
Home electrical company plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and functionality of your home. From basic wiring to complex smart home installations, a reliable electrical company is essential for a comfortable and secure living environment. This guide will explore the importance of choosing the right electrical company, common services they offer, and the latest advancements in home electrical technology.
Understanding the basics of electrical systems, adhering to safety codes, and staying informed about potential hazards are vital for homeowners. We will delve into these aspects and provide practical tips to help you make informed decisions regarding your home’s electrical needs.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Home Electrical Company
Your home’s electrical system is essential for your safety and comfort. It powers everything from your lights and appliances to your heating and cooling systems. That’s why it’s crucial to choose a reputable and experienced home electrical company for any electrical work you need.
Hiring an unqualified or unreliable electrician can lead to serious consequences, including:
Potential Consequences of Hiring an Unqualified Electrician
- Electrical shocks and fires: Improper wiring or faulty installations can create a fire hazard or lead to electrical shocks. In some cases, these incidents can result in serious injuries or even death.
- Damage to your home: An inexperienced electrician may damage your home’s wiring or other structures during the installation process.
- Costly repairs: Fixing mistakes made by an unqualified electrician can be expensive, as you may need to hire a qualified electrician to correct the problem.
- Voiding warranties: Some appliance manufacturers may void their warranties if the installation was not performed by a qualified electrician.
Benefits of Working with a Reputable Home Electrical Company
Working with a reputable and experienced home electrical company offers numerous benefits, including:
- Safety: Reputable electricians are licensed and insured, ensuring they meet industry standards and are equipped to handle any electrical work safely.
- Quality workmanship: Experienced electricians have the knowledge and skills to perform electrical work efficiently and correctly, minimizing the risk of errors or damage.
- Peace of mind: Knowing that your electrical work is being handled by a qualified professional gives you peace of mind, knowing that your home and family are safe.
- Warranty: Many reputable electrical companies offer warranties on their work, providing additional protection against defects or malfunctions.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Home Electrical Company
When choosing a home electrical company, consider the following factors:
- Licensing and insurance: Ensure that the company and its electricians are licensed and insured in your state. This demonstrates their compliance with industry standards and provides protection in case of accidents.
