
How long is a bachelor’s degree? It’s a question that often pops up in the minds of prospective students. While a standard four-year timeframe is often assumed, the reality is that the length of a bachelor’s degree program can vary significantly depending on a multitude of factors. This guide explores the factors that influence program duration, delves into the intricacies of accelerated programs, and ultimately provides a comprehensive understanding of the bachelor’s degree journey.
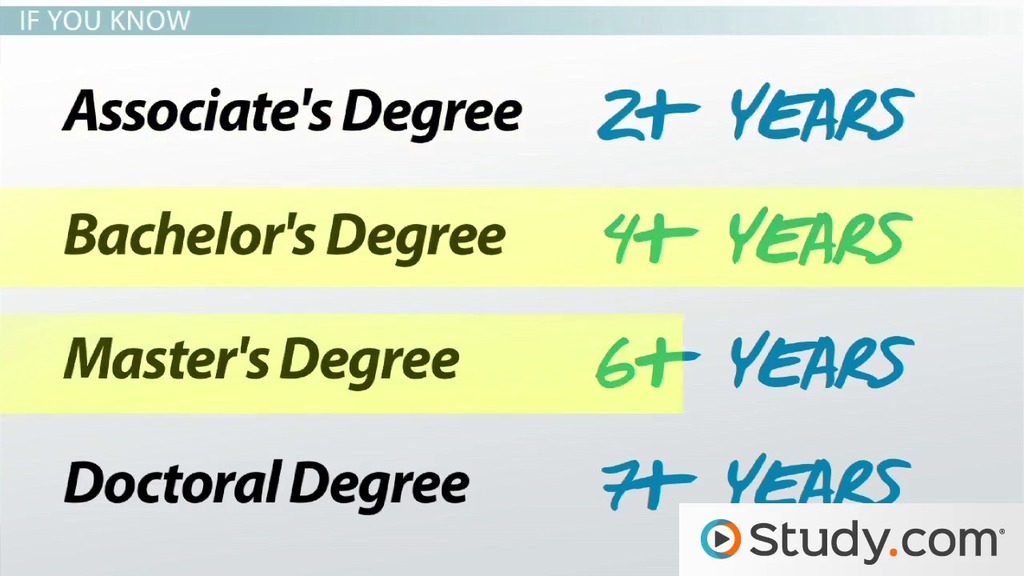
The standard duration for a full-time bachelor’s degree program is four years, encompassing eight semesters. However, this is just a starting point. Factors such as course load, transfer credits, academic standing, and even personal choices like internships or study abroad can impact the overall timeline. Understanding these factors is crucial for planning your academic path and setting realistic expectations.
Bachelor’s Degree Duration: How Long Is A Bachelor’s Degree
A bachelor’s degree is a foundational academic achievement, typically pursued after high school. It signifies a significant commitment to a chosen field of study and can open doors to various career opportunities. Understanding the duration of a bachelor’s degree program is crucial for planning your academic journey and setting realistic expectations.
