
Compare electricity companies, and you’ll discover a world of options, each with its own unique pricing structure, customer service, and environmental impact. Understanding your energy needs, comparing plans, and evaluating providers are crucial steps in finding the perfect electricity solution for your home or business.
From fixed-rate to variable-rate plans, and even renewable energy options, this guide will help you navigate the complexities of the electricity market and make informed decisions that save you money and reduce your environmental footprint.
Understanding Your Electricity Needs
To choose the best electricity company, you need to understand your electricity needs. Knowing how much electricity you use will help you compare plans and find the best deal.
Factors Influencing Electricity Consumption
Several factors influence your electricity consumption. These include:
- Size of your home or business: Larger homes or businesses naturally require more electricity to power appliances, lighting, and other systems.
- Number of occupants: More people living in a household generally means higher electricity consumption due to increased use of appliances and lighting.
- Appliance usage: Appliances like refrigerators, air conditioners, and ovens consume significant amounts of electricity. The more you use them, the higher your bill will be.
- Heating and cooling systems: Heating and cooling systems are major electricity consumers, especially in extreme weather conditions. Energy-efficient systems can significantly reduce consumption.
- Lighting: Replacing traditional incandescent bulbs with LED bulbs can dramatically lower your electricity bill.
- Climate: Extreme temperatures can increase the need for heating and cooling, leading to higher electricity consumption.
- Lifestyle: Your daily habits, such as how often you use appliances and how you heat and cool your home, influence your electricity consumption.
Common Electricity Usage Patterns and Costs
Understanding common electricity usage patterns and their corresponding costs can help you estimate your own electricity usage:
- High electricity consumption: Homes with large families, multiple appliances, and energy-intensive heating and cooling systems often have high electricity consumption. These homes typically pay more for electricity.
- Average electricity consumption: Homes with moderate appliance usage, efficient heating and cooling systems, and a reasonable number of occupants usually fall into the average consumption category.
- Low electricity consumption: Homes with small families, limited appliance usage, and energy-efficient features tend to have low electricity consumption. These homes typically pay less for electricity.
Estimating Your Average Monthly Electricity Usage, Compare electricity companies
You can estimate your average monthly electricity usage by following these tips:
- Review your past electricity bills: Check your previous bills to see your average monthly usage over a year. This will give you a good starting point.
- Use an online electricity usage calculator: Many websites offer free online calculators that estimate your electricity usage based on factors like your home size, appliance usage, and climate.
- Monitor your electricity usage: Some electricity companies offer smart meters or online portals that allow you to track your real-time electricity consumption. This can help you identify areas where you can save energy.
Comparing Electricity Plans
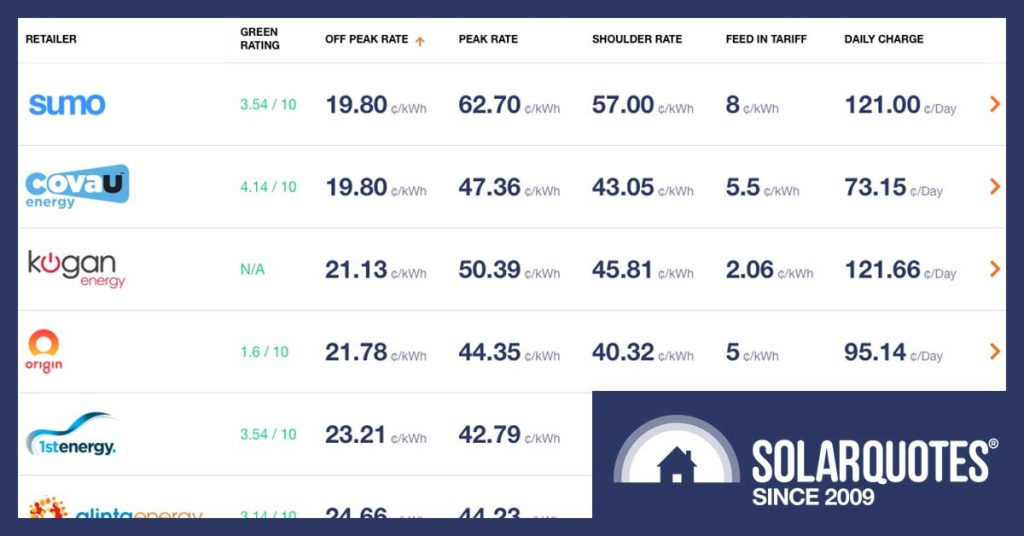
Choosing the right electricity plan can significantly impact your energy bills. Understanding the different plan types and their features is crucial for making an informed decision. This section will delve into the various types of electricity plans available, their advantages and disadvantages, and the key terms and conditions associated with them.