- Experience: Choose a company with a proven track record of experience in handling various electrical projects, from simple repairs to complex installations.
- Customer reviews: Read online reviews from previous customers to gauge the company’s reputation, quality of service, and customer satisfaction.
- Pricing: Obtain quotes from multiple companies to compare pricing and ensure the price is reasonable and competitive.
- Communication: Choose a company that communicates effectively, providing clear explanations of the work to be done and answering your questions thoroughly.
Common Home Electrical Services
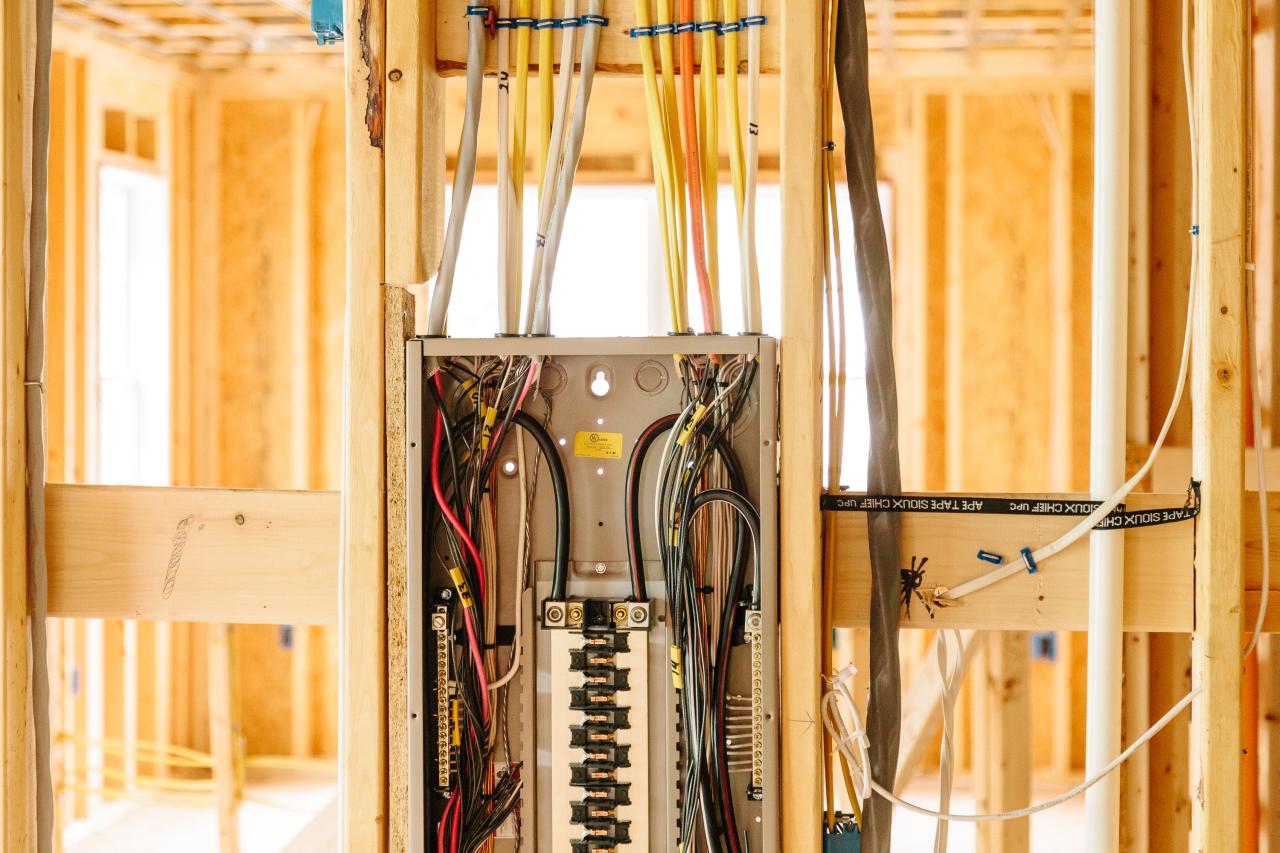
A reliable home electrical system is crucial for comfort, safety, and the functionality of your home. From basic wiring to complex installations, there are a variety of common electrical services that homeowners may require. Understanding these services and the importance of regular maintenance can help you ensure a safe and efficient electrical system.
Wiring and Installation
Proper wiring is the foundation of a safe and functional electrical system. This includes everything from installing new circuits and outlets to rewiring older homes to meet modern safety standards. Wiring services encompass:
- New Circuit Installation: Adding new circuits for appliances, lighting, or other electrical needs.
- Outlet Installation: Installing new outlets for increased convenience and safety.
- Rewiring: Updating older wiring to meet current safety codes and improve efficiency.
- Wiring for Appliances: Installing dedicated circuits for major appliances like stoves, ovens, and washing machines.
Lighting
Lighting plays a vital role in both the functionality and aesthetic appeal of your home. Electrical services related to lighting include:
- Fixture Installation: Installing new light fixtures, such as chandeliers, pendant lights, or recessed lighting.
- Lighting Control Systems: Installing dimmers, smart switches, and other systems to enhance lighting control and energy efficiency.
- Outdoor Lighting: Installing security lights, landscape lighting, and other outdoor lighting solutions for safety and aesthetics.
Appliance Installation
Proper installation of appliances is crucial for their safety and performance. Electrical services for appliance installation include:
- Dishwasher Installation: Connecting the dishwasher to the electrical system and plumbing.
- Oven and Stove Installation: Installing and connecting ovens and stoves to the electrical system and gas line (if applicable).
- Washing Machine and Dryer Installation: Connecting the washing machine and dryer to the electrical system and plumbing.
- Garbage Disposal Installation: Connecting the garbage disposal to the electrical system and plumbing.
Electrical Maintenance and Safety Inspections
Regular electrical maintenance and safety inspections are essential for preventing electrical hazards and ensuring the longevity of your electrical system.
- Regular Inspections: A qualified electrician should inspect your electrical system periodically to identify potential problems and ensure compliance with safety codes.
