
Bachelors degree years – Bachelor’s degree years represent a pivotal period in an individual’s life, marking a significant step towards academic and professional aspirations. This journey involves navigating the complexities of curriculum, financial considerations, and the pursuit of knowledge.
From understanding the structure and duration of programs to exploring the benefits and alternatives, this guide delves into the multifaceted aspects of obtaining a bachelor’s degree, providing insights for those seeking to embark on this transformative educational path.
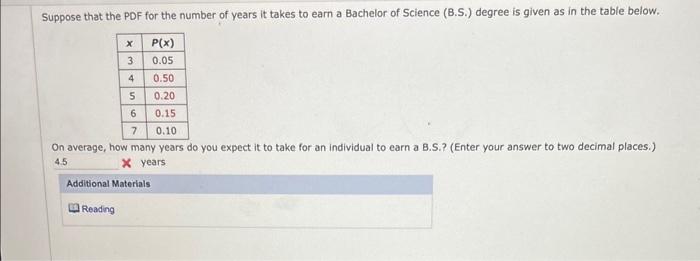
Duration of Bachelor’s Degree Programs: Bachelors Degree Years

A bachelor’s degree program is a standard undergraduate program pursued by students after completing their secondary education. The duration of these programs can vary significantly across different countries and institutions, influenced by several factors, such as the chosen field of study, the academic institution, and the course load.
Typical Duration in Various Countries
The duration of bachelor’s degree programs typically ranges from three to five years, depending on the country and the specific program.
- United States: Most bachelor’s degree programs in the United States take four years to complete, with some programs, such as engineering and architecture, requiring five years.
- Canada: Similar to the United States, bachelor’s degrees in Canada typically require four years of full-time study.
- United Kingdom: In the UK, bachelor’s degrees are typically three years long, although some programs, such as medicine and law, may take longer.
- Australia: Bachelor’s degrees in Australia usually require three years of full-time study, with some programs requiring four years.
- Europe: The duration of bachelor’s degree programs in Europe varies depending on the country and the specific program. In some countries, such as Germany and France, bachelor’s degrees can be completed in three years. However, in other countries, such as the Netherlands and Belgium, they may take four years.
Factors Influencing Program Duration
Several factors can influence the length of a bachelor’s degree program.
- Field of Study: Programs in certain fields, such as engineering, medicine, and law, often require more extensive coursework and practical experience, resulting in longer program durations.
- Academic Institution: The academic institution’s curriculum and requirements can also impact the length of a bachelor’s degree program. Some institutions may offer accelerated programs that allow students to graduate in a shorter period, while others may have more rigorous course requirements that extend the program duration.
- Course Load: The number of courses a student takes per semester can also affect the program duration. Students who take a heavier course load can potentially graduate sooner, while those who take a lighter course load may take longer to complete their degree.
Program Durations: Full-Time, Part-Time, and Accelerated
The duration of a bachelor’s degree program can also vary depending on the mode of study.
- Full-Time Programs: Full-time programs are designed for students who dedicate themselves to their studies full-time and typically take four years to complete in the United States and Canada.
- Part-Time Programs: Part-time programs are designed for students who work or have other commitments and study at a slower pace. Part-time programs can take longer to complete, often extending the program duration to five or six years.
- Accelerated Programs: Accelerated programs allow students to complete their bachelor’s degree in a shorter time frame. These programs typically involve taking a heavier course load or attending classes year-round, potentially shortening the program duration to three years.
Structure of Bachelor’s Degree Programs
A bachelor’s degree program is a structured educational journey designed to equip students with a comprehensive understanding of a specific field of study. This structure typically involves a set number of semesters or quarters, with each semester or quarter encompassing a defined period of academic instruction.
Course Credits and Program Completion, Bachelors degree years
Course credits are units of academic measurement used to quantify the amount of work required for a particular course. Each course carries a specific credit value, reflecting the time commitment and workload involved. The accumulation of these course credits is crucial for program completion.
A typical bachelor’s degree program requires a total of 120-130 semester credit hours or their equivalent in quarter credits.
Course Load for Full-Time Students
Full-time students typically enroll in a course load of 12-18 credit hours per semester. This translates to 3-4 courses per semester, depending on the credit value of each course. This workload allows students to make significant progress toward their degree while maintaining a balance between academic pursuits and other commitments.
Academic Requirements for a Bachelor’s Degree
Earning a bachelor’s degree involves completing a set of academic requirements designed to provide a comprehensive and well-rounded educational experience. These requirements typically encompass general education courses, major-specific coursework, and elective courses, each serving a distinct purpose in shaping a student’s knowledge and skills.
General Education Courses
General education courses, often referred to as core courses, are designed to provide students with a broad foundation in various disciplines, fostering critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving skills. These courses typically cover areas such as:
- Humanities: Literature, history, philosophy, and the arts, fostering critical analysis, cultural understanding, and communication skills.
