
- General Overview of Bachelor’s Degrees
- Factors Influencing Credit Hour Requirements
- Transfer Credits and Prior Learning
- Credit Hour Breakdown by Major
- Impact of Credit Hours on Graduation Timeline
- Credit Hours and Cost of Education
- Final Summary
- Expert Answers: How Many Credit Hours For Bachelor Degree
How many credit hours for bachelor degree – How many credit hours for a bachelor’s degree? This is a question that many prospective students ask as they embark on their academic journey. The answer, however, is not a simple one. The number of credit hours required for a bachelor’s degree varies depending on a multitude of factors, including the specific major, the university, and even the student’s individual academic path.
Understanding the credit hour system is crucial for students to plan their academic goals and make informed decisions about their course load. This guide delves into the intricacies of credit hour requirements, exploring the key factors that influence the total number of credits needed for graduation, the impact of transfer credits, and the relationship between credit hours and the cost of education.
General Overview of Bachelor’s Degrees

A bachelor’s degree is a foundational academic achievement that signifies a student’s successful completion of a comprehensive undergraduate program. Earning a bachelor’s degree typically requires a specific number of credit hours, which represent the units of academic work completed.
Standard Credit Hour Requirement
The standard credit hour requirement for a bachelor’s degree in the United States is 120 credit hours. This number may vary slightly depending on the specific institution and program of study. However, 120 credit hours is the most common requirement across universities and colleges.
Credit Hours Required for Different Majors
The number of credit hours required for different majors can vary considerably. Some majors, such as engineering or science, may require more credit hours due to the intensive nature of their coursework. Other majors, such as the humanities or social sciences, may have slightly lower credit hour requirements. Here are some examples of typical credit hour requirements for different majors:
- Engineering: 128-132 credit hours
- Science: 124-128 credit hours
- Business: 120-124 credit hours
- Humanities: 116-120 credit hours
- Social Sciences: 118-122 credit hours
Credit Hours and Course Load
Credit hours are directly related to the amount of time and effort required for a course. The number of credit hours assigned to a course reflects the expected workload, including class time, assignments, and exams. Here’s how credit hours translate to typical course loads:
- Full-time student: Typically takes 12-18 credit hours per semester, which equates to 4-6 courses.
- Part-time student: Takes fewer than 12 credit hours per semester, usually 3-6 courses.
Factors Influencing Credit Hour Requirements
The number of credit hours required for a bachelor’s degree can vary significantly depending on several factors. Understanding these factors can help students plan their academic journey effectively and make informed decisions about their course selection.
University Policies and Accreditation Standards, How many credit hours for bachelor degree
University policies and accreditation standards play a significant role in determining the credit hour requirements for a degree.
- Accreditation Bodies: Accrediting bodies like the Higher Learning Commission (HLC) or the Middle States Commission on Higher Education (MSCHE) set minimum credit hour requirements for institutions to maintain accreditation. These standards ensure that institutions provide a comprehensive and rigorous education to their students.
- Institutional Policies: Each university has its own policies regarding credit hour requirements. Some institutions may have specific requirements for different majors or concentrations, while others may offer more flexibility. For example, some universities may require a minimum number of credits in general education courses, while others may allow students to focus more on their major.
Elective Courses and Specialization Choices
The choice of elective courses and specialization can also influence the total credit hours needed for a degree.
- Elective Courses: Elective courses offer students the opportunity to explore areas of interest outside their major. Depending on the university and the specific program, the number of elective credits required may vary. Some universities may require a certain number of elective credits, while others may allow students to choose a more focused path.
- Specialization: Students may choose to specialize within their major, which can lead to additional credit hour requirements. Specializations often involve taking advanced courses in a specific area of study, which can add to the total credit hours needed for graduation.
Transfer Credits and Prior Learning
Transferring credits from previous institutions or acknowledging prior learning can significantly impact the total credit hours required for a bachelor’s degree. This process can help students expedite their degree completion and save both time and money.
