require students to complete specific tasks and assignments related to their field of study.
- Transfer Credits: Students who have taken courses at other institutions may be able to transfer those credits to their current university. The transferability of credits depends on the receiving institution’s policies and the course content. Students should consult with their academic advisor to determine which credits are eligible for transfer.
- Advanced Placement (AP) Credits: Students who have taken and passed AP exams in high school may be eligible for college credit. The number of credit hours awarded for each AP exam varies depending on the university’s policies and the specific exam.
- CLEP Exams: The College-Level Examination Program (CLEP) offers exams that assess college-level knowledge in various subjects. Students who pass CLEP exams may be able to earn college credit. This can be particularly beneficial for students who have prior learning experience or who wish to challenge themselves in a particular subject.
Course Load and Credit Hour Accumulation Rates
Here is a table comparing different course loads and their corresponding credit hour accumulation rates:
| Course Load (Credit Hours) | Number of Courses (Typical) | Credit Hours per Year (Fall/Spring) | Credit Hours per Semester |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 3-4 | 24 | 12 |
| 15 | 4-5 | 30 | 15 |
| 16 | 4-5 | 32 | 16 |
| 18 | 5-6 | 36 | 18 |
Note: These are general guidelines, and actual course loads and credit hour accumulation rates may vary depending on the specific program of study, university policies, and individual student needs.
Graduation Requirements and Credit Hour Completion: How Many Credit Hours For Bachelor’s Degree
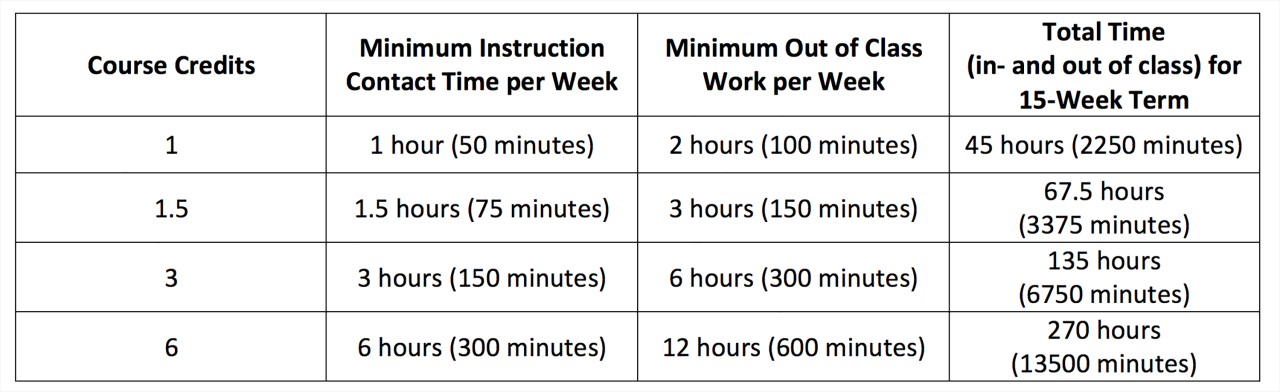
Earning a bachelor’s degree requires completing a specific number of credit hours and fulfilling other academic requirements. These requirements ensure that graduates have a comprehensive understanding of their chosen field and are prepared for their chosen career paths.
Minimum Credit Hour Requirement for Graduation
Most bachelor’s degree programs require students to complete a minimum of 120 credit hours. This number can vary slightly depending on the specific program and institution. For instance, some programs may require 124 credit hours, while others might require 128 credit hours. This variation is often influenced by the program’s specialization or the institution’s curriculum structure.
Credit Hour Verification and Degree Conferral
Once students have completed the required credit hours and met all other graduation requirements, they can apply for graduation. The institution’s registrar’s office verifies the student’s academic record, including their completed courses and credit hours. Upon verification, the institution confers the bachelor’s degree.
Common Graduation Requirements Beyond Credit Hours
Beyond credit hour completion, several other graduation requirements are common. These requirements ensure that students have a well-rounded educational experience and are prepared for the challenges of their chosen field.
Residency Requirements
Most institutions require students to complete a certain number of credit hours in residence. This requirement ensures that students have a meaningful academic experience at the institution and are familiar with its policies and resources. Typically, students must complete a minimum of 30 credit hours in residence, which translates to a significant portion of their overall credit hour requirements.
GPA Requirements
Many institutions also have a minimum GPA requirement for graduation. This requirement ensures that students maintain a certain level of academic achievement and demonstrate their ability to succeed in their studies. The minimum GPA requirement varies by institution and program, but it is typically around 2.0 on a 4.0 scale.
Other Requirements
Other common graduation requirements may include:
- General education requirements: These courses ensure students have a broad understanding of different academic disciplines, such as humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences.
- Major-specific requirements: These courses provide students with in-depth knowledge and skills in their chosen field of study.
- Electives: These courses allow students to explore other areas of interest and broaden their academic horizons.
- Capstone projects or theses: These projects allow students to apply their knowledge and skills to a real-world problem or research question.
- Foreign language requirements: Some institutions require students to demonstrate proficiency in a foreign language, which can be beneficial for career opportunities in a globalized world.
Credit Hour Variations and Considerations
The number of credit hours required for a bachelor’s degree can vary depending on the specific major and institution. While most institutions follow a general guideline of 120 credit hours for a bachelor’s degree, certain programs may require more or fewer credit hours to fulfill all program requirements.
