
- Overview of Healthcare Administration Bachelor’s Degree
- Curriculum and Coursework
- Skills and Competencies
- Admission Requirements and Application Process
- Accreditation and Professional Organizations
- Future Trends in Healthcare Administration: Healthcare Administration Bachelor’s Degree
- Epilogue
- Detailed FAQs
A Healthcare Administration Bachelor’s Degree equips individuals with the knowledge and skills to lead and manage within the complex and ever-evolving healthcare industry. This program delves into the core principles of healthcare administration, covering essential topics like finance, policy, law, and ethics.
Graduates emerge prepared for a wide range of rewarding careers in hospitals, clinics, insurance companies, and government agencies. They play a vital role in ensuring the efficient and effective delivery of healthcare services, optimizing resources, and advocating for patient well-being.
Overview of Healthcare Administration Bachelor’s Degree
A Bachelor of Science in Healthcare Administration (BSHA) is a comprehensive program designed to equip students with the knowledge, skills, and leadership qualities needed to navigate the complex and ever-evolving healthcare industry. This degree program provides a solid foundation in the principles and practices of healthcare administration, preparing graduates for diverse roles in hospitals, clinics, insurance companies, and other healthcare organizations.
Core Concepts and Principles of Healthcare Administration
Healthcare administration is a multifaceted field that encompasses various aspects of managing healthcare organizations effectively and efficiently. The core concepts and principles underpinning this discipline include:
- Financial Management: Healthcare administrators play a crucial role in managing the financial resources of healthcare organizations. This includes budgeting, cost control, revenue generation, and financial reporting.
- Human Resources Management: Effective management of human resources is essential for healthcare organizations to attract, retain, and motivate a skilled workforce. This involves tasks such as recruitment, training, performance evaluation, and employee relations.
- Quality Improvement: Healthcare administration emphasizes continuous improvement in the quality of patient care. This involves implementing strategies to enhance patient safety, reduce medical errors, and improve overall patient satisfaction.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: Healthcare administrators must be well-versed in the legal and ethical frameworks governing healthcare practices. This includes understanding HIPAA regulations, patient privacy laws, and ethical decision-making in healthcare settings.
- Healthcare Policy and Regulation: The healthcare landscape is constantly evolving, influenced by government policies, regulations, and industry trends. Healthcare administrators need to stay informed about these changes and adapt their practices accordingly.
- Information Technology: Technology plays a critical role in modern healthcare. Healthcare administrators must understand how to leverage technology to improve efficiency, enhance patient care, and manage data effectively.
Importance of Healthcare Administration in the Modern Healthcare System
The healthcare industry is facing numerous challenges, including rising costs, an aging population, and an increasing demand for healthcare services. Healthcare administrators play a vital role in addressing these challenges and ensuring the efficient and effective delivery of healthcare. Their responsibilities include:
- Optimizing Resource Allocation: Healthcare administrators are responsible for allocating resources efficiently to meet the needs of patients and the organization. This involves making strategic decisions about staffing, equipment, and other resources.
- Improving Patient Care: By implementing quality improvement initiatives and ensuring adherence to best practices, healthcare administrators contribute to enhancing patient care and safety.
- Managing Costs: Healthcare administrators are tasked with controlling costs and ensuring financial sustainability of healthcare organizations. This involves finding ways to reduce expenses without compromising quality of care.
- Leading and Motivating Teams: Healthcare administrators lead and motivate teams of healthcare professionals to work collaboratively towards common goals. This includes fostering a positive work environment and promoting teamwork.
- Staying Current with Industry Trends: Healthcare administrators must stay informed about the latest developments in healthcare, including technological advancements, policy changes, and industry best practices.
Key Skills and Knowledge Required for a Successful Career in Healthcare Administration
A successful career in healthcare administration requires a unique blend of skills and knowledge. Here are some essential attributes:
- Strong Communication Skills: Effective communication is crucial for healthcare administrators to interact with patients, staff, physicians, and other stakeholders.
- Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills: Healthcare administrators must be able to analyze data, identify problems, and develop solutions to improve efficiency and patient care.
- Leadership and Management Skills: Healthcare administrators need to lead and motivate teams, delegate tasks effectively, and make strategic decisions.