Fixed-Rate Plans
Fixed-rate plans offer a predictable and consistent price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) for a set period, typically 12 to 24 months. This predictability allows you to budget your electricity expenses effectively, as you know exactly how much you’ll be paying for each unit of energy consumed.
Advantages of Fixed-Rate Plans:
- Predictable energy costs, making budgeting easier.
- Protection against fluctuating energy prices, providing peace of mind.
- Suitable for consumers who prefer stability and certainty.
Disadvantages of Fixed-Rate Plans:
- You may miss out on potential savings if energy prices decline during the fixed period.
- Early termination fees may apply if you cancel the plan before the fixed period ends.
- Fixed rates may not be the most competitive option if energy prices are low.
Variable-Rate Plans
Variable-rate plans offer a price per kWh that fluctuates based on wholesale energy market prices. These plans can be advantageous when energy prices are low, but they also carry the risk of higher bills if prices rise.
Advantages of Variable-Rate Plans:
- Potential for lower energy bills if wholesale energy prices decline.
- No fixed-term contracts, allowing for greater flexibility.
Disadvantages of Variable-Rate Plans:
- Unpredictable energy costs, making budgeting challenging.
- Exposure to higher energy bills if wholesale prices increase.
- May not be suitable for consumers seeking stability and predictable expenses.
Time-of-Use Plans
Time-of-use (TOU) plans charge different rates for electricity consumption during peak, off-peak, and shoulder periods. These plans encourage energy conservation by incentivizing customers to use electricity during off-peak hours when demand is lower and prices are typically cheaper.
Advantages of Time-of-Use Plans:
- Potential for significant savings by shifting energy consumption to off-peak hours.
- Encourages energy conservation and reduces peak demand.
Disadvantages of Time-of-Use Plans:
- Requires careful monitoring of energy usage and adjustment of consumption patterns.
- May not be suitable for consumers with inflexible schedules or high energy demands during peak hours.
Key Terms and Conditions
Understanding the key terms and conditions associated with electricity plans is crucial for making informed decisions. These terms include:
Rate Periods
Rate periods define the different time blocks during which electricity rates apply. TOU plans typically have three rate periods:
- Peak: The highest demand period, usually during the hottest or coldest hours of the day.
- Off-Peak: The lowest demand period, typically during the night or early morning hours.
- Shoulder: The intermediate demand period, between peak and off-peak hours.
Fees
Electricity plans may include various fees, such as:
- Monthly service fee: A fixed charge for providing electricity service.
- Early termination fee: A penalty for canceling the plan before the contract period ends.
- Late payment fee: A charge for making payments after the due date.
Contracts
Electricity plans are typically governed by contracts that Artikel the terms and conditions of the service. These contracts may include:
- Contract length: The duration of the plan, typically 12 to 24 months for fixed-rate plans.
- Renewal options: Whether the plan automatically renews at the end of the contract period.
- Cancellation policies: The procedures for canceling the plan and any associated fees.
Evaluating Electricity Providers
Once you understand your electricity needs and have compared various plans, the next step is to evaluate the electricity providers themselves. This involves analyzing their pricing structures, customer service, and environmental practices to determine the best fit for your needs and values.
Provider Comparison
A thorough comparison of electricity providers involves evaluating various aspects, such as pricing structures, customer service, and environmental practices. This section will guide you through the process of comparing these factors to make an informed decision.
- Pricing Structures: Different providers offer various pricing structures, including fixed-rate, variable-rate, and tiered-rate plans. Fixed-rate plans offer predictable monthly bills, while variable-rate plans fluctuate with market prices. Tiered-rate plans charge different rates based on the amount of electricity consumed. When comparing pricing structures, consider your budget and energy consumption patterns to determine the most suitable plan.
