
- Definition of a Bachelor’s Degree
- Purpose and Benefits of a Bachelor’s Degree
- Requirements for Earning a Bachelor’s Degree
- Choosing a Bachelor’s Degree Program
- Career Opportunities with a Bachelor’s Degree
- Continuing Education After a Bachelor’s Degree
- Final Summary: Bachelor’s Degree What Is
- User Queries
Bachelor’s degree what is – Bachelor’s Degree: What Is It? This phrase, a simple question, holds the key to unlocking a world of possibilities. It’s a stepping stone to countless careers, a pathway to personal growth, and a foundation for a brighter future. But what exactly is a bachelor’s degree, and what makes it so valuable?
A bachelor’s degree is a post-secondary academic qualification awarded by universities and colleges around the world. It typically involves a minimum of three to four years of full-time study, depending on the program and institution. The purpose of a bachelor’s degree is to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of a specific field of study, equipping them with the knowledge, skills, and critical thinking abilities necessary for success in their chosen careers.
Definition of a Bachelor’s Degree
A bachelor’s degree is a foundational academic qualification awarded by universities and colleges upon successful completion of an undergraduate program. It signifies a student’s mastery of a specific field of study and their readiness for advanced education or professional careers.
A bachelor’s degree is typically pursued after completing high school or equivalent secondary education. It serves as a stepping stone for individuals seeking to further their knowledge, develop critical thinking skills, and prepare for diverse career paths.
Types of Bachelor’s Degrees
Bachelor’s degrees are awarded in various disciplines, each tailored to specific areas of study. Some common types of bachelor’s degrees include:
- Bachelor of Arts (BA): This degree is typically awarded in humanities and social science fields, such as English, history, psychology, and sociology. BA programs emphasize critical thinking, communication skills, and a broad understanding of diverse perspectives.
- Bachelor of Science (BS): This degree is commonly awarded in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields. BS programs focus on scientific principles, analytical methods, and practical applications.
- Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA): This degree is awarded in creative fields like art, design, music, and theatre. BFA programs emphasize artistic development, technical skills, and creative expression.
Duration and Course Structure, Bachelor’s degree what is
The duration of a bachelor’s degree program varies depending on the institution and the specific field of study. In most cases, a bachelor’s degree requires four years of full-time study. Some programs may be completed in three years or less, while others may require more than four years.
The course structure of a bachelor’s degree program typically follows a credit-based system. Students are required to complete a specific number of credits by taking various courses within their chosen major and electives. The curriculum is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the chosen field and to develop essential skills and knowledge.
Purpose and Benefits of a Bachelor’s Degree
A bachelor’s degree is a valuable investment in your future, offering a wide range of opportunities and benefits. It’s a significant step towards achieving personal and professional goals, equipping you with the knowledge, skills, and credentials to succeed in today’s competitive job market.
Career Advancement and Earning Potential
A bachelor’s degree is often a requirement for entry-level positions in many industries. It demonstrates your commitment to learning, your ability to think critically, and your capacity to solve complex problems. A bachelor’s degree opens doors to a wider range of career options, allowing you to pursue specialized fields and advance within your chosen profession.
The financial benefits of a bachelor’s degree are undeniable. Studies consistently show that individuals with a bachelor’s degree earn significantly more over their lifetime compared to those with only a high school diploma or an associate degree. This increased earning potential translates to a higher standard of living, greater financial security, and the ability to achieve your financial goals.
“According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, workers with a bachelor’s degree earn, on average, 67% more than those with only a high school diploma.”
Personal Growth and Development
Pursuing a bachelor’s degree is a transformative experience that fosters personal growth and development. It challenges you to think critically, develop your communication skills, and expand your knowledge base. You’ll learn how to research effectively, analyze information, and present your ideas persuasively. These skills are invaluable not only in the workplace but also in your personal life.
A bachelor’s degree also provides you with the opportunity to explore your interests, discover new passions, and broaden your horizons. You’ll meet people from diverse backgrounds, learn about different cultures, and gain a deeper understanding of the world around you.
Comparison to Other Educational Pathways
While a bachelor’s degree offers numerous advantages, it’s important to consider other educational pathways, such as vocational training or associate degrees. Vocational training provides specialized skills for specific trades or industries, and can be a good option for those seeking immediate employment. Associate degrees offer a more focused curriculum than a bachelor’s degree, and can be a stepping stone to a bachelor’s degree or a direct pathway to certain careers.
