
Forex hedging is a strategy used by businesses and individuals to mitigate the risk of currency fluctuations in the foreign exchange market. It involves taking positions in financial instruments that offset potential losses from unfavorable exchange rate movements.
The concept of forex hedging is rooted in the principle of risk management, aiming to protect against losses stemming from unpredictable currency fluctuations. This can be particularly crucial for businesses that operate internationally, where fluctuations in exchange rates can significantly impact profitability.
Introduction to Forex Hedging

Forex hedging is a risk management strategy employed by traders to mitigate potential losses arising from unfavorable currency fluctuations. It involves taking an offsetting position in the market, such as a futures contract or an option, to counterbalance the risk associated with an existing forex position. The primary objective of hedging is to reduce the impact of adverse price movements, thereby protecting the trader’s capital.
Risk Mitigation in Forex Trading
Forex trading inherently involves exposure to market risk, which arises from unpredictable fluctuations in exchange rates. Hedging aims to minimize this risk by reducing the potential for losses. Consider a scenario where a trader holds a long position in the EUR/USD currency pair, anticipating the euro to appreciate against the US dollar. However, if the market moves against the trader’s expectations, the value of their position will decline. By implementing a hedging strategy, the trader can offset the potential losses associated with this long position by taking an offsetting short position in the same currency pair.
Types of Forex Hedging Strategies
There are various hedging strategies that forex traders can utilize to manage risk, each with its unique characteristics and suitability for different trading scenarios. The most common types of forex hedging strategies include:
- Forward Contracts: Forward contracts are agreements between two parties to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. They are typically used to hedge against currency fluctuations over a specific period. For example, a company that expects to receive payment in euros in three months could enter into a forward contract to sell euros and buy US dollars at a fixed rate. This would lock in the exchange rate and protect the company from potential losses if the euro depreciates against the US dollar.
- Futures Contracts: Futures contracts are standardized agreements to buy or sell a specific amount of a currency at a predetermined price on a future date. They are traded on organized exchanges and offer a more liquid and flexible hedging option compared to forward contracts. Futures contracts are typically used by traders to hedge against short-term price fluctuations. For example, an importer expecting to pay for goods in Japanese yen could buy yen futures contracts to lock in the exchange rate and avoid potential losses if the yen appreciates against their local currency.
- Options Contracts: Options contracts give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a predetermined price on or before a specific date. They offer more flexibility than forward or futures contracts, allowing traders to limit their potential losses while retaining the potential for profit. For example, an exporter receiving payment in Canadian dollars could buy put options on the USD/CAD currency pair to protect against a decline in the Canadian dollar. This would give them the right to sell Canadian dollars at a predetermined rate if the currency weakens.
- Currency Pairs: Hedging can also be achieved by trading multiple currency pairs. For instance, a trader holding a long position in the EUR/USD could take a short position in the USD/JPY currency pair. If the euro weakens against the US dollar, the long position would incur losses. However, if the US dollar weakens against the Japanese yen, the short position in the USD/JPY would generate profits, offsetting some of the losses from the long position in the EUR/USD. This strategy involves carefully selecting currency pairs with a high correlation to minimize risk.
Common Forex Hedging Techniques
Forex hedging involves employing strategies to mitigate potential losses from unfavorable currency fluctuations. Various techniques are available, each with its unique characteristics and applications.
Forward Contracts
Forward contracts are agreements to buy or sell a specific currency at a predetermined exchange rate on a future date. These contracts are customized and negotiated between two parties, providing flexibility in terms of the amount, currency pair, and maturity date.
Forward contracts are particularly useful for hedging against exchange rate risk in future transactions. For instance, an importer expecting to pay for goods in foreign currency can enter into a forward contract to buy the required currency at a fixed rate, ensuring they know the exact cost in their domestic currency.
- Forward contracts offer certainty regarding the exchange rate, eliminating the uncertainty associated with market fluctuations.
- They are customizable, allowing for tailoring to specific needs, such as the desired currency pair, maturity date, and contract size.
- However, forward contracts involve a commitment to buy or sell at the agreed-upon rate, potentially leading to losses if the market moves in the opposite direction.
Futures Contracts
Futures contracts are standardized contracts traded on exchanges, obligating the buyer to purchase and the seller to sell a specific quantity of a currency at a predetermined price on a specific future date. Unlike forward contracts, futures contracts are standardized, with pre-defined contract sizes, maturity dates, and currency pairs.
Futures contracts are widely used for hedging against exchange rate fluctuations in future transactions. For example, an exporter expecting to receive payment in foreign currency can sell futures contracts to lock in a specific exchange rate, mitigating the risk of currency depreciation.
- Futures contracts offer liquidity and transparency due to their standardized nature and exchange trading.
- They provide a cost-effective way to hedge against exchange rate risk, with relatively low transaction costs.
- However, futures contracts involve margin requirements, where traders need to deposit a certain amount of funds as collateral.
