
Forex com leverage – Forex.com leverage, a powerful tool in the forex trading world, allows traders to amplify their potential profits and losses. This concept, often described as “borrowing” funds from a broker to increase trading size, can be a double-edged sword. While it offers the opportunity to generate significant returns, it also magnifies the risk associated with every trade. Understanding how leverage works, its potential benefits and drawbacks, and the importance of risk management is crucial for any forex trader.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of forex.com leverage, exploring its calculation, application, and the regulatory landscape surrounding it. We will also discuss the psychological aspects of leverage, how it can impact trading decisions, and provide insights into best practices for leveraging this powerful tool effectively.
Forex Trading Basics
Forex trading, short for foreign exchange trading, is the simultaneous buying of one currency and selling of another. This exchange happens in the global forex market, the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. Traders aim to profit from the fluctuations in currency exchange rates.
Leverage in Forex Trading
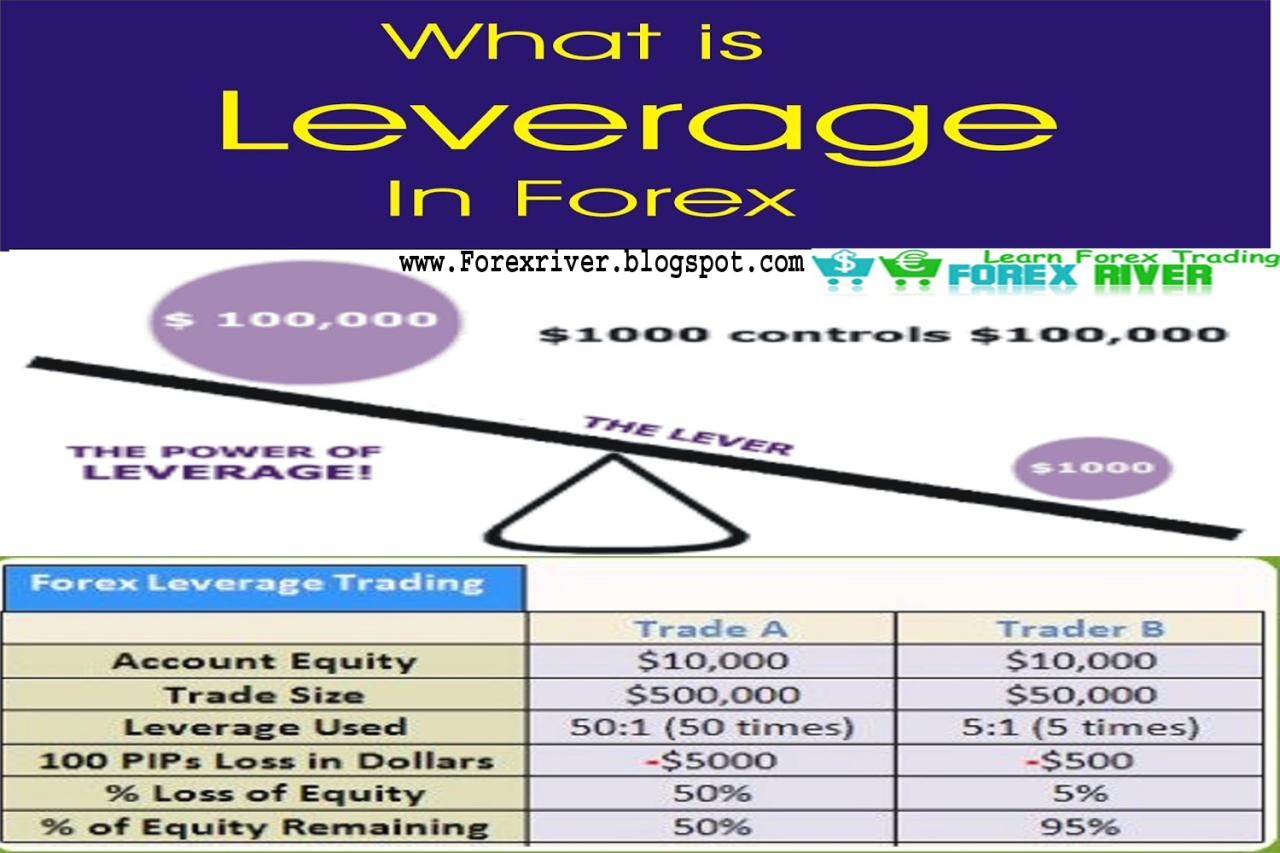
Leverage is a powerful tool that allows traders to control a larger position in the market with a smaller initial investment. It essentially magnifies potential profits and losses. In simple terms, leverage acts as a multiplier for your investment.