The best educational path for you depends on your individual goals, interests, and circumstances. A bachelor’s degree is a highly valued credential that opens doors to a wide range of opportunities, but other educational pathways may be more suitable for some individuals.
Requirements for Earning a Bachelor’s Degree
Earning a bachelor’s degree is a significant accomplishment that requires dedication, hard work, and meeting specific requirements. Universities have established guidelines to ensure a consistent standard of education and prepare graduates for their chosen fields.
Admission Requirements
To be admitted into a bachelor’s degree program, prospective students typically need to meet certain academic prerequisites and standardized test scores.
Academic Prerequisites
- High School Diploma or Equivalent: A high school diploma or its equivalent, such as a General Educational Development (GED) certificate, is usually the minimum requirement. This demonstrates a foundational level of academic preparedness.
- Minimum GPA: Most universities have a minimum GPA requirement, typically ranging from 2.0 to 3.5, depending on the institution and program. A higher GPA indicates strong academic performance and increases the chances of admission.
- Specific Coursework: Certain programs may require specific high school courses, such as math, science, English, or foreign language. These prerequisites ensure that students have a solid foundation in relevant subjects.
Standardized Test Scores
- SAT or ACT: The Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT) or the American College Testing (ACT) are standardized tests widely used for college admissions. Scores on these tests provide an objective measure of a student’s readiness for college-level work. Some universities require these scores, while others may consider them optional.
- Subject-Specific Tests: Depending on the program, additional standardized tests may be required, such as the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) for graduate programs or the Law School Admission Test (LSAT) for law school.
Core Curriculum and Elective Courses
Once admitted, students must complete a specific set of courses to earn a bachelor’s degree. These courses typically include a core curriculum and elective courses.
Core Curriculum
- General Education Courses: These courses provide a broad foundation in different disciplines, such as humanities, social sciences, natural sciences, and communication. Examples include English composition, history, mathematics, and psychology.
- Major-Specific Courses: These courses delve deeper into the student’s chosen field of study, providing specialized knowledge and skills. For example, a computer science major might take courses in programming, data structures, and algorithms.
Elective Courses
- Free Electives: These courses allow students to explore areas of interest outside their major. They can choose from a wide range of subjects, such as art, music, foreign languages, or philosophy.
- Major Electives: Some programs offer elective courses within the major, allowing students to specialize in specific areas. For instance, a biology major might choose electives in genetics, ecology, or microbiology.
Methods of Assessment
To evaluate student learning, universities employ various methods of assessment, including exams, assignments, and projects.
Exams
- Midterm and Final Exams: These exams assess students’ understanding of course material covered throughout the semester. They typically involve multiple-choice, true/false, short-answer, or essay questions.
- Quizzes: Quizzes are shorter assessments that focus on specific topics or concepts covered in class. They can be used to gauge student comprehension and provide feedback on their progress.
Assignments
- Essays: Essays require students to analyze, synthesize, and critically evaluate information. They assess writing skills, research abilities, and analytical thinking.
- Research Papers: Research papers involve in-depth exploration of a specific topic, requiring students to gather and synthesize information from various sources.
- Problem Sets: Problem sets provide students with opportunities to apply theoretical concepts to real-world situations. They assess problem-solving skills and understanding of course material.
Projects
- Group Projects: Group projects allow students to collaborate and work together on a shared goal. They assess teamwork skills, communication abilities, and problem-solving skills.
- Individual Projects: Individual projects provide students with the opportunity to demonstrate their creativity, innovation, and independent thinking. They can range from research projects to design projects or presentations.
Choosing a Bachelor’s Degree Program
Selecting the right bachelor’s degree program is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your future career and personal growth. Carefully considering your aspirations, interests, and goals is essential to ensure a fulfilling and successful academic journey.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Bachelor’s Degree Program
When choosing a bachelor’s degree program, several factors should be taken into account to ensure a good fit. These include:
- Career Aspirations: Determine your career goals and research the educational requirements and skills needed for your desired profession. Some careers may require specific degrees, while others may accept a broader range of programs. For example, if you aspire to be a software engineer, a computer science degree would be a suitable choice.
