
- Introduction to Forex Trade Brokers
- Choosing the Right Forex Trade Broker
- Forex Trading Platforms and Tools
- Forex Trading Strategies and Techniques
- Forex Trade Broker Regulation and Security
- Understanding Forex Trading Costs
- Resources and Education for Forex Traders
- Case Studies and Real-World Examples
- Closing Notes
- FAQ Corner
Forex trade brokers are the linchpin of the global foreign exchange market, facilitating trades between buyers and sellers of currencies. They provide access to a vast and volatile market, enabling individuals and institutions to participate in the world’s largest financial market. Forex trade brokers offer a range of services, including trading platforms, research tools, and educational resources, empowering traders to make informed decisions.
Understanding the intricacies of forex trade brokers is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of this dynamic market. This comprehensive guide delves into the key aspects of forex trade brokers, from choosing the right broker to mastering trading strategies and managing risk effectively.
Introduction to Forex Trade Brokers

Forex trade brokers act as intermediaries between traders and the global foreign exchange market. They provide the necessary infrastructure and tools for individuals and institutions to participate in forex trading. These brokers offer trading platforms, access to liquidity, and various other services that facilitate trading activities.
Types of Forex Trade Brokers
Forex brokers can be categorized based on their business models and the way they execute trades. Here are the most common types:
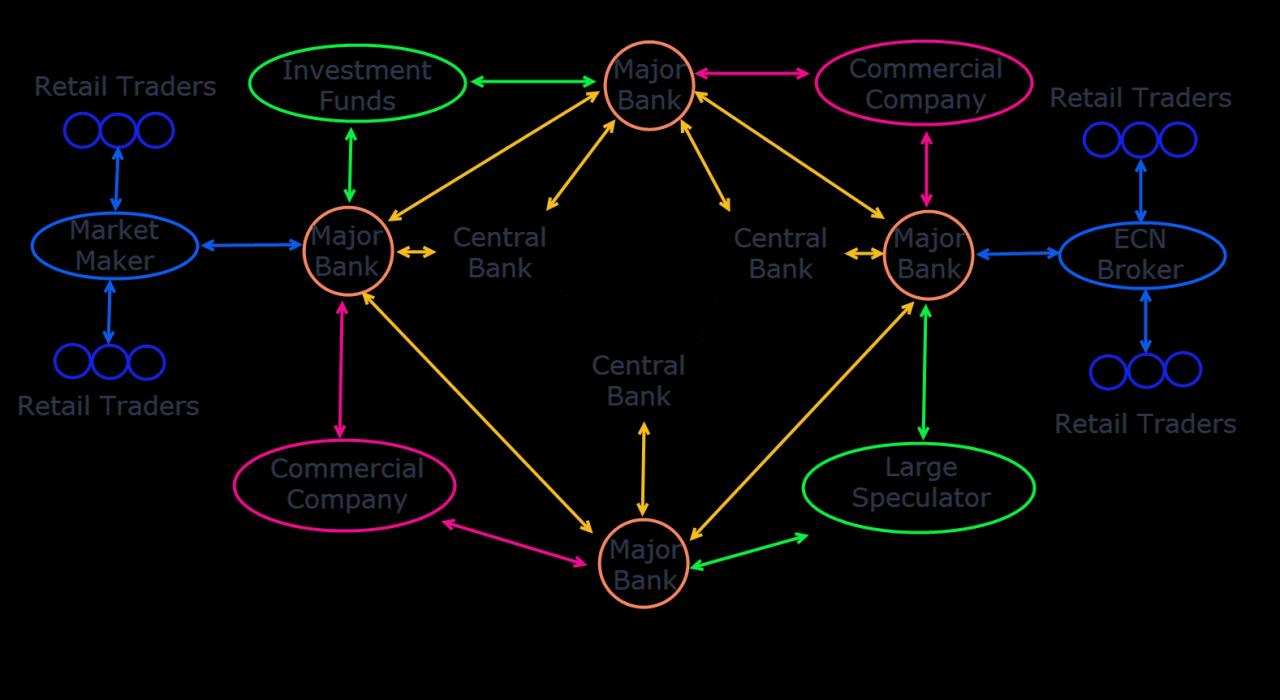
- Market Makers: These brokers act as counterparties to their clients’ trades. They profit from the spread, which is the difference between the buy and sell prices they quote. Market makers typically offer tight spreads and fast execution speeds, but they may have conflicts of interest, as they are essentially betting against their clients.
- Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs): ECNs are electronic platforms that connect traders directly with other traders, eliminating the need for a broker as an intermediary. This means that trades are executed at the best available prices, and there is no conflict of interest. ECNs usually offer wider spreads than market makers but provide more transparency and control over trade execution.
- Straight-Through Processing (STP) Brokers: STP brokers act as intermediaries between traders and liquidity providers, such as banks and other financial institutions. They pass trades directly to the liquidity providers, ensuring that trades are executed at the best available prices. STP brokers offer a balance between tight spreads and transparency, making them a popular choice for many traders.
Key Features and Benefits of Using a Forex Trade Broker
Using a forex trade broker offers several advantages for traders:
- Access to the Global Forex Market: Brokers provide traders with access to the world’s largest and most liquid financial market, offering a wide range of trading opportunities.
- Trading Platforms: Forex brokers offer advanced trading platforms with various features, including charting tools, technical indicators, order types, and real-time market data, facilitating informed trading decisions.
- Leverage: Brokers allow traders to leverage their capital, amplifying potential profits but also increasing risk. Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller initial investment.
- Educational Resources: Many brokers offer educational resources, including articles, webinars, and tutorials, to help traders develop their skills and knowledge.
- Customer Support: Forex brokers provide customer support to assist traders with any questions or issues they may encounter.
Choosing the Right Forex Trade Broker
Finding the right Forex trade broker is crucial for your success in the market. It’s like choosing the right tools for any job – the wrong ones can hinder your progress, while the right ones can significantly enhance your performance. This section will guide you through the essential factors to consider when selecting a broker, compare different broker types, and provide tips for researching and evaluating potential options.
Essential Factors to Consider
Choosing the right Forex trade broker is a critical decision for any trader. Here are some key factors to consider when evaluating potential brokers:
- Regulation and Security: Ensure the broker is regulated by a reputable financial authority, such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK or the National Futures Association (NFA) in the US. This indicates that the broker adheres to certain standards and practices, protecting your funds and trading activities. Look for brokers that have robust security measures in place, including encryption and two-factor authentication.
- Trading Platform: The trading platform is your interface with the market. It should be user-friendly, offer a wide range of features, and provide access to real-time data. Some popular platforms include MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), and cTrader. Consider factors like ease of use, charting capabilities, order execution speed, and mobile accessibility.
- Spreads and Commissions: Spreads are the difference between the bid and ask price of a currency pair. Lower spreads generally mean lower trading costs. Some brokers charge commissions in addition to spreads. Carefully compare spreads and commissions across different brokers to find the most cost-effective option.
- Account Types and Minimum Deposit: Brokers offer different account types, each with varying features and minimum deposit requirements. Choose an account type that aligns with your trading style and capital. Some brokers offer micro accounts with lower minimum deposits, suitable for beginners. Ensure the minimum deposit requirement is within your budget.
- Leverage and Margin Requirements: Leverage allows you to control larger positions with a smaller initial investment. However, leverage also magnifies potential profits and losses. Choose a leverage level that suits your risk tolerance and trading strategy. Understand the margin requirements, which represent the amount of capital you need to hold to open and maintain a position.
- Customer Support: Look for a broker with responsive and knowledgeable customer support. Availability of support channels, such as phone, email, and live chat, is essential. Ensure the broker offers multilingual support if necessary.
- Educational Resources: Many brokers provide educational resources, such as webinars, tutorials, and market analysis, to help traders improve their skills. Consider the quality and comprehensiveness of these resources when choosing a broker.
- Trading Instruments: Ensure the broker offers the currency pairs and other trading instruments you are interested in. Some brokers specialize in specific markets, while others offer a wider range of instruments.
Types of Forex Trade Brokers
Forex brokers come in different forms, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the different types can help you choose the broker that best suits your needs.
- Market Makers: Market makers act as counterparties to your trades. They profit from the spread, the difference between the bid and ask price. They typically offer tight spreads but may have limited liquidity and slower execution speeds. Market makers may also engage in practices like price slippage, where the actual execution price differs from the quoted price.
- Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs): ECNs act as platforms that connect traders directly with other traders and institutions. They typically offer deeper liquidity and faster execution speeds, but spreads may be wider than market makers. ECNs often charge commissions in addition to spreads.