For example, if you have $1,000 and a leverage of 1:100, you can control a position worth $100,000 ($1,000 x 100). This means that even small changes in the exchange rate can result in significant gains or losses.
Advantages of Using Leverage
- Amplified Profits: Leverage allows traders to amplify potential profits. Even small price movements can lead to substantial gains, especially with high leverage.
- Access to Larger Positions: With leverage, traders can control larger positions in the market with a smaller capital investment, enabling them to take advantage of market trends.
- Increased Flexibility: Leverage allows traders to adjust their trading strategies and adapt to changing market conditions more easily.
Disadvantages of Using Leverage
- Amplified Losses: Leverage can magnify both profits and losses. If the market moves against your position, losses can be significant and potentially exceed your initial investment.
- Increased Risk: Leverage increases the overall risk associated with trading. It is crucial to understand and manage risk effectively when using leverage.
- Margin Calls: Leverage requires traders to maintain a certain amount of funds, known as margin, in their trading account. If the market moves against your position and your margin falls below a certain threshold, you may receive a margin call, requiring you to deposit additional funds to cover potential losses.
Leverage Calculation and Application
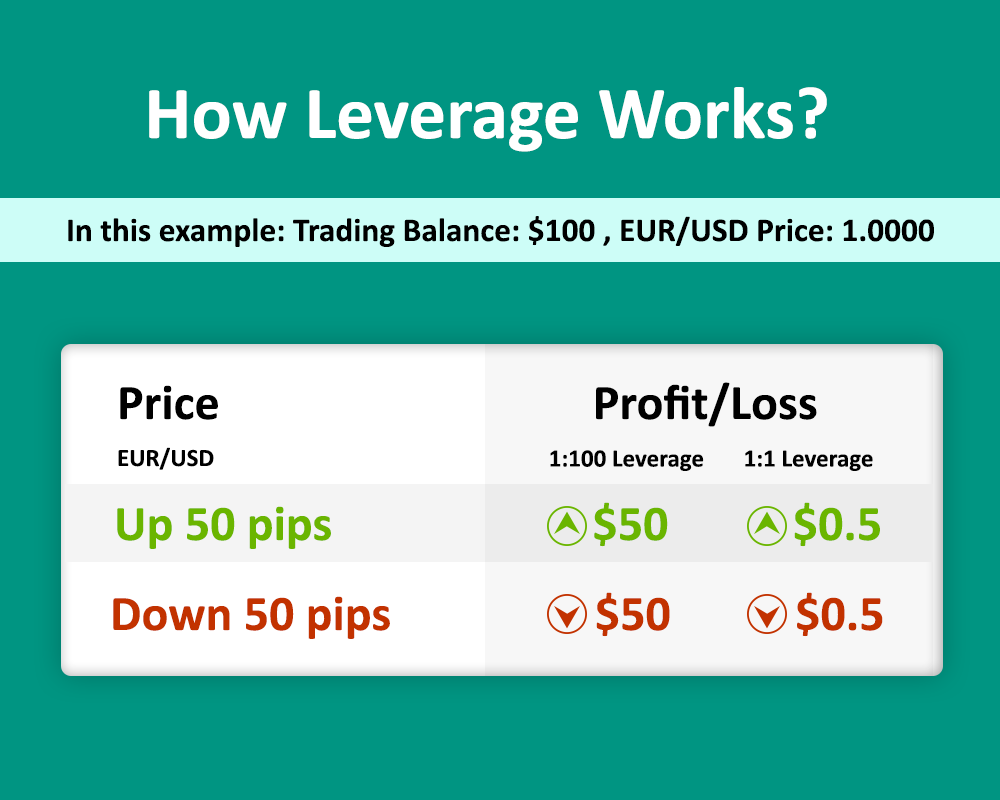
Leverage is a powerful tool in forex trading, allowing traders to control larger positions with a smaller initial investment. Understanding how leverage is calculated and applied is crucial for maximizing potential profits and managing risks effectively.