- Interests: Choose a program that aligns with your passions and interests. Studying a subject you enjoy will make the learning process more engaging and rewarding. For instance, if you are passionate about environmental issues, an environmental science degree might be a good fit.
- Personal Goals: Consider your personal goals and how a bachelor’s degree can help you achieve them. Whether you want to pursue further education, start a business, or simply expand your knowledge base, choose a program that supports your aspirations.
- Job Prospects: Research the job market and explore the employment opportunities available for graduates with the degree you are considering. Factors such as industry demand, salary potential, and career growth opportunities should be considered.
- Program Curriculum: Review the course offerings and curriculum of the program to ensure it covers the topics and skills that are relevant to your career aspirations. Look for programs that provide a strong foundation in the core subjects and offer elective courses that align with your interests.
- Faculty and Resources: Consider the reputation and expertise of the faculty, as well as the availability of resources such as libraries, laboratories, and career services. A strong faculty and supportive resources can enhance your learning experience and career prospects.
- Location and Campus Culture: The location and campus culture of the institution can also influence your decision. Consider factors such as proximity to your home, the size of the campus, and the overall learning environment.
Comparison of Bachelor’s Degree Programs
Here is a table comparing different bachelor’s degree programs based on key criteria:
| Program | Job Prospects | Salary Expectations | Required Coursework |
|---|---|---|---|
| Computer Science | High | High | Programming, data structures, algorithms, software engineering |
| Business Administration | Moderate | Moderate | Accounting, finance, marketing, management |
| Nursing | High | Moderate | Anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, nursing practice |
| Education | Moderate | Moderate | Child development, curriculum design, teaching methods |
| Engineering | High | High | Physics, mathematics, calculus, engineering principles |
Researching and Choosing a Bachelor’s Degree Program
The process of researching and choosing a bachelor’s degree program can be broken down into the following steps:
Step 1: Self-Assessment: Identify your career aspirations, interests, and personal goals.
Step 2: Research Potential Programs: Explore different degree programs that align with your interests and career goals.
Step 3: Compare Program Options: Evaluate programs based on factors such as job prospects, salary expectations, curriculum, faculty, and resources.
Step 4: Visit Campuses: If possible, visit the campuses of the institutions you are considering to get a firsthand feel for the learning environment and culture.
Step 5: Make a Decision: Based on your research and evaluation, choose the program that best fits your needs and aspirations.
Career Opportunities with a Bachelor’s Degree
A bachelor’s degree is a valuable asset in today’s competitive job market. It opens doors to a wide range of career paths and enhances earning potential.
A bachelor’s degree equips individuals with the knowledge, skills, and critical thinking abilities sought after by employers across various industries.
Industries and Occupations
A bachelor’s degree is often a requirement for entry-level positions and advancement opportunities in numerous industries. Some common industries that require a bachelor’s degree include:
- Healthcare: Nurses, doctors, pharmacists, physical therapists, and other healthcare professionals require a bachelor’s degree or higher.
- Business and Finance: Accountants, financial analysts, marketing managers, and business development professionals typically need a bachelor’s degree in business administration or a related field.
- Technology: Software engineers, data analysts, web developers, and cybersecurity professionals often have a bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field.
- Education: Teachers, professors, and educational administrators typically hold a bachelor’s degree in education or a related field.
- Law: Lawyers and paralegals require a bachelor’s degree and often a Juris Doctor (JD) degree for legal practice.
- Government and Public Service: Positions in government agencies, non-profit organizations, and public service often require a bachelor’s degree in public administration, political science, or a related field.
Career Options by Degree
Here is a table listing some common bachelor’s degrees and their corresponding career options, including job titles and average salaries:
| Bachelor’s Degree | Career Options | Average Salary (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Business Administration | Accountant, Financial Analyst, Marketing Manager, Business Development Manager | $65,000 – $100,000 |
| Computer Science | Software Engineer, Data Analyst, Web Developer, Cybersecurity Analyst | $80,000 – $150,000 |
| Education | Teacher, Professor, School Administrator | $45,000 – $80,000 |
| Engineering | Civil Engineer, Mechanical Engineer, Electrical Engineer, Chemical Engineer | $70,000 – $120,000 |
| Nursing | Registered Nurse, Nurse Practitioner, Certified Nursing Assistant | $60,000 – $100,000 |
| Psychology | Psychologist, Social Worker, Counselor, Human Resources Manager | $50,000 – $85,000 |
Continuing Education After a Bachelor’s Degree

A bachelor’s degree is a valuable accomplishment, but it can be just the beginning of your educational journey. Many individuals choose to pursue further education after earning their bachelor’s degree, seeking to enhance their knowledge, skills, and career prospects.