- Safety Testing: Testing of electrical components like outlets, switches, and wiring can identify faulty wiring or overloaded circuits.
- Circuit Breaker and Fuse Checks: Inspecting circuit breakers and fuses to ensure they are functioning correctly and are not overloaded.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Testing: Testing GFCIs to ensure they are working properly and can protect against electrical shocks.
Preventing Electrical Hazards
Here are some tips for preventing electrical hazards in your home:
- Avoid Overloading Circuits: Do not plug too many appliances into one outlet or circuit, as this can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Use Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs): Install GFCIs in areas where water is present, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoors, to protect against electrical shocks.
- Inspect Electrical Cords Regularly: Check electrical cords for damage and replace any that are frayed or worn. Avoid running cords under rugs or furniture.
- Unplug Appliances When Not in Use: Unplug appliances when not in use to reduce the risk of electrical fires.
- Avoid Using Extension Cords Long-Term: Extension cords should only be used temporarily. If you need a permanent solution, consult with a qualified electrician to install a new outlet.
Understanding Electrical Codes and Regulations: Home Electrical Company

Navigating the world of home electrical work can be confusing, but one thing is clear: adhering to local and national electrical codes is crucial for safety and preventing potential hazards. These codes act as a set of guidelines that dictate how electrical systems should be designed, installed, and maintained, ensuring they operate safely and efficiently. Understanding these codes is essential for both homeowners and electrical professionals.
Importance of Electrical Codes
Electrical codes serve as a safety net, safeguarding homeowners and their families from the dangers of electrical malfunctions. These codes are developed by experts in the field and are constantly updated to reflect the latest advancements in electrical technology and safety practices. By adhering to these codes, homeowners can minimize the risk of electrical fires, shocks, and other hazards.
Common Electrical Code Violations and Consequences
While many homeowners are unaware of the specific details of electrical codes, understanding common violations and their consequences can help them make informed decisions regarding their electrical systems. Here are some common violations and their potential outcomes:
- Improper Wiring: Using the wrong type of wire for a particular application can lead to overheating, short circuits, and fire hazards. For example, using thin-gauge wire for high-amperage appliances can result in overheating and potential fires.
- Overloaded Circuits: Connecting too many appliances or devices to a single circuit can overload the wiring and cause overheating, potentially leading to fires.
- Defective Wiring: Damaged or worn-out wiring can create electrical hazards. This can occur due to age, improper installation, or environmental factors.
- Improper Grounding: Grounding provides a path for electricity to flow safely to the earth in case of a fault. Improper grounding can lead to electric shocks and electrocution.
- Improper Installation of Electrical Outlets and Switches: Outlets and switches should be installed in accordance with code requirements to ensure safe operation and prevent hazards.
The consequences of violating electrical codes can be severe, ranging from minor electrical malfunctions to catastrophic fires and injuries. In some cases, code violations can even lead to legal penalties and fines.
Types of Electrical Systems

Home electrical systems are the backbone of modern living, powering everything from lights and appliances to entertainment systems and security devices. Understanding the different types of electrical systems used in homes is crucial for making informed decisions about your home’s electrical infrastructure.
Types of Electrical Systems
There are two main types of electrical systems used in homes: AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current).
- AC (Alternating Current): This is the most common type of electrical system used in homes and businesses worldwide. AC electricity flows in a cyclical pattern, alternating its direction at a specific frequency. This alternating current is more efficient for transmitting electricity over long distances and is easily transformed to different voltage levels.
- DC (Direct Current): DC electricity flows in a single direction, unlike AC, which changes direction. It is commonly used in devices like smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. While DC is more efficient for powering smaller devices, it is less efficient for transmitting electricity over long distances.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AC and DC Systems
Each type of electrical system has its advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications.
AC Systems
- Advantages:
- Efficient Transmission: AC electricity can be transmitted over long distances with minimal energy loss, making it ideal for large-scale power grids.
- Easy Transformation: AC voltage can be easily transformed to different levels using transformers, allowing for efficient distribution and use in various devices.
- Wide Availability: AC systems are the standard in most parts of the world, making it readily available for homes and businesses.
- Disadvantages:
- Safety Concerns: AC electricity can be more dangerous than DC electricity due to its alternating nature, requiring careful installation and maintenance.