- Financial Management Skills: Understanding financial principles, budgeting, and cost control is essential for managing healthcare organizations effectively.
- Knowledge of Healthcare Regulations and Policies: Staying current with healthcare regulations, policies, and industry trends is crucial for compliance and effective decision-making.
- Technological Proficiency: Healthcare administrators need to be proficient in using healthcare information systems, data analytics tools, and other technologies to manage operations and improve patient care.
Curriculum and Coursework

A healthcare administration bachelor’s degree program provides students with a comprehensive understanding of the healthcare industry and prepares them for leadership roles in various healthcare settings. The curriculum typically covers a wide range of subjects, encompassing both theoretical knowledge and practical skills.
The program’s curriculum is designed to equip students with the necessary skills and knowledge to manage healthcare organizations effectively. It typically covers core areas such as healthcare finance, healthcare policy, healthcare law, and healthcare ethics.
Healthcare Finance
Healthcare finance is a critical aspect of healthcare administration. It involves understanding the financial operations of healthcare organizations, including budgeting, cost accounting, and financial analysis. Students learn about various financial concepts and tools used in healthcare settings, such as:
- Cost Accounting: This involves tracking and analyzing the costs associated with providing healthcare services. Students learn how to calculate and interpret cost data, which helps healthcare organizations make informed decisions about pricing, resource allocation, and operational efficiency.
- Financial Management: Students learn about financial planning, budgeting, and forecasting, which are essential for ensuring the financial stability and sustainability of healthcare organizations. They also gain an understanding of investment strategies, debt management, and risk assessment.
- Healthcare Reimbursement: This involves understanding the complex system of healthcare reimbursement, including different payment models, such as fee-for-service, managed care, and value-based care. Students learn about coding and billing practices, as well as the impact of regulations on healthcare reimbursement.
Healthcare Policy
Healthcare policy encompasses the laws, regulations, and guidelines that govern the healthcare industry. Students learn about the political, social, and economic factors that influence healthcare policy. They also explore the role of government agencies, such as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), in shaping healthcare policy.
- Health Policy Analysis: Students learn to analyze the impact of different healthcare policies on healthcare access, quality, and cost. They also develop skills in policy research, evaluation, and advocacy.
- Healthcare Reform: Students explore the history of healthcare reform in the United States and analyze the current state of healthcare policy. They also discuss the challenges and opportunities for future healthcare reform.
- Public Health Policy: This area of study focuses on policies that promote public health, such as vaccination programs, tobacco control measures, and environmental protection.
Healthcare Law
Healthcare law is a complex and evolving field that covers legal issues related to healthcare providers, patients, and healthcare organizations. Students learn about the legal principles and regulations that govern healthcare practice.
- Medical Malpractice: This area of law deals with legal claims filed against healthcare providers for negligence or misconduct. Students learn about the elements of a malpractice claim, the process of litigation, and the role of insurance in protecting healthcare providers from liability.
- Patient Rights: Students learn about the legal rights of patients, such as the right to informed consent, privacy, and confidentiality. They also explore the legal implications of patient safety and quality of care.
- Healthcare Compliance: This area of law focuses on ensuring that healthcare organizations comply with all applicable laws and regulations. Students learn about compliance programs, risk management, and the role of compliance officers.
Healthcare Ethics
Healthcare ethics deals with moral principles and values that guide healthcare professionals in their decision-making. Students explore ethical issues related to patient care, resource allocation, and research.
- Bioethics: This area of ethics focuses on ethical issues related to biotechnology, such as genetic testing, stem cell research, and end-of-life care.
- Professional Ethics: Students learn about the ethical principles that govern the behavior of healthcare professionals, such as honesty, integrity, and confidentiality.
- Ethical Decision-Making: Students develop skills in ethical decision-making, which involves identifying ethical dilemmas, considering different perspectives, and making informed judgments based on ethical principles.
Skills and Competencies
Healthcare administration is a dynamic field that demands a diverse set of skills and competencies. Employers seek individuals who can effectively manage complex healthcare systems, lead teams, and navigate the ever-evolving healthcare landscape.
This section will explore the essential skills and competencies that employers value in healthcare administrators. We will delve into the importance of communication, leadership, and problem-solving skills, as well as the role of technology and data analysis in this field.