There are various options for continuing education after obtaining a bachelor’s degree, each offering unique benefits and challenges.
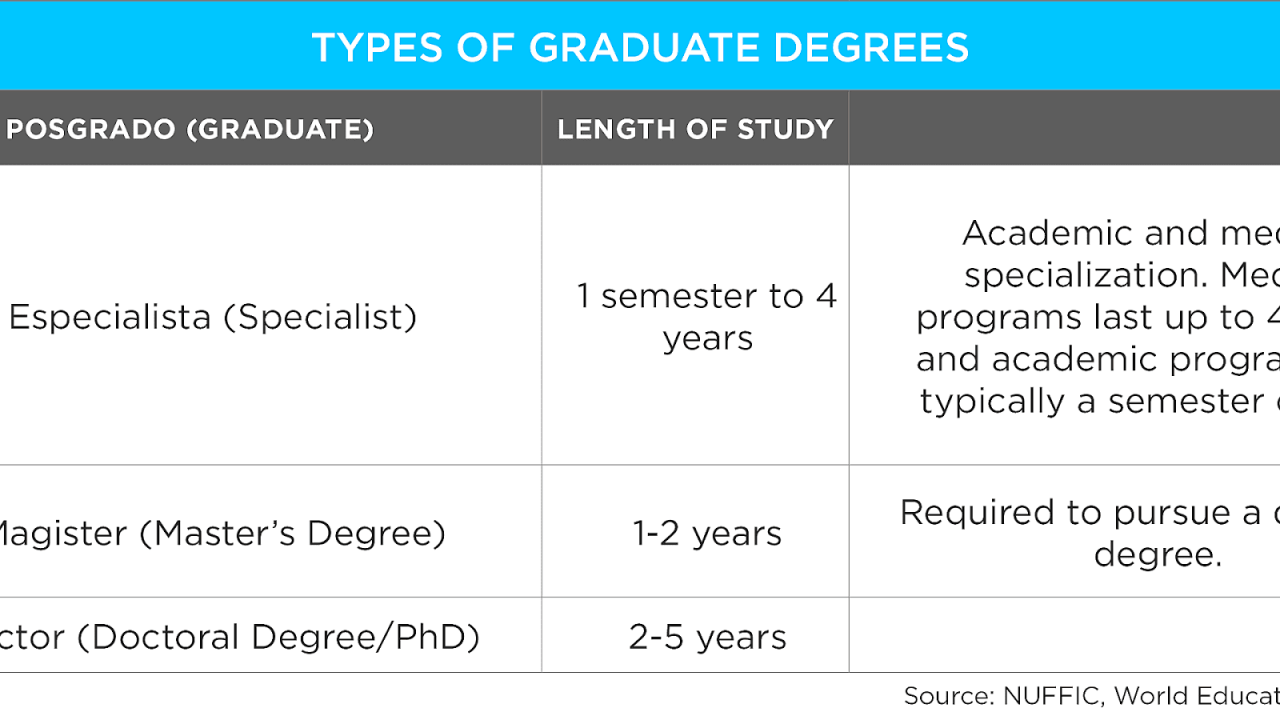
Master’s Programs
Master’s programs provide specialized knowledge and advanced skills in a specific field of study. They typically require two years of full-time study and involve coursework, research, and often a thesis or capstone project.
Benefits of Pursuing a Master’s Degree
- Increased earning potential: Master’s degree holders often earn higher salaries than those with only a bachelor’s degree.
- Enhanced career opportunities: A master’s degree can open doors to more senior positions and leadership roles.
- Specialized knowledge and skills: Master’s programs provide in-depth knowledge and specialized skills that can make you more competitive in the job market.
- Networking opportunities: Master’s programs offer opportunities to connect with other professionals in your field.
Challenges of Pursuing a Master’s Degree
- Time commitment: Master’s programs require significant time and effort.