- Electromagnetic Interference: AC systems can generate electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can affect sensitive electronic devices.
DC Systems
- Advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: DC systems are more efficient for powering smaller devices, as they minimize energy loss during conversion.
- Lower Maintenance: DC systems generally require less maintenance compared to AC systems, as they have fewer moving parts.
- Safety: DC electricity is generally safer than AC electricity due to its unidirectional flow, reducing the risk of electric shocks.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited Transmission Distance: DC electricity is less efficient for transmitting over long distances compared to AC electricity, making it unsuitable for large-scale power grids.
- Cost: DC systems can be more expensive to install and maintain compared to AC systems, especially for large-scale applications.
- Limited Availability: DC systems are not as widely available as AC systems, limiting their use in homes and businesses.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Electrical System
When choosing an electrical system for a new home or renovation project, several factors should be considered:
- Size and Scope of the Project: The size and complexity of the project will influence the type of electrical system required. Larger homes or projects with high energy demands may require a more robust AC system, while smaller homes or projects with limited energy needs may be suitable for a DC system.
- Energy Efficiency: If energy efficiency is a priority, consider the advantages of DC systems for powering smaller devices and appliances. However, AC systems are more efficient for transmitting electricity over long distances, which can be a factor in larger homes or projects with multiple appliances.
- Safety: Both AC and DC systems have their own safety considerations. AC systems require careful installation and maintenance to minimize the risk of electric shocks, while DC systems offer a lower risk of shocks but may have other safety concerns related to voltage conversion.
- Budget: The cost of installing and maintaining an electrical system can vary depending on the type of system chosen. AC systems are generally more affordable than DC systems, especially for larger projects.
- Future Plans: Consider your future plans for the home, such as adding new appliances or devices, and choose an electrical system that can accommodate your future needs.
Modern Home Electrical Technologies
Modern home electrical technology is rapidly evolving, offering homeowners a range of innovative solutions to enhance comfort, convenience, and energy efficiency. These advancements encompass smart home automation, energy-efficient lighting, and renewable energy sources, transforming the way we interact with our homes and manage energy consumption.
Smart Home Automation
Smart home automation systems integrate various home appliances and devices, enabling remote control and automation through a central hub or app. These systems leverage internet connectivity and sensors to provide enhanced convenience, security, and energy savings.
- Remote Control: Smart home automation allows homeowners to control lighting, temperature, appliances, and security systems remotely from anywhere with an internet connection. This feature offers flexibility and convenience, enabling users to adjust their home environment based on their needs and preferences.
- Automation: Automated tasks, such as turning off lights when a room is empty or adjusting the thermostat based on occupancy, can significantly reduce energy consumption and optimize home comfort. These automated functions contribute to a more efficient and sustainable living environment.
- Security: Smart home automation systems can integrate with security cameras, door locks, and motion sensors to provide real-time monitoring and alerts. This enhanced security feature offers peace of mind and allows homeowners to proactively address potential threats.
Energy-Efficient Lighting, Home electrical company
Energy-efficient lighting technologies, such as LED and CFL bulbs, offer significant energy savings compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. These technologies consume less energy to produce the same amount of light, reducing electricity bills and minimizing environmental impact.
- LED (Light Emitting Diode): LED bulbs are highly energy-efficient, consuming up to 80% less energy than incandescent bulbs while offering a longer lifespan. They also produce less heat, reducing the risk of fire hazards and improving indoor comfort.
- CFL (Compact Fluorescent Lamp): CFL bulbs are more energy-efficient than incandescent bulbs but less efficient than LEDs. They typically last longer than incandescent bulbs but produce more heat and contain mercury, requiring proper disposal.
- Smart Lighting: Smart lighting systems allow homeowners to control lighting remotely, schedule lighting schedules, and adjust brightness levels based on preferences and occupancy. These features enhance convenience, security, and energy savings.
Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, harness natural resources to generate electricity. These sources offer sustainable and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional fossil fuel-based power generation, reducing carbon emissions and dependence on non-renewable energy sources.