Options for Forex Hedging
Options contracts give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific currency at a predetermined price on or before a specific date. Unlike forward and futures contracts, options provide flexibility by allowing the holder to choose whether to exercise the option based on market conditions.
Options are valuable for hedging against exchange rate risk in uncertain market conditions. For example, an importer expecting to pay for goods in foreign currency can buy a call option, giving them the right to buy the currency at a fixed rate if the exchange rate rises.
- Options provide flexibility, allowing the holder to choose whether to exercise the option based on market conditions.
- They offer downside protection, limiting potential losses in unfavorable market movements.
- However, options have a premium associated with them, which needs to be paid upfront, and they may expire worthless if the market moves in a favorable direction.
Currency Swaps
Currency swaps are agreements between two parties to exchange principal amounts in different currencies at a predetermined exchange rate, with simultaneous reverse exchange at a later date. They are commonly used by businesses and institutions to manage currency risk associated with foreign investments or debt.
For instance, a company with debt in foreign currency can enter into a currency swap to exchange its debt obligations for equivalent debt in its domestic currency. This reduces the risk of currency depreciation, as the company’s debt obligations are now in its own currency.
- Currency swaps provide a cost-effective way to manage currency risk associated with foreign investments or debt.
- They offer flexibility in terms of the currencies exchanged, the amount of principal, and the maturity date.
- However, currency swaps involve complex transactions that require expertise and understanding of the underlying market dynamics.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Forex Hedging
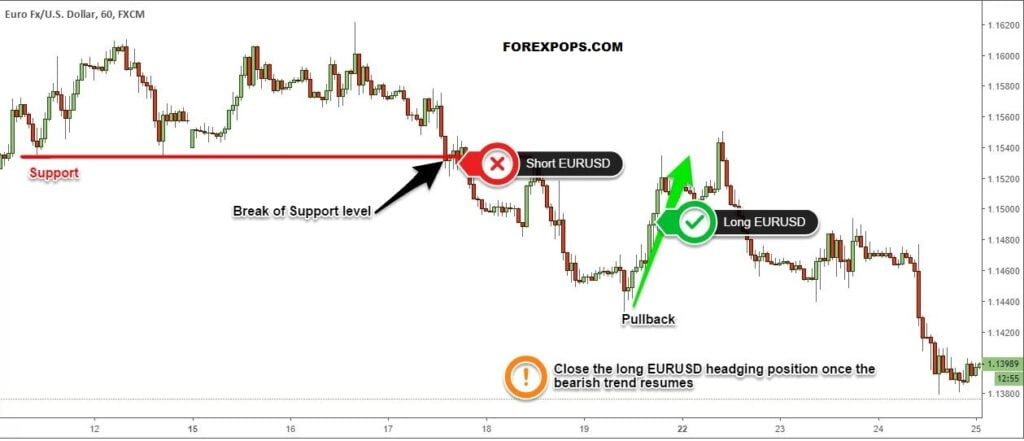
Forex hedging is a powerful tool that can help businesses and individuals mitigate risk in the foreign exchange market. It involves taking a position in the market that offsets potential losses from another existing position. However, like any financial strategy, it comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding both sides of the coin is crucial for making informed decisions.
Advantages of Forex Hedging
Hedging strategies can offer several benefits, including:
- Reducing Currency Risk: The primary advantage of hedging is to minimize losses due to fluctuations in exchange rates. By taking a counterbalancing position, you can lock in a specific exchange rate, protecting your profits or investments from adverse movements.
- Increased Predictability: Hedging helps create a more predictable financial environment. It allows businesses to forecast their financial performance with greater accuracy, even in the face of fluctuating exchange rates. This predictability is crucial for budgeting, pricing, and long-term planning.
- Enhanced Profitability: Hedging can enhance profitability by ensuring that profits from foreign exchange transactions are not eroded by unfavorable exchange rate movements. This is particularly important for businesses that generate revenue or incur expenses in multiple currencies.
- Improved Cash Flow Management: Hedging can help improve cash flow management by providing certainty about the value of future foreign currency transactions. This allows businesses to better plan for their financial needs and avoid surprises due to currency fluctuations.
- Competitive Advantage: By mitigating currency risk, hedging can give businesses a competitive advantage. They can confidently expand into international markets, knowing that their financial performance will not be significantly impacted by exchange rate volatility.
Disadvantages of Forex Hedging
While hedging offers significant advantages, it also comes with potential drawbacks:
- Cost: Hedging strategies involve transaction costs, including commissions, fees, and spreads. These costs can eat into profits, especially for smaller transactions.
- Complexity: Hedging can be complex and requires a good understanding of the foreign exchange market. Implementing the right hedging strategy can be challenging, and mistakes can lead to significant losses.