- Financial cost: Master’s programs can be expensive, with tuition fees and living expenses.
- Rigorous coursework: Master’s programs involve challenging coursework and research.
Examples of Master’s Programs
- Master of Business Administration (MBA): This program is designed for individuals seeking careers in management, finance, and consulting.
- Master of Science (MS) in Engineering: This program provides advanced knowledge and skills in specific engineering disciplines.
- Master of Arts (MA) in Education: This program prepares individuals for careers in teaching, curriculum development, and educational administration.
Professional Certifications
Professional certifications demonstrate specialized knowledge and skills in a particular field. They are often required or preferred for specific jobs and can enhance your credibility and marketability.
Benefits of Pursuing Professional Certifications
- Increased earning potential: Professionals with certifications often earn higher salaries than those without.
- Enhanced career opportunities: Certifications can open doors to more senior positions and leadership roles.
- Specialized knowledge and skills: Certifications demonstrate specialized knowledge and skills that can make you more competitive in the job market.
- Networking opportunities: Professional organizations often offer networking events and resources for certified professionals.
Challenges of Pursuing Professional Certifications
- Time commitment: Preparing for and taking certification exams can require significant time and effort.
- Financial cost: Certification programs and exams can be expensive.
- Continuing education requirements: Many certifications require ongoing education and recertification to maintain validity.
Examples of Professional Certifications
- Certified Public Accountant (CPA): This certification is required for individuals who want to work as accountants or auditors.
- Project Management Professional (PMP): This certification is for professionals who manage projects and have demonstrated expertise in project management methodologies.
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): This certification is for individuals who work in cybersecurity and have expertise in information security.
Doctoral Degrees
Doctoral degrees, such as a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) or Doctor of Education (EdD), are the highest level of academic achievement. They involve rigorous research and scholarly work and typically require four to seven years of full-time study.
Benefits of Pursuing a Doctoral Degree
- Advanced knowledge and skills: Doctoral programs provide in-depth knowledge and advanced skills in a specific field of study.
- Research opportunities: Doctoral programs offer opportunities to conduct original research and contribute to the advancement of knowledge.
- Teaching and research positions: Doctoral degrees are often required for teaching and research positions at universities and colleges.
- Expertise and credibility: Doctoral degree holders are recognized as experts in their field and have high credibility.
Challenges of Pursuing a Doctoral Degree
- Time commitment: Doctoral programs require significant time and effort, often involving years of full-time study.
- Financial cost: Doctoral programs can be expensive, with tuition fees and living expenses.
- Rigorous coursework and research: Doctoral programs involve challenging coursework, research, and a dissertation.
- Competition for funding and positions: There is often intense competition for funding and research positions in academia.
Examples of Doctoral Programs
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Biology: This program prepares individuals for careers in research, teaching, and academia.
- Doctor of Education (EdD) in Educational Leadership: This program prepares individuals for leadership roles in education, such as school administration or policy development.
- Doctor of Medicine (MD): This program prepares individuals for careers as physicians.
Final Summary: Bachelor’s Degree What Is
In conclusion, a bachelor’s degree is a transformative investment in your future. It opens doors to exciting career opportunities, enhances earning potential, and fosters personal growth. Whether you aspire to become a doctor, engineer, artist, or entrepreneur, a bachelor’s degree can provide you with the necessary foundation to achieve your dreams. As you navigate the world of higher education, remember that a bachelor’s degree is not just a piece of paper; it’s a testament to your dedication, perseverance, and intellectual curiosity.
User Queries
What are the different types of bachelor’s degrees?
There are many types of bachelor’s degrees, including Bachelor of Arts (BA), Bachelor of Science (BS), Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA), and many others, depending on the field of study.
How do I choose the right bachelor’s degree program for me?
Consider your interests, career goals, and personal strengths when choosing a bachelor’s degree program. Research different programs and talk to professionals in your field of interest.
What are the admission requirements for a bachelor’s degree program?
Admission requirements vary by institution and program. Typically, you’ll need a high school diploma or equivalent, a certain GPA, and standardized test scores like the SAT or ACT.
Can I get a job without a bachelor’s degree?
While some jobs may not require a bachelor’s degree, having one can significantly increase your earning potential and career options.