- Dealing Desk Brokers: Dealing desk brokers act as intermediaries between traders and the market. They typically offer tight spreads and fast execution but may have conflicts of interest. Dealing desk brokers may also engage in practices like re-quoting, where the quoted price changes after you place an order.
- Straight-Through Processing (STP) Brokers: STP brokers route orders directly to liquidity providers, such as banks and institutions. They typically offer transparency and fast execution speeds, but spreads may be wider than dealing desk brokers.
Research and Evaluation
Thorough research is crucial when choosing a Forex trade broker. Here are some tips for evaluating potential brokers:
- Read Reviews and Testimonials: Look for reviews and testimonials from other traders on reputable websites and forums. This can provide valuable insights into the broker’s reputation, customer service, and trading platform.
- Check the Broker’s Website: Explore the broker’s website for information about their services, regulation, trading platform, and educational resources. Pay attention to the website’s design, content, and overall professionalism.
- Open a Demo Account: Most brokers offer demo accounts that allow you to practice trading without risking real money. This is a great way to familiarize yourself with the trading platform, test different strategies, and evaluate the broker’s execution speed and spreads.
- Contact Customer Support: Reach out to the broker’s customer support team with questions about their services and trading conditions. This will give you an idea of their responsiveness and knowledge.
- Compare Brokers: Don’t settle for the first broker you find. Compare multiple brokers based on the factors discussed above. Look for brokers that offer the best combination of features, costs, and reliability.
Forex Trading Platforms and Tools
A trading platform is your gateway to the forex market. It’s where you place orders, monitor your trades, and access essential tools for analysis and research. Choosing the right platform is crucial, as it significantly impacts your trading experience.
Types of Trading Platforms
Trading platforms are broadly classified into two categories: desktop platforms and web-based platforms. Desktop platforms are downloaded and installed on your computer, offering more features and customization options. Web-based platforms are accessed through a web browser, providing convenience and accessibility from any device.
Popular Trading Platforms
- MetaTrader 4 (MT4) is a widely used and highly regarded platform, known for its user-friendly interface, advanced charting tools, and extensive customization options. MT4 is available as a desktop platform and a mobile app, allowing traders to access the market from anywhere. It’s renowned for its Expert Advisors (EAs), which are automated trading programs that can execute trades based on pre-defined rules.
- MetaTrader 5 (MT5) is the successor to MT4, offering a more advanced platform with enhanced features, including a wider range of order types, a built-in economic calendar, and improved charting capabilities. MT5 is also available as a desktop platform and a mobile app, providing traders with a comprehensive trading experience.
- cTrader is a relatively new platform gaining popularity for its speed, advanced order types, and intuitive user interface. It’s particularly well-suited for scalping and high-frequency trading, as it allows for fast order execution and advanced charting tools. cTrader is available as a desktop platform and a web-based platform, offering traders flexibility and convenience.
Trading Tools and Resources
Trading tools and resources play a vital role in forex trading, providing traders with the information and insights they need to make informed decisions.
- Technical Indicators are mathematical formulas used to analyze price charts and identify potential trading opportunities. Popular indicators include Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands.
- Economic Calendars provide traders with a schedule of upcoming economic events and their potential impact on currency prices. This information helps traders anticipate market volatility and make informed trading decisions.
- News Feeds keep traders informed about global events and their impact on the forex market. This information can help traders identify potential trading opportunities and manage risk.
Forex Trading Strategies and Techniques
Forex trading involves buying and selling currencies in the foreign exchange market. Successful forex trading requires a well-defined strategy and an understanding of the market dynamics. Here, we will explore various forex trading strategies, delve into the role of technical and fundamental analysis, and highlight the importance of risk management.
Common Forex Trading Strategies
Forex trading strategies are designed to capitalize on market trends and price movements. Different strategies cater to various risk appetites and trading styles. Here are some common forex trading strategies:
- Scalping: This strategy involves taking advantage of small price fluctuations in the market, aiming for quick profits. Scalpers typically use high leverage and hold trades for a short duration, often just a few seconds or minutes. They rely heavily on technical analysis and real-time market data.
- Day Trading: Day traders open and close positions within a single trading day. They seek to profit from intraday price movements and typically close all positions before the market closes. Day trading requires a high level of focus and discipline, as it involves constant monitoring of market activity.
- Swing Trading: This strategy involves holding trades for a longer period, ranging from a few days to a few weeks. Swing traders aim to capitalize on larger price swings and focus on identifying trend reversals. They utilize technical analysis and fundamental analysis to identify potential trading opportunities.
