
How many credit hours do you need for bachelor’s degree – How many credit hours do you need for a bachelor’s degree? It’s a common question for prospective students navigating the complex world of higher education. While a standard number exists, the actual credit hour requirement can vary significantly depending on factors like your chosen program, the university you attend, and even your individual course load.
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of credit hour requirements for bachelor’s degrees, exploring the typical breakdown, influencing factors, and practical implications for students. We’ll also address common questions about credit hour equivalency and how they relate to tuition costs and program duration.
Bachelor’s Degree Requirements
Earning a bachelor’s degree typically requires completing a certain number of credit hours. Credit hours are units of academic work, and the total number needed varies depending on the institution and program of study.
General Credit Hour Requirements
Most bachelor’s degree programs in the United States require students to complete between 120 and 130 credit hours. However, this number can fluctuate based on the specific program and institution. Some programs may require fewer or more credit hours, depending on their complexity and the depth of study.
Credit Hour Breakdown
The total number of credit hours required for a bachelor’s degree varies depending on the specific program and institution. However, a typical bachelor’s degree program requires around 120-130 credit hours. These credit hours are typically distributed across different academic areas, such as core courses, major courses, and electives.
Credit Hour Distribution
Credit hours are typically distributed across different academic areas to ensure a well-rounded education. Here’s a breakdown of how credit hours are typically distributed:
- Core Courses: These are foundational courses that are required for all students, regardless of their major. They typically cover subjects such as mathematics, English, humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences. Core courses typically account for 30-40 credit hours.
- Major Courses: These are courses that are specific to a student’s chosen major. They provide in-depth knowledge and skills in the student’s field of study. Major courses typically account for 40-50 credit hours.
- Electives: These are courses that students can choose from a variety of subjects, allowing them to explore their interests and expand their knowledge base. Electives typically account for 20-30 credit hours.
Sample Credit Hour Breakdown
Here’s a sample credit hour breakdown for a typical bachelor’s degree program in Business Administration:
| Course Category | Credit Hours |
|---|---|
| Core Courses | 36 |
| Major Courses | 48 |
| Electives | 24 |
| Total | 108 |
Note: This is just a sample breakdown, and the actual credit hour requirements may vary depending on the specific program and institution.
Factors Affecting Credit Hour Needs

While a standard bachelor’s degree typically requires 120 credit hours, several factors can influence the exact number of credit hours you need to graduate. Understanding these factors can help you plan your academic journey effectively.
The number of credit hours needed for a bachelor’s degree can vary significantly based on the specific program, the institution you attend, and your individual academic choices.
Program Type
The type of program you choose can have a major impact on the total credit hours required. Some programs, such as engineering or pre-med, may require more specialized courses and labs, leading to a higher credit hour requirement. Conversely, programs like liberal arts or general studies might have a lower credit hour requirement.
Institution
Different institutions have different policies and requirements regarding credit hours. Some institutions might require a specific number of credit hours for a particular degree, while others might have more flexible guidelines. It’s crucial to check the specific requirements of the institution you plan to attend.
Individual Course Load
The number of courses you take per semester can also affect the total credit hours you accumulate. Taking a heavier course load will allow you to earn more credit hours per semester, potentially reducing the overall time needed to graduate. However, it’s important to balance course load with your personal commitments and academic performance.
Transfer Credits
Transfer credits can significantly impact your credit hour requirements. If you have previously earned college credit at another institution, these credits might be transferable to your current program. Transfer credits can reduce the total number of credit hours you need to earn at your current institution.
Prior Learning Assessments
Prior learning assessments (PLAs) allow you to earn college credit for knowledge and skills acquired outside of a traditional classroom setting. This could include work experience, professional certifications, or even personal projects. Successful completion of a PLA can reduce the total credit hours you need to earn.
Credit Hour Equivalency: How Many Credit Hours Do You Need For Bachelor’s Degree
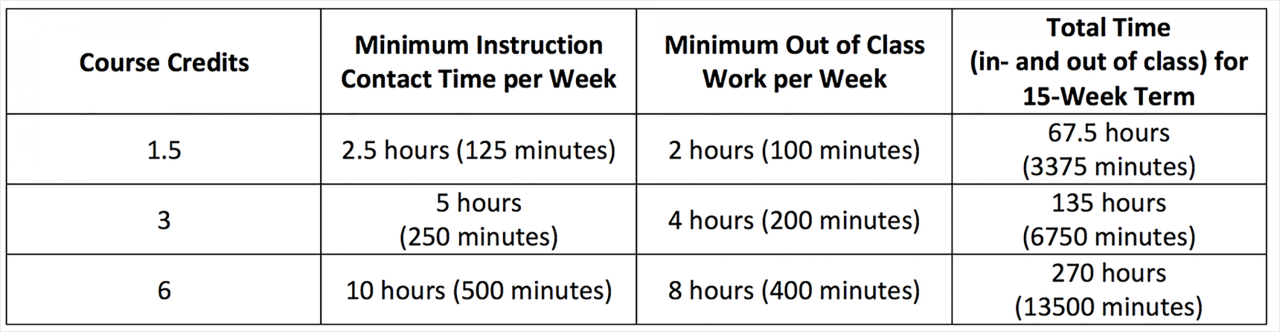
The credit hour system is the primary way to measure academic work in the United States. However, other academic measurement systems are used internationally. Understanding credit hour equivalency is essential for students transferring from one institution to another, especially when transferring from an international institution to a U.S. institution.
Credit hour equivalency refers to the process of determining how many credit hours a course taken at one institution is equivalent to at another institution. This is particularly important for students who are transferring from an institution that uses a different academic measurement system.