Communication Skills
Effective communication is paramount in healthcare administration. Healthcare administrators must be able to communicate clearly and concisely with a wide range of stakeholders, including patients, physicians, nurses, staff, and executives.
- Written Communication: Healthcare administrators must be able to draft clear and concise reports, memos, and other documents. They must also be able to effectively communicate complex information in a way that is easily understood by their audience.
- Verbal Communication: Effective verbal communication skills are essential for conducting meetings, presenting information, and resolving conflicts. Healthcare administrators must be able to listen actively, provide feedback, and communicate their ideas in a persuasive and professional manner.
- Interpersonal Communication: Building strong relationships with colleagues, patients, and other stakeholders is crucial for success in healthcare administration. Healthcare administrators must be able to work effectively in teams, build consensus, and resolve conflicts diplomatically.
Leadership Skills
Leadership skills are essential for healthcare administrators who are responsible for managing teams, motivating staff, and achieving organizational goals.
- Visionary Leadership: Effective healthcare administrators have a clear vision for the future of their organizations and can inspire their teams to work towards common goals. They must be able to articulate a compelling vision that motivates staff and stakeholders.
- Strategic Thinking: Healthcare administrators must be able to think strategically and make decisions that align with the organization’s overall goals. They must be able to analyze complex situations, identify opportunities, and develop innovative solutions.
- Team Building: Building and managing high-performing teams is crucial for success in healthcare administration. Healthcare administrators must be able to create a positive and collaborative work environment that fosters teamwork and innovation.
Problem-Solving Skills
Healthcare administrators face a wide range of challenges, from managing budgets to improving patient care. They must be able to identify problems, analyze situations, and develop creative solutions.
- Analytical Skills: Healthcare administrators must be able to analyze data, identify trends, and draw conclusions. They must be able to use their analytical skills to make informed decisions and solve complex problems.
- Critical Thinking: Healthcare administrators must be able to think critically and evaluate different perspectives. They must be able to identify assumptions, analyze arguments, and make sound judgments.
- Decision-Making: Healthcare administrators must be able to make timely and effective decisions. They must be able to weigh the risks and benefits of different options and make decisions that are in the best interests of the organization and its stakeholders.
Technology and Data Analysis
Technology plays a crucial role in modern healthcare administration. Healthcare administrators must be able to utilize technology to improve efficiency, enhance patient care, and manage data effectively.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): EHRs are a critical component of modern healthcare systems. Healthcare administrators must be familiar with EHR systems and be able to use them to manage patient data, track patient outcomes, and improve care coordination.
- Data Analytics: Healthcare administrators must be able to analyze data to identify trends, improve efficiency, and make informed decisions. They must be able to use data analytics tools to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and measure the effectiveness of programs and initiatives.
- Healthcare Information Systems (HIS): HIS are software applications that manage administrative, financial, and clinical data in healthcare organizations. Healthcare administrators must be familiar with HIS and be able to use them to manage patient information, track financial performance, and improve operational efficiency.
Admission Requirements and Application Process
Gaining admission to a healthcare administration bachelor’s degree program typically involves meeting specific academic criteria and completing an application process. The requirements and procedures may vary depending on the specific institution, but common elements are Artikeld below.
Typical Admission Requirements
Admission requirements for healthcare administration bachelor’s degree programs typically include:
- A high school diploma or equivalent.
- A minimum GPA, often around 2.5 or higher.
- Completion of prerequisite courses, such as biology, chemistry, and math.
- Standardized test scores, such as the SAT or ACT, may be required, though this is becoming less common.
Application Process
The application process for healthcare administration programs typically involves:
- Submitting an online application form, often through the Common Application or the institution’s website.
- Providing official transcripts from all previously attended colleges or universities.
- Submitting standardized test scores, if required.
- Providing letters of recommendation from academic advisors, professors, or employers.
- Writing a personal essay that explains your interest in healthcare administration and your career goals.
- Participating in an interview, which may be conducted in person or via video conference.
Standardized Test Scores, Healthcare administration bachelor’s degree
While some healthcare administration programs may require standardized test scores, such as the SAT or ACT, this is becoming less common. However, it’s always a good idea to check the specific requirements of the programs you’re interested in.
Letters of Recommendation
Letters of recommendation are an important part of the application process, as they provide insight into your academic abilities, work ethic, and character. Choose recommenders who can speak to your strengths and your potential for success in a healthcare administration program.