Leverage Calculation
Leverage is expressed as a ratio, indicating the amount of borrowed funds relative to the trader’s own capital. For example, a leverage ratio of 1:100 means that for every $1 the trader deposits, they can control $100 worth of currency.
Leverage Ratio = Total Position Value / Trader’s Capital
For instance, if a trader deposits $1000 and uses a leverage ratio of 1:100, they can control a position worth $100,000.
Leverage and Profit/Loss
Leverage magnifies both profits and losses. While it can amplify gains, it also increases the potential for significant losses.
- Profit Example: A trader buys 10,000 units of EUR/USD at an exchange rate of 1.1000 with a leverage ratio of 1:50. The initial margin requirement is $200 (10,000 units / 50). If the exchange rate rises to 1.1100, the trader makes a profit of $100 (10,000 units x 0.0100). This represents a 50% return on their initial margin investment.
- Loss Example: If the exchange rate falls to 1.0900, the trader incurs a loss of $100 (10,000 units x 0.0100). This represents a 50% loss on their initial margin investment.
Risks of High Leverage
High leverage can amplify potential profits, but it also increases the risk of significant losses.
- Margin Calls: If the market moves against a trader’s position, the broker may issue a margin call, demanding additional funds to cover potential losses. Failure to meet a margin call can result in the liquidation of the trader’s position.
- Increased Volatility: High leverage can exacerbate market volatility, making it difficult to manage trades effectively.
- Emotional Trading: The potential for large profits and losses can lead to emotional trading, which can negatively impact decision-making.
Margin Requirements and Stop-Loss Orders

Margin requirements are a fundamental aspect of forex trading, especially when using leverage. Understanding margin requirements and how they interact with leverage is crucial for managing risk effectively. This section will delve into the concept of margin requirements and explore the role of stop-loss orders in mitigating potential losses.
Margin Requirements, Forex com leverage
Margin requirements are the amount of money you need to deposit in your trading account to open and maintain a forex position. This deposit acts as a security for the broker, ensuring they can cover potential losses from your trades. Margin requirements are expressed as a percentage of the total trade value, and they are inversely proportional to the leverage you are using.
- Leverage and Margin Requirements: Higher leverage implies a lower margin requirement. For example, if you are trading with a leverage of 1:100, you would only need to deposit 1% of the total trade value as margin. Conversely, with a leverage of 1:10, you would need to deposit 10% of the trade value as margin.
- Calculating Margin Requirements: Margin requirements are calculated by dividing the total trade value by the leverage. For instance, if you are trading 1 lot (100,000 units) of EUR/USD with a leverage of 1:50, the margin requirement would be: (100,000 / 50) = $2,000.
Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are essential risk management tools for forex traders. They allow you to automatically close a position when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting your potential losses. This is particularly crucial when using leverage, as even small price fluctuations can result in significant losses.
- Setting Stop-Loss Orders: When placing a stop-loss order, you specify a price level at which you want the trade to close. If the price moves against your position and reaches the stop-loss level, your trade will be automatically closed, preventing further losses.
- Importance of Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders help you manage risk by limiting potential losses. They are particularly important in volatile markets or when using leverage, as they provide a safety net against unexpected price movements.
- Placement of Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders should be placed at a level that is reasonable and based on your risk tolerance. Placing them too close to the entry price may lead to frequent stops being triggered by minor price fluctuations, while placing them too far away may not effectively limit losses in case of significant market movements.
Stop-loss orders are not a guarantee against losses, but they can significantly reduce the impact of negative price movements.
Leverage Strategies and Best Practices
Leverage is a powerful tool in forex trading, but it can also be risky if not used wisely. This section explores various leverage strategies and best practices to help you navigate the complexities of leveraging your trading capital effectively.
Leverage Strategies
Leverage strategies can be broadly categorized into two primary approaches:
– Scalping: This strategy aims to profit from small price fluctuations by opening and closing trades rapidly. Scalpers often utilize high leverage to amplify their gains from these minor movements.