Technical Analysis in Forex Trading
Technical analysis is a method of studying past market data, such as price charts and indicators, to identify patterns and predict future price movements. Technical analysts believe that historical price data provides valuable insights into market sentiment and can help traders make informed decisions.
- Chart Patterns: Technical analysts study various chart patterns, such as head and shoulders, double tops, and triangles, to identify potential trend reversals or continuations.
- Technical Indicators: Technical indicators are mathematical formulas applied to price data to generate signals and identify trends. Popular technical indicators include moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and MACD.
Fundamental Analysis in Forex Trading
Fundamental analysis focuses on economic and political factors that can influence currency values. Fundamental analysts study economic data, such as GDP growth, inflation, interest rates, and political events, to understand the underlying forces driving currency movements.
- Economic Data: Economic data releases, such as employment reports, inflation figures, and interest rate decisions, can have a significant impact on currency valuations.
- Political Events: Political events, such as elections, policy changes, and geopolitical tensions, can also influence currency movements.
Risk Management Techniques in Forex Trading
Risk management is crucial in forex trading, as it involves significant financial risk. Proper risk management techniques help traders protect their capital and mitigate potential losses.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders are pre-set orders that automatically close a trade when the price reaches a specific level, limiting potential losses.
- Position Sizing: Position sizing refers to determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to each trade. It involves considering factors such as risk tolerance, account balance, and the potential profit and loss.
- Diversification: Diversifying trading strategies and currency pairs can help spread risk across different markets and reduce overall portfolio volatility.
Forex Trade Broker Regulation and Security
The Forex market is a global marketplace, and as such, it is subject to a wide range of regulations from different jurisdictions. Understanding these regulations is crucial for traders, as they play a vital role in ensuring the safety and security of their funds. This section will explore the regulatory landscape for forex trade brokers, emphasizing the importance of choosing a regulated and reputable broker, and the security measures implemented by brokers to protect client funds.
Regulatory Landscape for Forex Trade Brokers
Different jurisdictions have established their own regulatory frameworks for forex trade brokers. These regulations vary in their scope and stringency, but generally aim to protect investors from fraud and malpractice.
- Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK: The FCA is one of the most respected financial regulators globally. It sets strict requirements for forex brokers operating within the UK, including capital adequacy, client segregation, and reporting obligations.
- CySEC in Cyprus: The Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC) is another prominent regulator for forex brokers. It has implemented robust regulations for brokers operating in Cyprus, including licensing requirements, client fund protection, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) in Australia: ASIC is responsible for regulating financial markets in Australia. It sets out rules for forex brokers operating in the country, covering aspects such as licensing, capital adequacy, and investor protection.
- National Futures Association (NFA) in the US: The NFA regulates futures and forex brokers in the United States. It requires brokers to adhere to specific rules and regulations, including client fund segregation, capital adequacy, and reporting requirements.
Importance of Choosing a Regulated Forex Broker
Choosing a regulated forex broker is essential for traders, as it provides several key benefits:
- Client Fund Protection: Regulated brokers are required to segregate client funds from their own operating capital. This means that even if the broker goes bankrupt, client funds are protected and are not at risk.
- Transparency and Accountability: Regulated brokers are subject to regular audits and reporting requirements, which ensure transparency in their operations and accountability to clients. This helps build trust and confidence in the broker.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanisms: Regulated brokers are required to have in place dispute resolution mechanisms to address any complaints or disagreements between clients and the broker. This provides a fair and independent process for resolving disputes.
- Financial Stability: Regulated brokers are required to meet certain capital adequacy requirements, which ensure their financial stability and ability to meet their obligations to clients.
Security Measures Implemented by Forex Brokers
Forex brokers employ a range of security measures to protect client funds and data. These measures include:
- Client Fund Segregation: As mentioned earlier, regulated brokers are required to segregate client funds from their own operating capital. This ensures that client funds are protected even if the broker experiences financial difficulties.
- Encryption: Brokers use encryption technologies to protect sensitive client data, such as personal information and trading activity, from unauthorized access.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA adds an extra layer of security to client accounts, requiring them to provide two forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code, before accessing their account.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems: Brokers employ firewalls and intrusion detection systems to prevent unauthorized access to their servers and networks.
- Regular Security Audits: Brokers conduct regular security audits to identify and address any vulnerabilities in their systems and processes.