Personal Essays
Your personal essay is your chance to showcase your passion for healthcare administration, your understanding of the field, and your career goals. Be sure to write a compelling and well-written essay that highlights your unique qualifications and experiences.
Tips for Applying to Healthcare Administration Programs
Here are some tips for applying to healthcare administration programs:
- Start the application process early to allow ample time for gathering all necessary materials.
- Thoroughly research the programs you’re interested in and choose those that align with your career goals.
- Meet with an academic advisor or counselor to discuss your application and receive guidance on the process.
- Prepare for interviews by practicing your answers to common questions and researching the institution and program.
- Be confident in your abilities and showcase your passion for healthcare administration in your application materials.
Accreditation and Professional Organizations
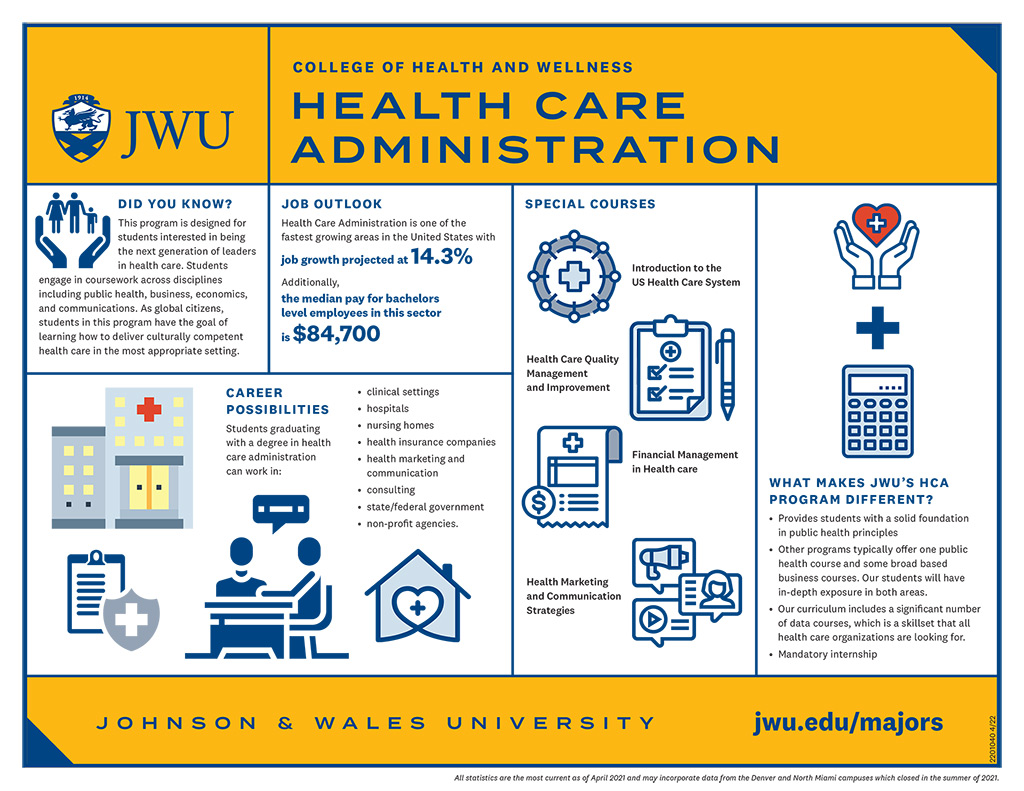
Earning a bachelor’s degree in healthcare administration from an accredited program is crucial for aspiring healthcare leaders. Accreditation signifies that a program meets rigorous standards of quality and prepares graduates for success in the field. Additionally, professional organizations play a vital role in supporting healthcare administrators throughout their careers.
Accreditation
Accreditation ensures that healthcare administration programs adhere to established quality standards and provide students with the necessary knowledge, skills, and competencies to succeed in the field. This process involves a rigorous evaluation by an independent body that assesses the program’s curriculum, faculty qualifications, resources, and student outcomes.
Key Accrediting Bodies
- The Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Management Education (CAHME): CAHME is the primary accrediting body for healthcare administration programs in the United States. It sets high standards for curriculum, faculty qualifications, and program resources. CAHME accreditation is widely recognized by employers and healthcare organizations, demonstrating the quality of a program and its graduates.