Credit Hour System vs. ECTS
The credit hour system is based on the amount of time a student is expected to spend on a course, including classroom time and outside work. One credit hour typically represents 15 hours of student work. In contrast, the European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS) is a credit system used in most European countries. ECTS credits are based on the workload required for a course, with one ECTS credit representing 25-30 hours of student work.
- Credit Hour System: Based on time spent on a course, including classroom time and outside work.
- ECTS: Based on the workload required for a course.
Determining Credit Hour Equivalency for International Students
Several factors are considered when determining credit hour equivalency for international students transferring to a U.S. institution.
- Course Content and Level: The content and level of the course taken at the international institution are compared to similar courses offered at the U.S. institution. This helps determine the appropriate credit hour equivalency.
- Course Description and Syllabus: The course description and syllabus are reviewed to assess the course’s depth and breadth. This information is used to determine the equivalent credit hours at the U.S. institution.
- Institution’s Policies: Each U.S. institution has its own policies regarding credit hour equivalency for international students. The policies may vary depending on the student’s country of origin and the institution’s agreements with international institutions.
- Course Evaluation: The international student’s transcript and course descriptions are often evaluated by the U.S. institution’s admissions office or a designated transfer credit evaluator. This evaluation determines the appropriate credit hour equivalency for each course.
For example, a student who has completed a course at a European university that is worth 6 ECTS credits may be awarded 3 credit hours at a U.S. institution. This is because 6 ECTS credits represent approximately 150 hours of student work, which is equivalent to 10 credit hours in the U.S. system. However, the actual credit hour equivalency may vary depending on the course content, level, and the U.S. institution’s policies.
Practical Implications of Credit Hours
Credit hours are not just abstract units; they have real-world implications that affect students’ financial, academic, and time management aspects. Understanding these implications can help students make informed decisions about their academic journey.
Tuition Costs, How many credit hours do you need for bachelor’s degree
The number of credit hours a student enrolls in directly impacts their tuition bill. Most institutions charge tuition based on a per-credit-hour rate. Therefore, taking a heavier course load translates to higher tuition costs.
For example, if a university charges $500 per credit hour, a student taking 12 credit hours will pay $6,000 in tuition for that semester. However, if they enroll in 15 credit hours, their tuition will increase to $7,500.
Program Duration
Credit hour requirements play a crucial role in determining the length of a bachelor’s degree program. A standard bachelor’s degree typically requires 120-130 credit hours. Students can graduate faster by taking a heavier course load and earning more credit hours per semester.
For instance, a student taking 15 credit hours per semester could potentially graduate in four years, while a student taking 12 credit hours per semester might need an additional semester or two to complete the required credit hours.
Academic Workload and Time Management
The number of credit hours a student takes directly influences their academic workload and time management demands. A heavier course load means more classes, assignments, exams, and readings. This can lead to increased stress and difficulty balancing academics with other commitments.
Students should carefully consider their individual capabilities and time constraints when deciding on their course load. For example, a student working full-time might need to take fewer credit hours per semester to manage their workload effectively.
Final Conclusion
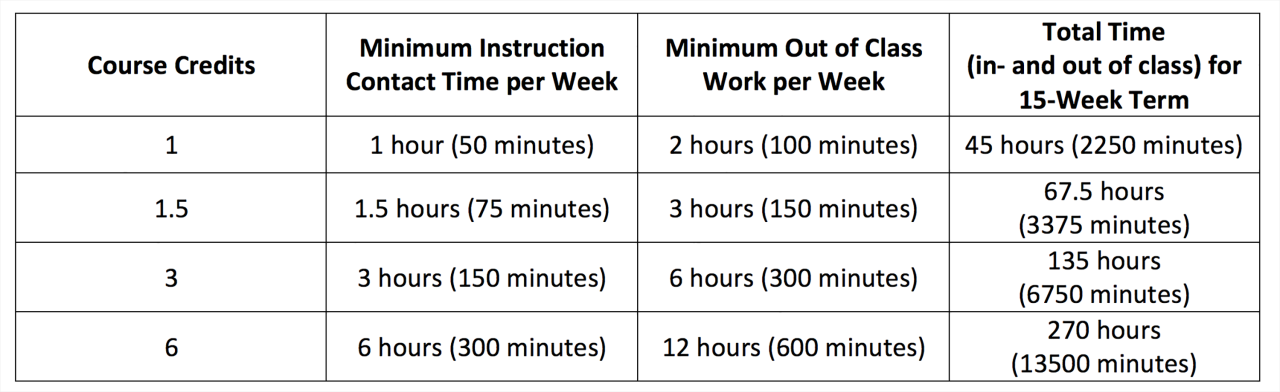
Understanding credit hour requirements is crucial for planning your academic journey. By carefully considering the factors discussed above, you can gain a clearer picture of your individual needs and make informed decisions about your program, institution, and course selections. Remember, your academic advisor is a valuable resource for personalized guidance and support throughout your undergraduate experience.
Expert Answers
What is a credit hour?
A credit hour represents a unit of academic work typically equivalent to one hour of classroom instruction per week for a 15-week semester.
Do all bachelor’s degrees require the same number of credit hours?
No, the number of credit hours needed for a bachelor’s degree can vary depending on the specific program and institution. Some programs may require more credit hours than others.
What happens if I take more than the required credit hours?
Taking extra credit hours can help you graduate early or pursue a minor or double major. However, it’s essential to consider your academic workload and financial implications.
Can I transfer credits from another institution?
Yes, you can often transfer credits from previous institutions. The number of transferable credits and their equivalency will vary based on the receiving institution’s policies.