– Swing Trading: This approach involves holding trades for a longer period, typically days or weeks, to capitalize on larger price swings. Swing traders might use lower leverage compared to scalpers due to the longer holding periods.
Risk Management in Leveraged Trading
Risk management is paramount when using leverage. Here’s why:
– Magnified Losses: Leverage amplifies both profits and losses. A small price movement against your position can result in significant losses due to the magnified effect of leverage.
– Margin Calls: When your losses exceed a certain threshold, you may receive a margin call, requiring you to deposit additional funds to cover the losses and maintain your position.
– Account Wipeout: In extreme cases, if losses exceed your margin, your entire trading account could be wiped out.
Best Practices for Using Leverage Effectively
– Understand Your Risk Tolerance: Before using leverage, assess your risk appetite and ensure you’re comfortable with the potential for magnified losses.
– Start Small: Begin with a small leverage ratio and gradually increase it as you gain experience and confidence.
– Use Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders are crucial for limiting your potential losses by automatically closing your position when the price reaches a predetermined level.
– Diversify Your Portfolio: Spread your trades across different currency pairs to reduce the impact of any single losing trade.
– Keep a Close Eye on Market Conditions: Be aware of economic news and events that can significantly affect currency prices and your leveraged trades.
– Don’t Over-Leverage: Avoid using leverage that exceeds your risk tolerance or financial capacity.
– Regularly Monitor Your Account: Keep track of your trading activity, including profits, losses, and open positions.
– Stay Informed and Learn: Continuously educate yourself about forex trading and leverage to improve your understanding and decision-making skills.
Leverage and Regulatory Considerations: Forex Com Leverage
Leverage, a powerful tool in forex trading, comes with its own set of regulatory considerations. Financial authorities around the world recognize the potential risks associated with high leverage and have implemented regulations to protect traders. Understanding these regulations is crucial for traders to operate within legal boundaries and manage their risk effectively.
Leverage Regulations Across Jurisdictions
Different jurisdictions have varying regulations regarding leverage in forex trading. These regulations aim to balance the benefits of leverage with the need to protect traders from excessive risk.
- European Union (EU): The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) has implemented a leverage cap of 1:30 for retail forex traders. This means that for every €1 a trader deposits, they can control up to €30 of the underlying asset.
- United States (US): The National Futures Association (NFA) does not impose a specific leverage cap for retail forex traders. However, brokers operating in the US are subject to regulations that require them to assess a trader’s risk tolerance and provide appropriate leverage levels.
- Australia: The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) has implemented a leverage cap of 1:50 for retail forex traders.
- Japan: The Financial Services Agency (FSA) has implemented a leverage cap of 1:25 for retail forex traders.
Impact of Regulatory Changes on Leverage Use
Regulatory changes can significantly impact how leverage is used in forex trading.
- Leverage Caps: Implementing leverage caps restricts the amount of leverage traders can access, potentially reducing their potential profits but also mitigating their potential losses.
- Margin Requirements: Regulatory changes can also affect margin requirements, which are the amount of funds a trader needs to deposit to open a position. Increased margin requirements can limit leverage and reduce the trading capacity of traders.
- Account Types: Some jurisdictions have introduced different account types based on trading experience and risk tolerance. For example, professional traders may be eligible for higher leverage levels than retail traders.
Leverage and Trading Psychology
Leverage, a powerful tool in forex trading, can amplify both profits and losses. While it offers the potential for substantial gains, it also introduces a significant psychological dimension that traders must navigate carefully. Understanding the interplay between leverage and trading psychology is crucial for maintaining a disciplined approach and mitigating potential risks.
The Psychological Impact of Leverage
Leverage can create a sense of exhilaration and excitement, particularly when trades are profitable. This feeling can lead to overconfidence and a tendency to take on more risk than initially intended. Conversely, losses magnified by leverage can trigger fear, anxiety, and frustration, leading to impulsive decisions and emotional trading.
Leverage and Overtrading
Leverage can exacerbate the tendency to overtrade, as the potential for quick profits may overshadow the risks involved. The amplified returns offered by leverage can create a false sense of security, encouraging traders to take on positions that are too large or too frequent. Overtrading can lead to increased trading costs, eroded capital, and a higher likelihood of significant losses.