Understanding Forex Trading Costs

Forex trading, like any other financial market, involves costs that traders need to consider. These costs can significantly impact trading profits, so understanding them is crucial for making informed trading decisions.
Spreads
Spreads are the difference between the bid price (the price at which a broker is willing to buy a currency) and the ask price (the price at which a broker is willing to sell a currency). When you buy a currency, you buy it at the ask price, and when you sell, you sell it at the bid price. The spread represents the broker’s profit margin and is a direct cost to the trader.
Spreads can vary depending on several factors, including:
- The currency pair being traded: Major currency pairs like EUR/USD typically have tighter spreads than exotic currency pairs like USD/ZAR.
- Market volatility: Spreads tend to widen during periods of high market volatility, such as during economic announcements or geopolitical events.
- The broker’s trading volume: Brokers with higher trading volumes can often offer tighter spreads.
- The trader’s account type: Some brokers offer different account types with varying spread levels, with professional accounts typically having tighter spreads.
It’s important to note that spreads are not always fixed and can fluctuate in real-time.
The impact of spreads on trading profits is directly proportional to the size of the trade. Larger trades will be affected more significantly by wider spreads.
Commissions
Commissions are fees charged by some brokers for executing trades. These fees are typically charged as a percentage of the trade value or as a fixed amount per trade.
Some brokers offer commission-free trading, while others charge commissions. When comparing brokers, it’s crucial to consider whether they charge commissions and, if so, what the commission structure is.
Commissions can be a significant cost, especially for high-volume traders. It’s essential to factor commissions into your trading strategy and profit calculations.
Swap Fees
Swap fees are charged by brokers when holding a trade overnight. These fees represent the interest rate differential between the two currencies in a currency pair.
If the interest rate on the base currency is higher than the interest rate on the quote currency, the trader will receive a swap fee. Conversely, if the interest rate on the quote currency is higher, the trader will pay a swap fee.
Swap fees can be a significant cost, especially for long-term trades. Traders should consider the swap fees associated with a currency pair before entering a trade.
Other Fees
In addition to spreads, commissions, and swap fees, brokers may charge other fees, such as:
- Account inactivity fees: Charged for accounts that are inactive for a certain period.
- Withdrawal fees: Charged for withdrawing funds from your trading account.
- Deposit fees: Charged for depositing funds into your trading account.
It’s important to be aware of all the fees associated with your broker and to factor them into your trading costs.
Comparing Trading Costs
Comparing trading costs across different brokers is crucial for finding the most cost-effective trading environment.
When comparing brokers, consider the following:
- Spreads: Compare the spreads offered on the currency pairs you trade most frequently.
- Commissions: Check whether the broker charges commissions and what the commission structure is.
- Swap fees: Compare the swap fees charged on the currency pairs you trade.
- Other fees: Be aware of any other fees charged by the broker, such as inactivity fees, withdrawal fees, and deposit fees.
By comparing trading costs, you can choose a broker that aligns with your trading style and budget.
Resources and Education for Forex Traders
The forex market is vast and complex, requiring continuous learning and adaptation. To succeed in this dynamic environment, traders need access to a wide range of resources and educational materials. This section will explore valuable resources for learning about forex trading, identifying reputable online courses and educational materials, and providing tips on staying informed about market trends and news.
Reputable Online Courses and Educational Materials, Forex trade broker
Online courses and educational materials offer structured learning pathways for forex traders of all levels. These resources provide a comprehensive understanding of forex trading fundamentals, strategies, and risk management techniques.
- Babypips: This popular website offers free forex education, covering topics from basic concepts to advanced strategies. Babypips’s interactive lessons, quizzes, and glossary make learning engaging and accessible.
- FXTM: FXTM, a regulated forex broker, provides a wide range of educational resources, including webinars, video tutorials, and ebooks. Their materials cover various aspects of forex trading, from fundamental analysis to technical analysis and risk management.
- Investopedia: Investopedia is a well-known financial website that offers comprehensive forex education. Their articles, tutorials, and glossary provide a solid foundation for understanding the forex market.
Staying Informed about Market Trends and News
Staying updated on market trends and news is crucial for making informed trading decisions. Traders need to be aware of global economic events, political developments, and central bank announcements that can impact currency prices.
- Financial News Websites: Websites like Bloomberg, Reuters, and Yahoo Finance provide real-time financial news and market data.
- Economic Calendars: Economic calendars list upcoming economic releases, such as interest rate decisions, inflation data, and employment figures. These releases can significantly influence currency movements.