- Customer Service: Customer service is a crucial aspect of any service provider, especially for utilities. Look for providers with positive customer reviews, responsive customer support channels, and clear communication regarding billing and account management. Consider factors like response times, resolution rates, and overall customer satisfaction when evaluating customer service.
- Environmental Practices: If you’re environmentally conscious, you’ll want to choose a provider committed to sustainability. Look for providers that source renewable energy, such as solar or wind power, and invest in energy efficiency initiatives. Consider their carbon footprint, renewable energy portfolio, and participation in green programs.
Provider Analysis
To help you compare electricity providers, here is a table outlining the key features of some major providers in your region. This table provides a snapshot of each provider’s pricing structure, customer service ratings, and environmental practices.
| Provider | Pricing Structure | Customer Service Rating | Environmental Practices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provider A | Fixed-rate, variable-rate, tiered-rate plans | 4.5 stars (based on customer reviews) | Offers renewable energy options, participates in green programs |
| Provider B | Fixed-rate, variable-rate plans | 3.8 stars (based on customer reviews) | Focuses on energy efficiency initiatives, offers limited renewable energy options |
| Provider C | Tiered-rate plans, fixed-rate options | 4.2 stars (based on customer reviews) | Committed to sustainability, sources a significant portion of its energy from renewable sources |
Remember, this table is a general overview, and it’s crucial to conduct your own research and compare the specific plans offered by each provider.
Understanding Renewable Energy Options

Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are becoming increasingly popular as consumers seek more sustainable and environmentally friendly options. This section explores the availability, cost, and environmental impact of renewable energy, as well as government incentives for adopting these technologies.
Availability and Cost of Renewable Energy
The availability of renewable energy sources varies depending on geographic location and climate. Solar energy is most abundant in sunny regions, while wind power is more prevalent in areas with consistent wind patterns. The cost of renewable energy technologies has decreased significantly in recent years, making them more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
- Solar Energy: Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, and the cost of solar panel installations has dropped significantly in recent years. The average cost of a residential solar panel system in the United States is between $15,000 and $25,000, depending on factors such as panel size, installation complexity, and local labor costs. Government incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, can further reduce the upfront cost of solar installations.
- Wind Energy: Wind turbines convert wind energy into electricity. The cost of wind turbines has also decreased in recent years, and wind energy is now a cost-competitive source of electricity in many regions. The average cost of a residential wind turbine system is between $5,000 and $15,000, depending on factors such as turbine size, installation complexity, and local labor costs. Government incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, can further reduce the upfront cost of wind turbine installations.
Environmental Impact of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources have a significantly lower environmental impact than traditional fossil fuels. They do not produce greenhouse gases or other pollutants, and they help to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels.
- Solar Energy: Solar panels have a minimal environmental impact during their lifecycle. The manufacturing process requires some energy and resources, but the panels themselves do not produce any emissions. At the end of their useful life, solar panels can be recycled or disposed of safely.
- Wind Energy: Wind turbines also have a minimal environmental impact during their lifecycle. The manufacturing process requires some energy and resources, but the turbines themselves do not produce any emissions. Wind turbines can have some impact on wildlife, such as birds and bats, but these impacts can be mitigated through careful siting and design.
Government Incentives for Renewable Energy
Many governments offer incentives to encourage the adoption of renewable energy technologies. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, and other financial assistance.
- Tax Credits: The federal government offers a 30% tax credit for residential solar installations. Many states also offer additional tax credits and rebates for renewable energy.
- Rebates: Some states offer rebates for the purchase and installation of renewable energy technologies. These rebates can help to offset the upfront cost of renewable energy systems.
- Net Metering: Net metering allows homeowners with solar panels to sell excess electricity back to the grid. This can help to offset the cost of electricity and provide additional income.
Choosing the Right Electricity Company
Now that you understand your electricity needs, have compared different electricity plans, and evaluated electricity providers, it’s time to make a decision. Choosing the right electricity company can save you money and ensure you’re getting the best service possible.