Standard Duration
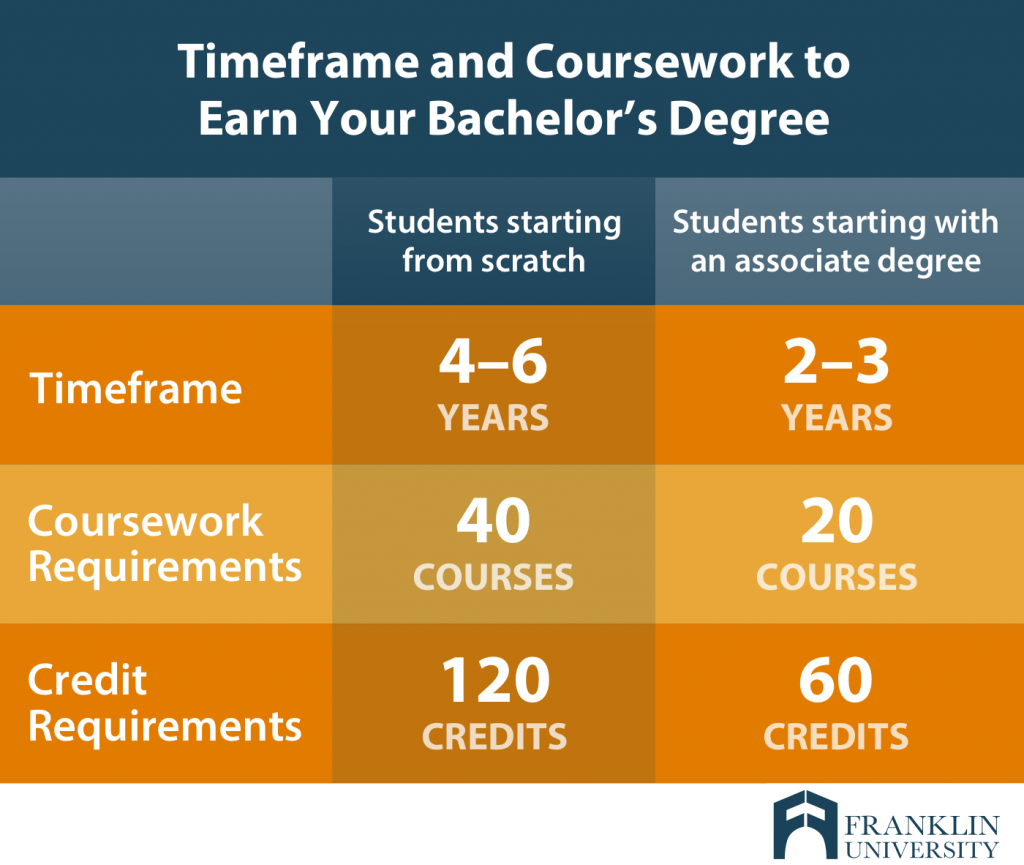
A standard bachelor’s degree program in the United States typically requires four years of full-time study to complete. This translates to eight semesters, with each semester lasting approximately 15 weeks.
Degree Programs and Their Lengths
The duration of a bachelor’s degree program can vary depending on the specific degree and the institution offering it. Here are some examples of common degree programs and their typical lengths:
- Bachelor of Arts (BA): Four years
- Bachelor of Science (BS): Four years
- Bachelor of Engineering (BE): Four to five years
- Bachelor of Architecture (BArch): Five to six years
Factors Influencing Duration
Several factors can influence the duration of a bachelor’s degree program:
- Full-time vs. Part-time Enrollment: Full-time students typically complete a bachelor’s degree in four years, while part-time students may take longer, depending on their course load and schedule.
- Transfer Credits: Students who have earned credits at other institutions can transfer them to their new university, potentially reducing the overall time needed to graduate.
- Course Load: Students who take a heavier course load per semester can graduate faster. However, this can also increase stress and workload.
- Summer Courses: Taking summer courses can help students accelerate their degree completion, especially if they need to make up for missed credits or want to graduate early.
- Double Major or Minor: Students pursuing a double major or a minor may need additional semesters to complete all the required courses.
Factors Affecting Program Length

While a standard bachelor’s degree typically takes four years to complete, several factors can influence this timeframe, leading to programs that are either shorter or longer.
The duration of a bachelor’s degree program can be affected by various factors, including course load, transfer credits, academic standing, and other experiences. Understanding these factors can help students plan their academic journey effectively.
Course Load
The number of courses a student takes each semester significantly impacts the program’s duration. Taking a full course load (typically 12-15 credit hours per semester) allows students to graduate within the standard four years. However, students may choose to take fewer courses per semester, especially if they have other commitments, such as work or family. This approach can extend the program’s length, potentially leading to a five-year or even longer graduation timeline. For example, a student taking only 9 credit hours per semester might need an extra year to complete the required credits.
Transfer Credits
Transfer credits are awarded for courses taken at other institutions that are equivalent to courses offered at the current university. Students who have successfully completed relevant courses at another college or university can often transfer these credits, reducing the overall number of courses they need to take. This can significantly shorten the program’s length. For instance, a student who has earned 30 transferable credits might be able to graduate in three years instead of four.