Variations in Credit Hour Requirements Across Majors
The credit hour requirements for different majors within the same institution can vary significantly due to the unique curriculum and course load associated with each program. Some majors, such as engineering or pre-med, may require more specialized coursework and laboratory experiences, leading to a higher credit hour requirement. In contrast, majors like the humanities or social sciences may have fewer required courses, resulting in a lower credit hour requirement.
For example, a bachelor’s degree in computer science at a particular university might require 130 credit hours, while a bachelor’s degree in English literature at the same university might only require 120 credit hours.
Elective Courses and Their Impact on Total Credit Hours
Elective courses are courses that students can choose to take outside of their major requirements. These courses provide students with the opportunity to explore other areas of interest, broaden their knowledge base, or develop specific skills. The number of elective courses required for a bachelor’s degree can vary depending on the institution and the specific major.
For instance, a university might require students to complete 20 credit hours of elective courses, while another university might require 30 credit hours.
Credit Hour Requirements for Different Majors
The following table provides a comparison of the credit hour requirements for different majors at a hypothetical university:
| Major | Credit Hours Required |
|—|—|
| Computer Science | 130 |
| English Literature | 120 |
| Biology | 125 |
| Business Administration | 128 |
| History | 120 |
| Nursing | 135 |
It’s important to note that these credit hour requirements are for illustrative purposes only and may vary from institution to institution. Students should consult with their academic advisor to determine the specific credit hour requirements for their chosen major.
Resources for Understanding Credit Hour Requirements
Navigating the world of credit hours can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re trying to figure out how many you need for your specific program. Thankfully, there are numerous resources available to help you understand these requirements.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of where to find information and how to seek clarification on credit hour requirements.
University Websites and Academic Catalogs
Your university’s website is the first place to look for information on credit hour requirements. Most universities have a dedicated section on their website for academics, which usually includes an academic catalog. The academic catalog is a comprehensive document that Artikels all academic policies and procedures, including credit hour requirements for each program.
- University Website: The academic information section on your university’s website typically contains links to the academic catalog, program-specific handbooks, and other relevant resources.
- Academic Catalog: The academic catalog is a valuable resource that provides detailed information about each program, including course descriptions, credit hour requirements, and graduation requirements.
Program-Specific Handbooks
Many programs have their own specific handbooks or guides that provide detailed information on credit hour requirements and other program-specific policies. These handbooks can be found on the university website or through your program’s department.
Contacting Academic Advisors and Program Coordinators
If you still have questions about credit hour requirements after reviewing the available resources, don’t hesitate to reach out to your academic advisor or program coordinator. These individuals are experts in your program and can provide personalized guidance.
- Academic Advisor: Your academic advisor is a valuable resource for general academic advising, including questions about credit hour requirements.
- Program Coordinator: The program coordinator is responsible for overseeing the specific program you are enrolled in. They can provide detailed information about credit hour requirements and other program-specific policies.
“When contacting your advisor or coordinator, be prepared to provide your program of study and any specific questions you have regarding credit hour requirements.”
Last Recap
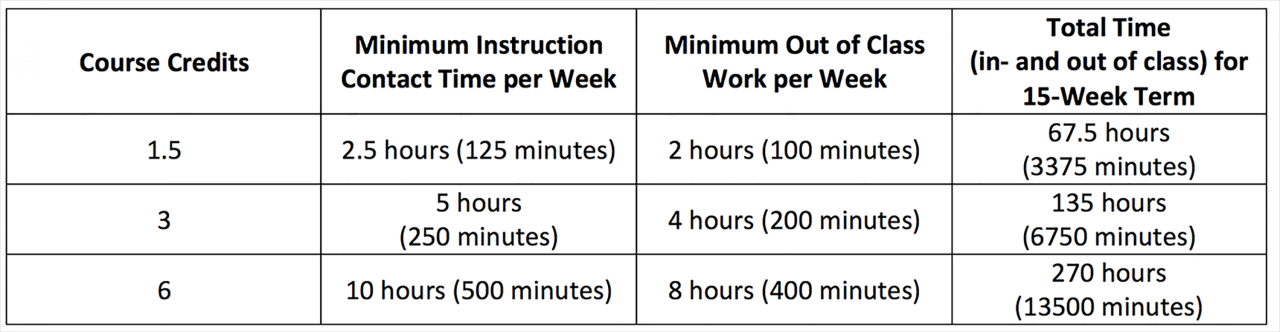
The credit hour requirement for a bachelor’s degree, while seemingly straightforward, involves a multitude of factors. From course intensity and program specifics to institutional policies, understanding these nuances empowers students to plan their academic journey effectively. By staying informed and engaging with academic advisors, students can navigate the credit hour system with confidence, ensuring they meet the requirements for a successful graduation.
FAQ Compilation
What is a credit hour?
A credit hour represents a unit of academic work typically equivalent to one hour of classroom instruction per week for a 15-week semester.
Can I transfer credit hours from another institution?
Yes, many institutions accept transfer credits from other accredited colleges and universities. The transferability of credits depends on the specific courses and the receiving institution’s policies.
How can I earn credit hours outside of traditional coursework?
Some institutions offer credit for prior learning experiences, such as work experience, military training, or standardized test scores. Additionally, students can earn credit through internships, study abroad programs, or CLEP exams.
What happens if I don’t meet the credit hour requirement for graduation?
If you fall short of the required credit hours, you may need to take additional courses or explore alternative options, such as petitioning for an exception or pursuing a different degree.