Step-by-Step Guide to Choosing an Electricity Company
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the best electricity company for your needs:
- Determine Your Electricity Needs: Start by assessing your energy consumption patterns. Consider your household size, appliance usage, and any special needs like electric heating or cooling. This will help you narrow down your choices to plans that best suit your energy usage.
- Compare Electricity Plans: Once you know your electricity needs, compare different plans offered by various providers. Pay attention to factors like price per kilowatt-hour (kWh), fixed or variable rates, contract terms, and any associated fees.
- Evaluate Electricity Providers: Research the reputation and reliability of each provider. Consider factors like customer service ratings, billing practices, and any previous complaints or issues. Look for companies with a track record of providing reliable service and transparent billing.
- Consider Renewable Energy Options: If you’re environmentally conscious, explore options for renewable energy, such as solar or wind power. Many electricity companies offer plans that utilize renewable sources, allowing you to reduce your carbon footprint.
- Read Reviews and Testimonials: Online reviews and testimonials from previous customers can provide valuable insights into a company’s service quality and customer satisfaction. Look for reviews that mention specific experiences and address factors that are important to you.
- Contact Customer Service: Before making a final decision, contact the customer service department of the provider you’re considering. This allows you to ask questions, get clarification on any unclear aspects of their plans, and gauge the responsiveness and helpfulness of their customer service team.
- Compare Prices and Plans: Use online comparison tools or contact multiple providers to get quotes for similar plans. This allows you to directly compare prices and features to find the best value for your needs.
- Review Contract Terms: Carefully review the terms and conditions of any contract before signing up. Pay attention to details like cancellation policies, renewal options, and any hidden fees.
- Choose the Right Plan: Based on your research and comparison, choose the electricity plan that best meets your needs and budget. Consider factors like price, contract terms, renewable energy options, and customer service.
Checklist for Evaluating Electricity Providers
Here’s a checklist to help you evaluate and compare electricity providers:
- Price per kWh: Compare the price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) offered by different providers.
- Fixed or Variable Rates: Determine whether the rates are fixed or variable, and understand the implications of each option.
- Contract Terms: Review the contract terms, including the length of the contract, cancellation policies, and any renewal options.
- Fees and Charges: Be aware of any additional fees or charges associated with the plan, such as early termination fees or monthly service charges.
- Renewable Energy Options: Check if the provider offers plans that utilize renewable energy sources.
- Customer Service: Research customer service ratings and reviews to gauge the provider’s responsiveness and helpfulness.
- Billing Practices: Understand the billing cycle and any online payment options available.
- Reliability and Availability: Evaluate the provider’s track record for reliable service and any history of outages or interruptions.
- Transparency and Communication: Assess the provider’s transparency in terms of pricing, contract terms, and communication practices.
Pros and Cons of Different Electricity Options
The best electricity option for you depends on your individual needs and preferences. Here’s a table showcasing the pros and cons of different electricity options:
| Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Utility Company | Reliable service, established infrastructure, typically offers a variety of plans | May have higher rates, limited renewable energy options, less flexibility in terms of customization |
| Alternative Energy Supplier | Competitive pricing, potential for renewable energy options, more flexibility in plan customization | May have less established infrastructure, potentially less reliable service, limited customer service options |
| Community Choice Aggregation (CCA) | Competitive pricing, potential for renewable energy options, local community support | May have limited availability, potentially less established infrastructure, limited customer service options |
| Solar Energy | Environmentally friendly, long-term cost savings, potential for increased home value | High upfront costs, weather-dependent energy production, requires maintenance and repairs |
Final Summary: Compare Electricity Companies
By carefully considering your electricity needs, comparing plans, and evaluating providers, you can empower yourself to choose the right electricity company for your specific situation. Remember, finding the best deal is not just about saving money but also about aligning your energy choices with your values and contributing to a more sustainable future.
User Queries
How often should I compare electricity plans?
It’s recommended to compare plans at least once a year, or whenever your current plan is about to expire, to ensure you’re getting the best rate.
What are the best ways to reduce my electricity consumption?
Simple measures like using energy-efficient appliances, turning off lights when leaving a room, and unplugging electronics when not in use can significantly reduce your energy consumption.
Are there any government incentives for installing solar panels?
Yes, many governments offer tax credits and rebates for homeowners who install solar panels. Contact your local energy authority for more information.