- Social Sciences: Psychology, sociology, economics, and political science, developing an understanding of human behavior, social structures, and global issues.
- Natural Sciences: Biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics, cultivating scientific literacy, analytical thinking, and problem-solving abilities.
- Communication: Writing, public speaking, and communication skills, enhancing effective expression and critical analysis.
Major-Specific Coursework
Major-specific coursework forms the core of a bachelor’s degree program, providing in-depth knowledge and skills within a chosen field of study. These courses delve into the theoretical foundations, practical applications, and contemporary trends within the major.
- Examples:
- Computer Science: Programming languages, data structures, algorithms, software engineering, and computer architecture.
- Business Administration: Accounting, finance, marketing, management, and organizational behavior.
- Biology: Cell biology, genetics, evolution, ecology, and microbiology.
Electives
Electives provide students with the opportunity to explore areas of interest outside their major, broadening their horizons and developing new skills. They can be chosen from a variety of disciplines, allowing students to pursue personal passions, explore new fields, or acquire specialized knowledge relevant to their career goals.
- Examples:
- A business major might choose electives in art history, creative writing, or foreign language to enhance their communication and cultural understanding.
- A biology major might take electives in environmental science, bioethics, or public health to broaden their knowledge and explore related fields.
Financial Considerations for a Bachelor’s Degree
Pursuing a bachelor’s degree is a significant investment, and understanding the associated costs is crucial for planning and budgeting. This section delves into the various financial aspects of obtaining a bachelor’s degree, covering tuition fees, living expenses, and other expenses, as well as exploring different funding options to help offset these costs.
Tuition Fees
Tuition fees are the primary expense associated with a bachelor’s degree. Tuition fees vary significantly depending on the institution, program, and state of residence. Public universities generally have lower tuition rates than private institutions. Some universities also charge additional fees for specific courses or programs, such as laboratory fees or technology fees.
Living Expenses
Living expenses are another significant financial consideration for students pursuing a bachelor’s degree. These expenses include housing, food, transportation, and personal expenses. The cost of living varies greatly depending on the location of the university. Students attending universities in major metropolitan areas typically face higher living expenses than those attending universities in rural areas.
Books and Other Materials
Textbooks and other course materials are essential for academic success. The cost of books can vary significantly depending on the course and the publisher. Some universities offer affordable textbook rental programs or digital access options to help students save money.
Financial Aid Options
There are various financial aid options available to help students finance their bachelor’s degree. These options include scholarships, grants, loans, and work-study programs.
Scholarships
Scholarships are free money that students do not have to repay. Scholarships are awarded based on academic merit, extracurricular activities, financial need, or other criteria. Students can search for scholarships through online databases, their university’s financial aid office, and private organizations.
Grants
Grants are similar to scholarships in that they are free money that students do not have to repay. Grants are typically awarded based on financial need. Students can apply for federal, state, and institutional grants through their university’s financial aid office.
Loans
Loans are borrowed money that students must repay with interest. There are two main types of loans: federal loans and private loans. Federal loans generally have lower interest rates and more flexible repayment options than private loans. Students can apply for federal loans through the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA).
Work-Study Programs
Work-study programs allow students to earn money while working part-time jobs on campus. These jobs are typically related to the student’s field of study or the university’s operations. Students can apply for work-study programs through their university’s financial aid office.
Resources for Exploring Financial Aid Opportunities
Students can utilize various resources to explore financial aid opportunities. These resources include:
- Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA): The FAFSA is the primary application for federal student aid, including grants, loans, and work-study programs. Students can complete the FAFSA online at the Federal Student Aid website.
- University Financial Aid Office: Each university has a financial aid office that provides information about scholarships, grants, loans, and work-study programs available to students.
- Online Scholarship Databases: Several online databases, such as Scholarship America, Fastweb, and Cappex, allow students to search for scholarships based on their criteria.
- Private Organizations: Many private organizations offer scholarships to students pursuing specific fields of study or with specific characteristics.
Benefits of a Bachelor’s Degree
A bachelor’s degree is a valuable investment that can open doors to a wide range of opportunities and significantly impact your future. Earning a bachelor’s degree can lead to increased earning potential, career advancement opportunities, and personal growth.
Impact on Employability and Career Satisfaction
A bachelor’s degree can significantly improve your chances of finding employment and securing a rewarding career. Employers often prefer candidates with a bachelor’s degree, as it demonstrates a commitment to education, a strong work ethic, and a foundation of knowledge and skills. Studies show that individuals with a bachelor’s degree have higher employment rates and earn significantly more than those with only a high school diploma.