- Limited Effectiveness: Hedging strategies are not always 100% effective. Exchange rates can still fluctuate, and hedging can only mitigate, not eliminate, currency risk. For example, if the exchange rate moves against you, you might still incur some losses, even with a hedging strategy in place.
- Opportunity Cost: By hedging, you may miss out on potential gains from favorable exchange rate movements. If the exchange rate moves in your favor, your hedged position might limit your potential profits.
- Risk of Counterparty Default: When using derivative contracts for hedging, there is a risk that the counterparty to the contract may default on their obligations. This can result in significant financial losses.
Effectiveness of Different Hedging Techniques
The effectiveness of different hedging techniques can vary depending on factors such as the specific currency pair, the time horizon, and the risk tolerance of the individual or business.
- Forward Contracts: Forward contracts are relatively simple and straightforward hedging instruments. They allow you to lock in a specific exchange rate for a future date. However, they are less flexible than other options and may not be suitable for all situations.
- Futures Contracts: Futures contracts are similar to forward contracts but are standardized and traded on exchanges. They offer greater liquidity and can be more efficient for hedging larger transactions.
- Options Contracts: Options contracts provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a specific price on or before a certain date. They offer greater flexibility than forward or futures contracts, but they also come with a premium cost.
- Currency Swaps: Currency swaps involve exchanging principal amounts and interest payments in different currencies. They can be used to hedge against currency risk over a longer period.
Real-World Examples of Forex Hedging
Forex hedging is a practical strategy employed by businesses to mitigate the financial risks associated with fluctuations in exchange rates. It allows companies to lock in a specific exchange rate for future transactions, ensuring predictable costs and revenue streams.
Examples of Businesses Using Forex Hedging
Here are some examples of how businesses utilize forex hedging to manage currency risk:
- Exporters: Companies that export goods or services to foreign markets are exposed to currency risk. If the value of the foreign currency weakens against their home currency, they receive less revenue when converting the foreign currency back to their home currency. To mitigate this risk, exporters can use forward contracts to lock in a favorable exchange rate for their future sales. This allows them to ensure a certain level of profitability, even if the exchange rate fluctuates.
- Importers: Similarly, importers face currency risk when they purchase goods or services from foreign suppliers. If the value of their home currency weakens against the foreign currency, they will have to pay more for the imported goods. Importers can use forward contracts or options to hedge against this risk, ensuring that the cost of their imports remains predictable.
- Multinational Corporations: Large corporations with operations in multiple countries are exposed to currency risk on a global scale. They need to manage the exchange rates between the currencies of their various subsidiaries. Hedging strategies, such as forward contracts and currency swaps, can be used to mitigate the impact of currency fluctuations on their global profits.
Case Studies of Successful Forex Hedging Implementations
Successful implementation of forex hedging strategies can significantly improve a business’s financial performance. Here are some case studies that illustrate the positive impact of hedging:
- A manufacturing company in the United States that exports its products to Europe hedged its exposure to the euro using forward contracts. When the euro weakened against the dollar, the company was able to lock in a favorable exchange rate for its exports, ensuring a steady stream of revenue in US dollars. This helped the company maintain its profitability despite the unfavorable currency movement.
- A technology company in India that imports components from China hedged its exposure to the Chinese yuan using options. When the yuan strengthened against the Indian rupee, the company was able to purchase the components at a fixed exchange rate, preventing a significant increase in its import costs. This allowed the company to maintain its competitive pricing and market share.
Impact of Hedging on Profitability and Risk Management
Forex hedging can have a significant impact on a business’s profitability and risk management.
- Reduced Currency Risk: By locking in a specific exchange rate, hedging strategies help businesses reduce the volatility of their earnings due to currency fluctuations. This provides greater predictability and stability in their financial performance.
- Improved Profitability: Hedging can enhance profitability by ensuring that businesses receive a certain level of revenue or pay a fixed cost for their imports, regardless of currency fluctuations. This can improve their margins and overall financial performance.
- Enhanced Risk Management: Hedging strategies are an integral part of a comprehensive risk management framework. By mitigating currency risk, businesses can focus on their core operations and strategic initiatives without being overly concerned about exchange rate volatility.
Closing Summary

Understanding and implementing effective forex hedging strategies can be a valuable tool for managing currency risk in the ever-changing global market. By carefully considering your risk tolerance, market conditions, and available resources, you can navigate the complexities of foreign exchange and protect your financial interests.
FAQ Corner
What are the main types of forex hedging strategies?
Common forex hedging strategies include forward contracts, futures contracts, options, and currency swaps.
How do I choose the right forex hedging strategy?
The best strategy depends on factors like your risk tolerance, market conditions, and the specific currency pair you’re trading.
Is forex hedging always effective?
While hedging can mitigate risk, it’s not foolproof. Market conditions can change, and unexpected events can impact the effectiveness of hedging strategies.
What are the costs associated with forex hedging?
Hedging strategies typically involve transaction costs, such as brokerage fees and premiums for options.