- The Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education (ACPE): While primarily focused on pharmacy programs, ACPE also accredits healthcare administration programs within schools of pharmacy. These programs often focus on pharmacy-specific administration and management.
Professional Organizations
Professional organizations provide valuable resources, networking opportunities, and support for healthcare administrators. These organizations offer professional development programs, certifications, publications, and advocacy efforts that enhance the knowledge and skills of their members.
Key Professional Organizations
- The American College of Healthcare Executives (ACHE): ACHE is the largest professional society for healthcare executives, with over 40,000 members worldwide. It offers a range of resources, including educational programs, certifications, and networking opportunities. ACHE is known for its commitment to advancing the field of healthcare administration and promoting ethical leadership.
- The Healthcare Financial Management Association (HFMA): HFMA is a professional organization dedicated to healthcare finance professionals. It offers resources and support for financial management in healthcare organizations, including education, certifications, and networking opportunities.
- The American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA): AHIMA focuses on health information management professionals, including those working in healthcare administration. It provides resources and support for managing health information, including education, certifications, and advocacy efforts.
Future Trends in Healthcare Administration: Healthcare Administration Bachelor’s Degree
The healthcare industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing demographics, and shifting healthcare policies. This dynamic environment presents both challenges and opportunities for healthcare administrators. Understanding emerging trends is crucial for professionals in this field to adapt, innovate, and lead effectively.
Impact of Telehealth
The rise of telehealth has significantly impacted the healthcare administration profession. Telehealth, the delivery of healthcare services remotely using technology, has expanded access to care, improved patient convenience, and reduced healthcare costs. This trend has created new roles and responsibilities for healthcare administrators, including:
- Developing and implementing telehealth strategies
- Managing telehealth infrastructure and technology
- Ensuring compliance with telehealth regulations
- Training staff on telehealth protocols
Telehealth has also presented challenges, such as ensuring data security and privacy, managing reimbursement models, and addressing ethical considerations.
Data Analytics in Healthcare
Healthcare data is increasingly valuable for improving patient outcomes, optimizing operations, and driving innovation. Data analytics plays a crucial role in extracting insights from this data to support decision-making. Healthcare administrators need to understand the principles of data analytics and its applications in healthcare. This includes:
- Identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) and data sources
- Using data analytics tools to analyze healthcare data
- Interpreting data insights and translating them into actionable strategies
- Collaborating with data scientists and other experts
Data analytics can help healthcare administrators improve resource allocation, identify trends in patient populations, predict future needs, and optimize service delivery.
Future Career Opportunities
The evolving healthcare landscape creates a wide range of future career opportunities for healthcare administrators. These opportunities will require a blend of traditional administrative skills and expertise in emerging areas such as telehealth, data analytics, and population health management. Some potential career paths include:
- Telehealth Manager: Overseeing the development, implementation, and operation of telehealth programs within healthcare organizations.
- Data Analyst: Analyzing healthcare data to identify trends, improve efficiency, and support decision-making.
- Population Health Manager: Focusing on improving the health outcomes of specific populations by coordinating care, managing risk, and implementing preventive measures.
- Healthcare Technology Consultant: Advising healthcare organizations on the adoption and implementation of new technologies.
- Healthcare Informatics Specialist: Managing and analyzing healthcare data to improve patient care, research, and public health.
Epilogue

Pursuing a Healthcare Administration Bachelor’s Degree opens doors to a fulfilling and impactful career path. By understanding the intricacies of the healthcare system, graduates can contribute to improving patient care, shaping healthcare policy, and leading the industry towards a brighter future.
Detailed FAQs
What are the typical job titles for healthcare administration graduates?
Common job titles include Healthcare Administrator, Health Services Manager, Hospital Administrator, and Director of Operations.
Is a master’s degree required for a successful career in healthcare administration?
While a bachelor’s degree is a good starting point, many advanced positions often require a Master of Healthcare Administration (MHA) or a Master of Business Administration (MBA) with a healthcare focus.
What are some of the key challenges facing the healthcare administration field?
Challenges include rising healthcare costs, increasing regulations, technological advancements, and the growing need for patient-centered care.