Academic Standing
Academic standing refers to a student’s performance in their courses. Students who consistently maintain a good GPA and meet the required academic standards can progress through their program efficiently. Conversely, students who struggle academically may need to retake courses or repeat semesters, which can extend the program’s length. For example, a student who fails a course might need to retake it during the summer or take an extra semester to graduate.
Internships and Study Abroad
Internships and study abroad experiences offer valuable opportunities for personal and professional growth. However, these experiences can also impact the program’s duration. Internships typically require a significant time commitment, potentially delaying graduation by a semester or more. Similarly, study abroad programs can last for a semester or even a full year, further extending the program’s length. For example, a student who completes a six-month internship might graduate a semester later than their peers who did not participate in an internship.
Accelerated Programs
Accelerated bachelor’s degree programs allow students to complete their undergraduate studies in a shorter timeframe than traditional programs. These programs are designed for students who want to graduate sooner and enter the workforce or pursue further education more quickly.
Accelerated programs offer various formats, including online and summer programs, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks.
Types of Accelerated Programs
Accelerated programs can be implemented in several ways, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. Here are some common types:
- Online Accelerated Programs: These programs allow students to complete their coursework at their own pace, often with flexible scheduling. They provide a convenient option for working professionals or students with family commitments.
- Summer Programs: These programs offer intensive coursework over the summer months, allowing students to complete a semester’s worth of material in a condensed timeframe. They are ideal for students who want to graduate early or accelerate their studies during their breaks.
- Year-Round Programs: These programs offer classes throughout the year, including summers, allowing students to complete their degree faster by taking more courses per year.
- Double Major Programs: These programs allow students to pursue two majors simultaneously, often leading to a shorter time to graduation. This option is suitable for students with a strong academic background and a clear career path.
Advantages of Accelerated Programs
Accelerated programs offer numerous advantages, including:
- Faster Graduation: Accelerated programs allow students to graduate sooner, enabling them to enter the workforce or pursue further education more quickly.
- Lower Overall Costs: By graduating earlier, students may spend less on tuition and living expenses.
- Increased Earning Potential: Entering the workforce sooner can lead to higher lifetime earnings.
- Greater Flexibility: Accelerated programs often offer more flexibility in scheduling, making them suitable for working professionals or students with family commitments.
Disadvantages of Accelerated Programs, How long is a bachelor’s degree
While accelerated programs offer numerous advantages, they also come with certain drawbacks:
- Increased Course Load: Accelerated programs often require students to take a heavier course load, which can lead to stress and burnout.
- Limited Flexibility: Some accelerated programs may have limited flexibility in course selection, requiring students to adhere to a specific curriculum.
- Less Time for Extracurricular Activities: The intensive nature of accelerated programs may leave less time for extracurricular activities, internships, or networking opportunities.
Bachelor’s Degree Structure
A bachelor’s degree program typically follows a structured curriculum designed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of their chosen field. This structure involves dividing the program into semesters or quarters, each encompassing a specific set of courses.
Semester and Quarter Systems
The most common ways to structure a bachelor’s degree program are through semesters or quarters. A semester system typically consists of two terms per academic year, while a quarter system comprises three terms.
