
Bachelor’s degree meaning extends far beyond a piece of paper; it signifies a culmination of dedication, intellectual pursuit, and a stepping stone to a fulfilling career. This academic milestone, rooted in centuries of tradition, serves as a testament to an individual’s knowledge and skills, opening doors to diverse professional paths and enriching personal growth.
The bachelor’s degree, a cornerstone of higher education, has evolved over time to encompass a vast array of disciplines. From the humanities to STEM fields, these programs provide a comprehensive foundation in theory and practice, preparing graduates for a competitive job market and a world of possibilities.
Career Paths and Industries
A bachelor’s degree opens doors to a wide array of career paths across numerous industries. This qualification serves as a foundation for specialized knowledge and skills, making graduates highly competitive in the job market.
Career Paths Available to Bachelor’s Degree Holders
A bachelor’s degree equips individuals with the necessary knowledge and skills to pursue a variety of career paths. These paths can be broadly categorized based on the specific field of study.
- Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM): STEM fields offer diverse career options, including software development, data analysis, research, and engineering roles.
- Business and Finance: Graduates with business degrees can pursue careers in management, marketing, finance, accounting, and consulting.
- Healthcare: Bachelor’s degrees in healthcare fields, such as nursing, pharmacy, and public health, prepare individuals for roles in hospitals, clinics, and research institutions.
- Education: Bachelor’s degrees in education qualify individuals to become teachers, educators, and curriculum developers.
- Arts and Humanities: Degrees in the arts and humanities can lead to careers in writing, journalism, museum work, and the creative industries.
- Social Sciences: Bachelor’s degrees in social sciences, such as psychology, sociology, and political science, prepare individuals for careers in research, social work, and policy analysis.
Industries That Commonly Require or Prefer Bachelor’s Degrees
A wide range of industries often require or prefer candidates with bachelor’s degrees. These industries include:
- Technology: The tech industry, driven by innovation and complex problem-solving, highly values candidates with STEM backgrounds and bachelor’s degrees.
- Finance and Banking: The financial sector requires individuals with strong analytical and problem-solving skills, often seeking candidates with degrees in finance, accounting, or economics.
- Healthcare: The healthcare industry relies on qualified professionals with bachelor’s degrees in nursing, pharmacy, and other related fields.
- Education: Teaching positions at various levels, from elementary to higher education, typically require a bachelor’s degree in education or a related field.
- Government and Public Service: Government agencies and public service organizations often require bachelor’s degrees for various roles, including policy analysis, administration, and research.
- Research and Development: Industries engaged in research and development, such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and energy, frequently seek candidates with advanced degrees, including bachelor’s degrees in STEM fields.
Career Options by Degree Type and Industry, Bachelor’s degree meaning
| Degree Type | Industry | Career Options |
|---|---|---|
| Computer Science | Technology | Software Engineer, Data Scientist, Web Developer, Cybersecurity Analyst |
| Business Administration | Finance | Financial Analyst, Investment Banker, Management Consultant |
| Nursing | Healthcare | Registered Nurse, Nurse Practitioner, Nurse Educator |
| Education | Education | Teacher, Curriculum Developer, Educational Researcher |
| Political Science | Government and Public Service | Policy Analyst, Political Strategist, Public Relations Specialist |
Further Education and Advancement
A bachelor’s degree is a valuable accomplishment, but it often serves as a stepping stone to further education and career advancement. Many individuals choose to pursue advanced degrees after completing their bachelor’s, opening doors to specialized fields, leadership roles, and higher earning potential.
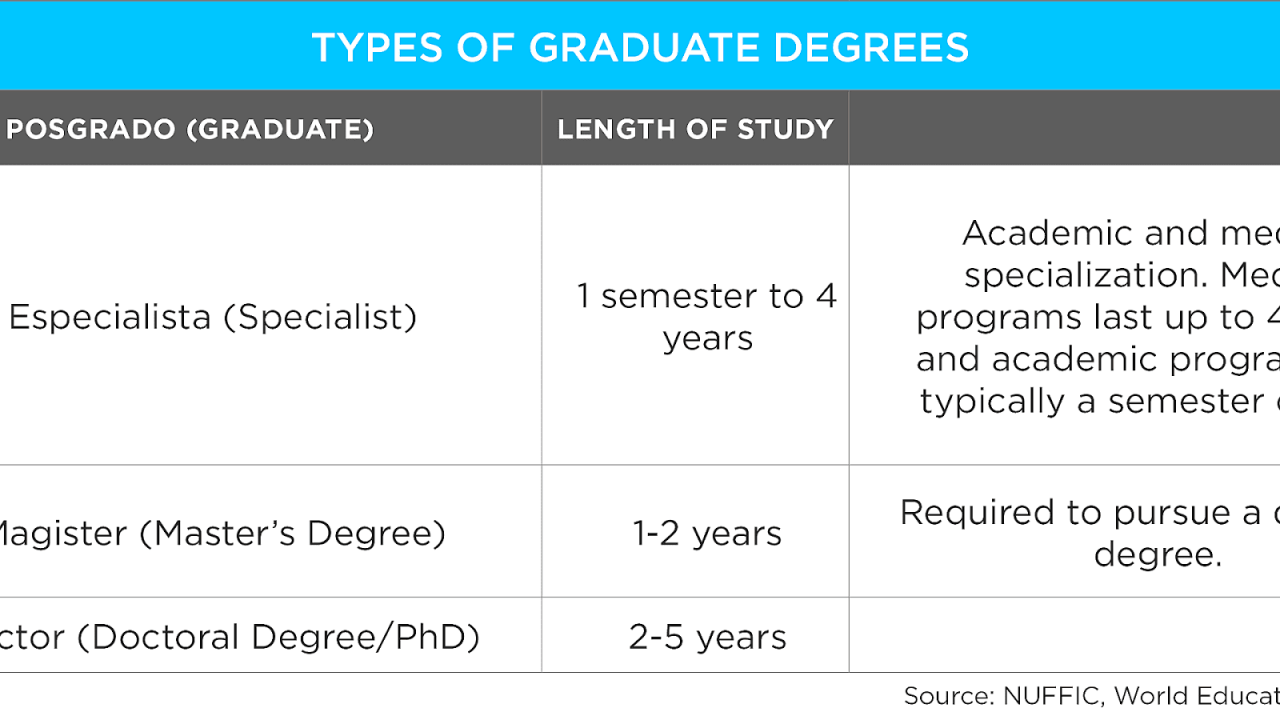
Paths to Advanced Degrees
Pursuing higher education after a bachelor’s degree involves various pathways, each leading to different types of degrees and career opportunities.