- Forex Forums and Communities: Engaging in online forex forums and communities allows traders to connect with other traders, share insights, and learn from their experiences.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Learning from the experiences of successful forex traders can provide valuable insights into effective trading strategies, market dynamics, and risk management techniques. This section explores real-world examples of successful forex trading strategies, analyzes the performance of different forex brokers based on client reviews and independent research, and sheds light on the challenges and opportunities faced by forex traders.
Successful Forex Trading Strategies
Examining real-world examples of successful forex trading strategies can offer valuable insights into the approaches employed by experienced traders. These strategies often incorporate a combination of technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and risk management principles.
- Trend Following: This strategy involves identifying and trading in the direction of established trends. Trend followers use technical indicators like moving averages and momentum oscillators to identify trends and enter trades when the trend is confirmed.
- Breakout Trading: This strategy involves identifying and trading price breakouts from established support and resistance levels. Traders look for strong price movements that break through these levels, indicating a potential shift in market sentiment.
- Scalping: This strategy focuses on capturing small profits from short-term price fluctuations. Scalpers use technical indicators and high-frequency trading algorithms to identify and execute trades quickly, aiming for numerous small profits.
- News Trading: This strategy involves trading based on the release of economic news events. Traders analyze the impact of news events on currency pairs and enter trades based on anticipated price movements.
Forex Broker Performance Analysis
Understanding the performance of different forex brokers is crucial for traders seeking a reliable and trustworthy platform. Client reviews and independent research provide valuable insights into broker reliability, trading conditions, customer support, and overall performance.
- Client Reviews: Websites like ForexPeaceArmy and Trustpilot offer platforms for traders to share their experiences with different forex brokers. Reviews can provide information about broker reliability, customer service, trading platform functionality, and withdrawal processing times.
- Independent Research: Organizations like the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and the National Futures Association (NFA) conduct independent research and publish reports on the performance of forex brokers. These reports can assess broker compliance with regulatory requirements, financial stability, and overall performance.
Challenges and Opportunities in Forex Trading
Forex trading presents both challenges and opportunities for traders. Understanding these aspects is essential for navigating the market effectively and maximizing potential returns.
- Market Volatility: The forex market is highly volatile, with rapid price fluctuations driven by various factors, including economic news, political events, and market sentiment. Volatility can create both opportunities and risks for traders.
- Global Economic Factors: Forex trading is influenced by global economic factors, including interest rates, inflation, and economic growth. Traders need to stay informed about these factors to make informed trading decisions.
- Technological Advancements: The forex market is constantly evolving, with technological advancements impacting trading strategies and platform capabilities. Traders need to adapt to these changes and embrace new tools and technologies.
- Learning Curve: Forex trading requires a significant learning curve, involving understanding market dynamics, technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and risk management. Traders need to invest time and effort in learning and developing their trading skills.
Closing Notes
The world of forex trade brokers is vast and dynamic, offering a myriad of opportunities for both seasoned traders and newcomers. By understanding the nuances of forex trade brokers, their services, and the regulatory landscape, individuals can navigate this exciting market with confidence. As you embark on your forex trading journey, remember to prioritize choosing a reputable and regulated broker, mastering trading strategies, and managing risk prudently. The journey may be challenging, but the potential rewards are significant.
FAQ Corner
What is the minimum deposit required to start forex trading?
The minimum deposit requirement varies widely among forex brokers. Some brokers may have a minimum deposit of a few hundred dollars, while others may require thousands. It’s essential to research and compare different brokers to find one that suits your budget and trading goals.
How do I choose the best forex trade broker for my needs?
Choosing the best forex trade broker involves considering factors such as regulation, trading platforms, fees, customer support, and educational resources. It’s crucial to research and compare different brokers before making a decision.
What are the risks associated with forex trading?
Forex trading involves inherent risks, including market volatility, leverage, and the potential for significant losses. It’s essential to understand and manage these risks effectively to minimize potential losses.
Is forex trading suitable for everyone?
Forex trading is not suitable for everyone. It requires a thorough understanding of the market, trading strategies, and risk management techniques. Individuals with limited experience or risk tolerance should proceed with caution.
Are there any educational resources available for forex traders?
Yes, numerous educational resources are available for forex traders, including online courses, webinars, books, and articles. Reputable brokers often provide educational materials and support to help traders learn and improve their skills.