Strategies for Maintaining Discipline with Leverage
- Set Clear Trading Goals: Define specific profit targets and risk tolerance levels before entering a trade. Leverage should be used strategically to achieve these goals, not to chase unrealistic returns.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders are essential for managing risk and limiting potential losses. They automatically close a trade when it reaches a predetermined price level, preventing further losses from accumulating.
- Maintain a Trading Journal: Regularly document trades, including entry and exit points, profit and loss, and the rationale behind each decision. This helps identify patterns, evaluate trading strategies, and track progress.
- Practice Risk Management: Allocate a specific portion of capital for trading, and avoid risking more than a predetermined percentage on any single trade. This helps control losses and prevents the depletion of trading capital.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consider consulting with experienced traders or financial advisors for guidance on leverage strategies and risk management techniques.
Leverage and Trading Platforms
Leverage is a powerful tool that can amplify both profits and losses in forex trading. Understanding how leverage is implemented on different trading platforms is crucial for traders of all levels. This section will explore how leverage is implemented on various platforms, compare leverage options offered by different brokers, and provide a detailed explanation of how to adjust leverage settings on trading platforms.
Leverage Implementation on Forex Trading Platforms
Leverage is a core feature of most forex trading platforms. The way leverage is implemented can vary slightly depending on the platform and broker, but the fundamental concept remains the same.
When you open a forex trading account, you choose a leverage level. This leverage level is applied to your trades, allowing you to control a larger position than your initial capital would normally allow. For example, if you have a $1,000 account and use a leverage of 1:100, you can control a position worth $100,000.
Most platforms display the leverage level clearly in the trade ticket or account settings. The leverage level can be adjusted based on your risk tolerance and trading strategy.
Leverage Options Offered by Brokers
Brokers offer different leverage levels to cater to various trader profiles and risk appetites. Here are some common leverage options offered by forex brokers:
* High Leverage: Leverage levels of 1:500 or higher are typically offered to experienced traders who are comfortable with higher risk.
* Moderate Leverage: Leverage levels of 1:100 to 1:200 are often preferred by intermediate traders who are seeking a balance between risk and reward.
* Low Leverage: Leverage levels of 1:10 or 1:20 are usually offered to beginners or conservative traders who prioritize risk management.
The leverage offered by a broker can be a significant factor in choosing a platform. It’s essential to compare the leverage options of different brokers and choose one that aligns with your trading style and risk tolerance.
Adjusting Leverage Settings on Trading Platforms
The process of adjusting leverage settings on trading platforms varies depending on the platform. However, the general steps are usually as follows:
1. Log in to your trading platform: Access your trading account through the platform’s website or mobile app.
2. Locate the leverage settings: The leverage settings are usually found in the account settings, trading settings, or trade ticket.
3. Select your desired leverage level: Choose the leverage level that suits your trading strategy and risk appetite.
4. Confirm the change: Once you have selected your desired leverage level, confirm the change by clicking on the “Save” or “Apply” button.
It’s important to note that some platforms may have limitations on the leverage levels you can choose. Additionally, some brokers may require you to contact customer support to adjust your leverage settings.
Last Recap
Navigating the world of forex.com leverage requires a balance of understanding, discipline, and responsible risk management. By carefully considering the advantages and disadvantages, implementing appropriate strategies, and adhering to best practices, traders can harness the power of leverage to enhance their trading journey. Remember, leverage is a tool, and like any tool, it should be used wisely and with a clear understanding of its potential impact.
Helpful Answers
What is the maximum leverage offered by Forex.com?
The maximum leverage offered by Forex.com varies depending on the trading account type and the specific trading instrument. It’s best to check their website or contact their customer support for the most up-to-date information.
How do I adjust my leverage settings on the Forex.com platform?
The process for adjusting leverage settings can vary depending on the platform you’re using. You can typically find the leverage options within your account settings or trading platform interface. If you’re unsure, consult the Forex.com help center or contact their customer support.
Is leverage suitable for all forex traders?
Leverage is not suitable for all traders. It’s best for experienced traders who understand the risks and have a solid risk management strategy. If you’re new to forex trading, it’s recommended to start with lower leverage and gradually increase it as you gain experience.