Transfer Credit Evaluation
Transfer credits are academic credits earned at one institution that are accepted for credit at another. The process of evaluating transfer credits involves determining whether the courses taken at the previous institution meet the requirements for the current degree program. This evaluation considers factors such as:
- Course content and learning outcomes
- Course level (e.g., introductory, advanced)
- Grading scale and minimum grade requirements
- The institution’s transfer credit policy
Prior Learning Assessment
Prior learning assessment (PLA) allows students to receive academic credit for knowledge and skills acquired through work experience, military service, or other non-traditional learning experiences. This process typically involves submitting documentation and evidence of the learning acquired, which is then evaluated by the institution. PLA can be a valuable option for students who have significant work experience or have completed training programs that align with their degree program.
Examples of Credit Transfer Impact
- A student who has completed an associate’s degree in business administration may be able to transfer up to 60 credit hours towards a bachelor’s degree in business. This can reduce the time needed to complete the bachelor’s degree by two years.
- A student who has worked as a software developer for several years may be able to receive credit for their work experience through PLA, potentially reducing the number of required courses.
Credit Hour Breakdown by Major
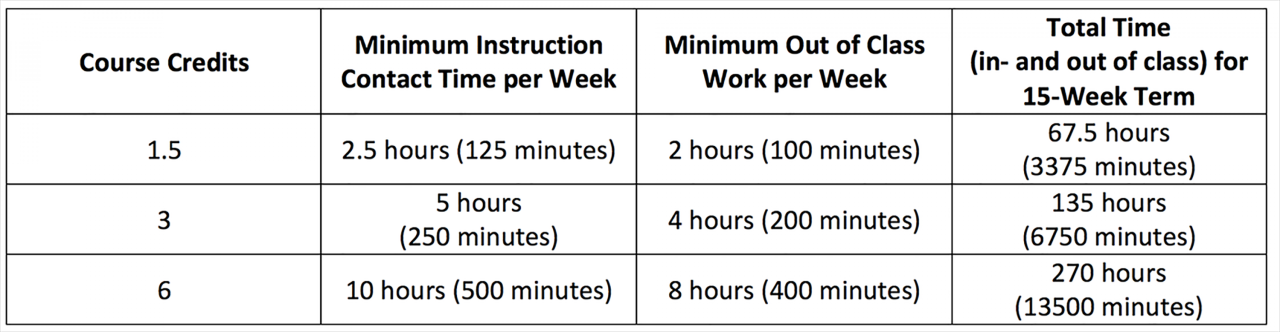
The number of credit hours required for a bachelor’s degree can vary significantly depending on the specific major. Each major has its own unique set of courses and requirements, which can affect the total credit hour count.
Credit Hour Requirements by Major
Here’s a table showing the typical credit hour requirements for some common majors:
| Major | Minimum Credit Hours | Maximum Credit Hours | Credit Hour Allocation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business Administration | 120 | 130 | Core business courses, elective courses in specific areas of business, general education courses |
| Computer Science | 120 | 130 | Core computer science courses, elective courses in specialized areas like software engineering or data science, general education courses |
| Engineering | 128 | 140 | Core engineering courses, elective courses in specialized areas like mechanical or electrical engineering, general education courses |
| Nursing | 120 | 130 | Core nursing courses, clinical rotations, general education courses |
| Education | 120 | 130 | Core education courses, elective courses in specific areas like early childhood education or special education, general education courses |
| Arts and Humanities | 120 | 130 | Core humanities courses, elective courses in specific areas like literature, history, or philosophy, general education courses |
| Social Sciences | 120 | 130 | Core social science courses, elective courses in specific areas like psychology, sociology, or political science, general education courses |
Impact of Credit Hours on Graduation Timeline
The number of credit hours required for a bachelor’s degree directly influences how long it takes to graduate. Understanding how credit hours impact your graduation timeline is crucial for planning your academic journey.
The typical length of a bachelor’s degree program is four years, assuming full-time enrollment. However, the actual time it takes to graduate can vary significantly depending on factors such as course load, transfer credits, and academic performance.
Full-Time vs. Part-Time Enrollment
The number of credit hours a student takes each semester directly impacts their graduation timeline. Full-time enrollment typically involves taking 12-18 credit hours per semester, while part-time enrollment allows students to take fewer courses.