Increased Earning Potential
A bachelor’s degree can lead to a higher earning potential throughout your career. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, workers with a bachelor’s degree earn, on average, about 67% more than those with only a high school diploma. This difference in earning potential can have a significant impact on your financial security and quality of life.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Many professions require a bachelor’s degree for entry-level positions and advancement opportunities. A bachelor’s degree provides you with the specialized knowledge and skills needed to succeed in your chosen field. It also demonstrates your ability to learn, adapt, and solve problems, making you a more desirable candidate for promotions and leadership roles.
Personal Growth and Development
Beyond career benefits, a bachelor’s degree can also contribute to your personal growth and development. The process of earning a bachelor’s degree challenges you intellectually, expands your knowledge base, and helps you develop critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving skills. These skills are valuable not only in the workplace but also in your personal life.
Professions That Typically Require a Bachelor’s Degree
A wide range of professions typically require a bachelor’s degree for entry-level positions. Here are a few examples:
- Healthcare: Doctors, nurses, pharmacists, physical therapists, and other healthcare professionals require a bachelor’s degree or higher.
- Engineering: Civil, mechanical, electrical, and chemical engineers typically need a bachelor’s degree in engineering.
- Business and Finance: Accountants, financial analysts, and management consultants often require a bachelor’s degree in business or a related field.
- Education: Teachers, professors, and school administrators typically need a bachelor’s degree in education or a related field.
- Technology: Software developers, computer programmers, and network administrators often require a bachelor’s degree in computer science or a related field.
- Law: Lawyers need a bachelor’s degree and a Juris Doctor (JD) degree from law school.
Alternatives to a Traditional Bachelor’s Degree
While a traditional four-year bachelor’s degree is the most common pathway to higher education, there are several alternative options available that can lead to a bachelor’s degree. These alternative pathways can be more flexible, affordable, and convenient for students with diverse needs and circumstances.
Alternative pathways to a bachelor’s degree can provide flexibility in terms of scheduling, cost, and program structure. They offer opportunities for individuals with prior learning or work experience to earn a degree more efficiently.
Associate Degrees
An associate degree is a two-year degree that can be earned at a community college or technical school. Associate degrees can be a stepping stone to a bachelor’s degree. They are often more affordable than bachelor’s degrees and can provide students with specialized skills in a particular field.
Many associate degrees are transferable to four-year institutions, allowing students to complete their bachelor’s degree in less time and at a lower cost. Students who earn an associate degree can transfer their credits to a four-year institution and complete their bachelor’s degree in two years or less.
Advantages of Associate Degrees
- Lower cost compared to a four-year bachelor’s degree.
- Shorter program length, typically two years.
- Focus on specialized skills in a particular field.
- Transferable credits to four-year institutions.
Disadvantages of Associate Degrees
- May not be as widely recognized as a bachelor’s degree.
- May limit career advancement opportunities in some fields.
Online Programs
Online bachelor’s degree programs offer students the flexibility to learn at their own pace and on their own schedule. They can be a good option for students who have work or family commitments or who live in remote locations.
Advantages of Online Programs
- Flexibility to study at your own pace and on your own schedule.
- Accessibility to students who live in remote locations or have work or family commitments.
- Wide range of program options available.
Disadvantages of Online Programs
- May require strong self-discipline and motivation.
- May lack the face-to-face interaction and networking opportunities of traditional programs.
- May not be as well-suited for hands-on or laboratory-based programs.
Accelerated Programs
Accelerated bachelor’s degree programs allow students to complete their degree in less than four years. These programs typically involve taking more courses per semester or attending classes year-round.
Advantages of Accelerated Programs
- Shorter program length, allowing students to graduate sooner.
- Can save time and money on tuition.
Disadvantages of Accelerated Programs
- May require a higher workload and more intense study schedule.
- May not be suitable for all students, especially those with work or family commitments.
Examples of Institutions that Offer Alternative Degree Programs
Many institutions offer alternative degree programs, including:
- Community colleges: Often offer associate degrees and transfer programs.
- Online universities: Offer a wide range of online bachelor’s degree programs.
- Traditional universities: May offer accelerated or evening programs.
Epilogue

Earning a bachelor’s degree is a valuable investment in one’s future, opening doors to diverse career opportunities and personal growth. Whether pursuing a traditional program or exploring alternative pathways, the journey to a bachelor’s degree is a testament to dedication, perseverance, and the pursuit of knowledge. As you navigate this path, remember the wealth of resources available to support your success, from financial aid options to career guidance and mentorship.
User Queries
How long does it typically take to earn a bachelor’s degree?
The typical duration of a bachelor’s degree program is four years for full-time students. However, factors such as program type, academic institution, and course load can influence the length.
What are some common career paths that require a bachelor’s degree?
Many professions, including healthcare, engineering, education, business, and law, typically require a bachelor’s degree for entry-level positions.
What are some financial aid options available for students pursuing a bachelor’s degree?
Students can explore various financial aid options, including scholarships, grants, loans, and work-study programs. Resources such as the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) can assist in identifying potential funding sources.