- Solar Panels: Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, reducing reliance on the grid and minimizing energy costs. They offer a clean and sustainable energy source for homes, reducing environmental impact and promoting energy independence.
- Wind Turbines: Wind turbines harness wind energy to generate electricity. They are suitable for homes in windy locations, offering a renewable energy source that reduces dependence on fossil fuels and promotes a cleaner environment.
- Hybrid Systems: Hybrid systems combine renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and batteries, to create a more robust and reliable energy system. These systems offer increased energy independence and reduced reliance on the grid.
Home Electrical Safety Tips
Electrical safety is paramount in any home. It’s not just about preventing accidents, but also about protecting your family and property from potential electrical hazards. By understanding and implementing these tips, you can create a safer environment for yourself and your loved ones.
Proper Wiring and Grounding
Proper wiring and grounding are fundamental for electrical safety. Grounding is a vital safety feature that provides a path for electrical current to flow to the ground in the event of a fault, preventing electrical shocks.
- Ensure all electrical wiring is installed by a qualified electrician: This ensures that the wiring meets all safety codes and standards, reducing the risk of electrical hazards.
- Regularly inspect wiring for signs of damage or wear: Look for frayed wires, loose connections, or any signs of overheating. Replace damaged wiring immediately.
- Ensure all electrical outlets and appliances are properly grounded: This provides a safe path for electrical current to flow to the ground in the event of a fault, minimizing the risk of electrical shocks.
- Use grounded extension cords: Ungrounded extension cords can be a safety hazard, especially when used with high-power appliances. Always use grounded extension cords, and avoid overloading them.
Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers are designed to interrupt the flow of electricity in the event of an overload or short circuit, preventing fires and electrical shocks.
- Ensure all electrical circuits are protected by circuit breakers: This is a crucial safety measure that prevents electrical overload and short circuits.
- Never tamper with or disable circuit breakers: Tampering with circuit breakers can compromise safety and increase the risk of electrical hazards.
- Replace faulty circuit breakers promptly: If a circuit breaker trips frequently, it may indicate a problem with the wiring or an overloaded circuit. Consult a qualified electrician to diagnose and resolve the issue.
Identifying Potential Electrical Hazards
Identifying and addressing potential electrical hazards is essential for maintaining a safe home environment.
- Look for frayed or damaged cords and wires: Damaged cords and wires can pose a significant fire hazard and should be replaced immediately.
- Avoid overloading electrical outlets: Overloading outlets can cause overheating and lead to fires. Use surge protectors to distribute power evenly.
- Check for loose or missing outlet covers: Exposed electrical outlets can be a safety hazard, especially for children and pets. Replace missing or damaged outlet covers promptly.
- Inspect appliances for signs of damage: Damaged appliances can pose a fire hazard and should be repaired or replaced by a qualified technician.
Taking Appropriate Action
Once you identify a potential electrical hazard, it’s important to take appropriate action to mitigate the risk.
- Turn off the power to the affected area: This is the first step in addressing any electrical hazard, preventing further damage or injury.
- Contact a qualified electrician: For any complex electrical issues, it’s essential to consult a qualified electrician to ensure the problem is addressed safely and effectively.
- Never attempt to repair electrical wiring yourself: Electrical repairs should always be performed by a qualified electrician to prevent further damage or injury.
Epilogue
Choosing a reputable home electrical company is an investment in your home’s safety and well-being. By understanding the factors to consider when selecting a provider, familiarizing yourself with common electrical services, and staying informed about safety regulations, you can ensure a secure and efficient electrical system for your home. Embrace the advancements in home electrical technology to enhance comfort, convenience, and energy efficiency, while always prioritizing safety and professional expertise.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the signs that I need to call an electrician?
Several signs indicate you need an electrician, including flickering lights, frequent tripping of circuit breakers, electrical outlets that are hot to the touch, and a burning smell coming from electrical wiring.
How often should I have my home’s electrical system inspected?
It’s recommended to have your home’s electrical system inspected every three to five years, or more frequently if you have older wiring or have made significant renovations.
What are some tips for preventing electrical hazards in the home?
Some tips include avoiding overloading electrical outlets, using grounded appliances and cords, and keeping electrical cords away from heat sources and water.