- Full-Time Enrollment: Students taking a full course load can typically graduate in four years, assuming they maintain good academic standing and complete all required courses.
- Part-Time Enrollment: Students enrolled part-time may take longer to graduate, potentially extending their studies beyond four years. For example, a student taking 6-9 credit hours per semester might take six years to complete a 120-credit hour degree program.
Graduation Timeline Examples
- Example 1: Graduating Early: A student who earns transfer credits for previous coursework or takes summer courses could potentially graduate in less than four years. For instance, a student who transfers 30 credit hours and takes 18 credit hours per semester could potentially graduate in three years.
- Example 2: Graduating Later: A student who takes a lighter course load, changes majors, or experiences academic challenges might take longer than four years to graduate. For example, a student who takes 12 credit hours per semester and repeats a few courses could potentially graduate in five years.
Credit Hours and Cost of Education
The number of credit hours required for a bachelor’s degree can significantly influence the overall cost of your education. Understanding how credit hours relate to tuition and fees is crucial for managing your expenses.
Tuition and Fee Calculation
Tuition and fees are often calculated based on the number of credit hours you take each semester. This means that taking a heavier course load can lead to higher costs. Most colleges and universities have a set tuition rate per credit hour, and you’ll pay this rate for each credit hour you register for. Additionally, you may also have to pay various fees, such as technology fees, student activity fees, and library fees, which can vary depending on the institution and the specific program of study.
Final Summary
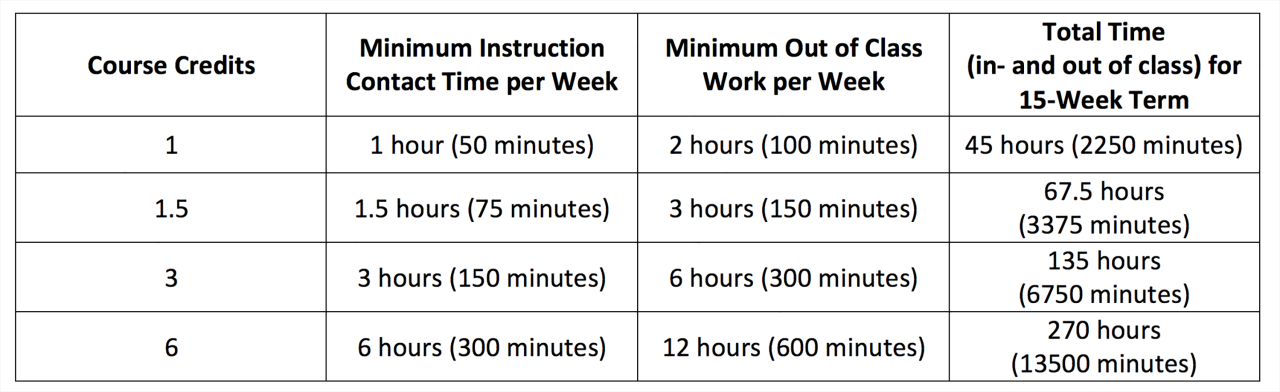
In conclusion, the number of credit hours required for a bachelor’s degree is a dynamic figure influenced by various factors. By understanding these factors and carefully planning their academic path, students can navigate the credit hour system effectively and achieve their educational goals. Whether pursuing a traditional four-year program or opting for a more flexible schedule, the journey to a bachelor’s degree is a rewarding one that requires careful consideration of credit hour requirements and the overall educational experience.
Expert Answers: How Many Credit Hours For Bachelor Degree
What are credit hours?
Credit hours represent units of academic work, typically based on the number of class hours per week. Each course is assigned a specific number of credit hours, and students accumulate credits by successfully completing courses.
Can I graduate early with extra credit hours?
While it’s possible to graduate early by taking a heavier course load, most universities have minimum residency requirements that must be met. Consult your academic advisor to determine the feasibility of early graduation.
How do I know how many credit hours I need to graduate?
The best way to determine your specific credit hour requirements is to consult your academic advisor or the university’s catalog.
Are credit hours the same across all universities?
Credit hour requirements can vary significantly between institutions. It’s essential to check the specific policies of the university you’re attending.