Sample Course Schedule
The following table presents a sample course schedule for a typical bachelor’s degree program in Business Administration, assuming a semester system:
| Semester | Course Name | Credits |
|---|---|---|
| Freshman Year, Fall | Introduction to Business | 3 |
| Freshman Year, Fall | Principles of Accounting | 3 |
| Freshman Year, Fall | College Algebra | 3 |
| Freshman Year, Fall | Introduction to Psychology | 3 |
| Freshman Year, Spring | Microeconomics | 3 |
| Freshman Year, Spring | Business Statistics | 3 |
| Freshman Year, Spring | Introduction to Marketing | 3 |
| Freshman Year, Spring | Introduction to Sociology | 3 |
| Sophomore Year, Fall | Financial Accounting | 3 |
| Sophomore Year, Fall | Managerial Accounting | 3 |
| Sophomore Year, Fall | Principles of Management | 3 |
| Sophomore Year, Fall | Introduction to Finance | 3 |
| Sophomore Year, Spring | Marketing Management | 3 |
| Sophomore Year, Spring | Organizational Behavior | 3 |
| Sophomore Year, Spring | Business Law | 3 |
| Sophomore Year, Spring | Introduction to International Business | 3 |
| Junior Year, Fall | Corporate Finance | 3 |
| Junior Year, Fall | Strategic Management | 3 |
| Junior Year, Fall | Operations Management | 3 |
| Junior Year, Fall | Electives (Business) | 3 |
| Junior Year, Spring | Marketing Research | 3 |
| Junior Year, Spring | Human Resource Management | 3 |
| Junior Year, Spring | Electives (Business) | 3 |
| Senior Year, Fall | Business Ethics | 3 |
| Senior Year, Fall | Capstone Project | 3 |
| Senior Year, Fall | Electives (Business) | 3 |
| Senior Year, Spring | International Business Strategy | 3 |
| Senior Year, Spring | Electives (Business) | 3 |
The Value of a Bachelor’s Degree
A bachelor’s degree is a valuable investment in your future, offering numerous benefits that extend far beyond the classroom. It is a testament to your dedication, knowledge, and skills, opening doors to a wider range of career opportunities and higher earning potential.
Career Opportunities
A bachelor’s degree is often a prerequisite for many professional careers. It equips individuals with the specialized knowledge and skills required to excel in their chosen fields. A bachelor’s degree demonstrates to potential employers that you possess the necessary foundation for success in a specific industry.
- Healthcare: A bachelor’s degree is essential for aspiring nurses, pharmacists, and physical therapists.
- Business: A bachelor’s degree in business administration or a related field can open doors to careers in management, finance, marketing, and accounting.
- Education: A bachelor’s degree is required to become a teacher, school counselor, or administrator.
- Engineering: A bachelor’s degree in engineering is necessary for engineers working in various fields, such as civil, mechanical, electrical, and chemical engineering.
- Technology: A bachelor’s degree in computer science or information technology is highly sought after in the tech industry, leading to careers in software development, cybersecurity, and data analysis.
Earning Potential
Studies consistently show that individuals with a bachelor’s degree earn significantly more over their lifetime than those with only a high school diploma. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that workers with a bachelor’s degree earn an average of 67% more than those with only a high school diploma.
“The median annual salary for workers with a bachelor’s degree is $78,000, while the median annual salary for workers with a high school diploma is $46,000.” – U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
This increased earning potential translates to greater financial security, allowing individuals to afford a higher standard of living, save for retirement, and manage their finances more effectively.
Ending Remarks
Earning a bachelor’s degree is a significant investment of time and effort. By understanding the factors that influence program length, you can make informed decisions to optimize your academic journey. Whether you choose a traditional four-year path or explore accelerated options, remember that the ultimate goal is to acquire the knowledge and skills that will empower you to achieve your personal and professional aspirations.
Quick FAQs
What is the minimum number of credits required for a bachelor’s degree?
The minimum number of credits required for a bachelor’s degree varies depending on the institution and program. Typically, it ranges from 120 to 130 credits.
Can I earn a bachelor’s degree online?
Yes, many universities offer fully online bachelor’s degree programs. These programs offer flexibility and convenience for students who cannot attend traditional on-campus classes.
Is a bachelor’s degree necessary for all careers?
While a bachelor’s degree is often required for professional and technical fields, some careers may only require an associate’s degree or a certificate. It’s important to research the specific requirements for your desired career path.
What is the difference between a bachelor’s degree and a master’s degree?
A bachelor’s degree is an undergraduate degree, typically earned after four years of study. A master’s degree is a graduate degree, earned after completing a bachelor’s degree and typically requiring an additional two years of study.