Master’s Degrees
Master’s degrees are designed to deepen knowledge and skills in a specific field, providing specialized training and advanced research experience. They are typically pursued after a bachelor’s degree and can be obtained in various disciplines, such as business, engineering, education, and the arts.
- Master of Arts (M.A.): Typically awarded in humanities and social sciences fields, focusing on research, critical thinking, and writing skills.
- Master of Science (M.S.): Commonly awarded in STEM fields, emphasizing scientific inquiry, technical skills, and applied knowledge.
- Master of Business Administration (MBA): A highly sought-after degree in business management, offering specialized training in areas like finance, marketing, and operations.
Doctoral Degrees
Doctoral degrees, such as the Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.), are the highest academic degrees, focusing on original research, scholarly contributions, and the development of expertise in a chosen field.
- Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.): The most common doctoral degree, typically requiring a dissertation based on original research and defense in front of a committee of experts.
- Doctor of Education (Ed.D.): Focuses on educational theory, research, and practice, often preparing individuals for leadership roles in education.
- Doctor of Jurisprudence (J.D.): A professional degree in law, preparing individuals for careers as lawyers, judges, or legal scholars.
Professional Degrees
Professional degrees are designed to prepare individuals for specific careers and are often required for entry into certain professions.
- Doctor of Medicine (M.D.): A professional degree in medicine, preparing individuals for careers as physicians.
- Doctor of Dental Surgery (D.D.S.): A professional degree in dentistry, preparing individuals for careers as dentists.
- Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D.): A professional degree in pharmacy, preparing individuals for careers as pharmacists.
Global Perspectives

A bachelor’s degree is a globally recognized qualification, but the structure and content of degree programs can vary significantly across countries. Understanding these differences is crucial for students considering international education or seeking employment in a globalized job market.
Comparison of Bachelor’s Degree Systems
The duration and structure of bachelor’s degrees can differ across countries. For example, in the United States, a bachelor’s degree typically takes four years to complete, while in some European countries, it may take three or even five years.
- United States: The American system is generally based on a liberal arts education, with a focus on broad-based learning and the development of critical thinking skills. Students typically choose a major and minor, and they are required to take a variety of courses in different disciplines.
- United Kingdom: The British system is more specialized, with students typically choosing a specific subject area from the outset. Degrees are often structured as three-year programs, with a strong emphasis on research and independent study.
- Germany: Germany’s system is known for its emphasis on practical training and work experience. Students often complete a dual-track program, combining academic study with a paid apprenticeship or internship.
International Recognition and Transferability
Bachelor’s degrees are generally recognized internationally, but the extent of recognition can vary depending on the specific country and institution. Some countries have established agreements for the mutual recognition of qualifications, such as the Bologna Process in Europe.
- Bologna Process: This agreement aims to create a unified higher education system in Europe, making it easier for students to study and work across borders. It has standardized the structure of degrees, with the bachelor’s degree typically taking three years to complete.
- International Organizations: Organizations like the World Education Services (WES) and the International Association of Universities (IAU) provide evaluation services to assess the equivalence of foreign qualifications.
- Transferability: The transferability of credits from one institution to another can be complex, particularly when moving between countries. Students should research the specific policies of their chosen institution to understand the requirements for transferring credits.
Challenges and Opportunities for International Students
Pursuing a bachelor’s degree internationally can present both challenges and opportunities.
- Language Barriers: One of the most significant challenges for international students is language proficiency. Students may need to demonstrate their language skills through standardized tests like the TOEFL or IELTS.
- Cultural Differences: Adjusting to a new culture and academic environment can be challenging. International students may need to learn about the local customs, values, and expectations in the classroom.
- Financial Considerations: Studying abroad can be expensive, and international students may need to consider the cost of tuition, living expenses, and visa fees.
- Opportunities for Global Exposure: Studying abroad provides an opportunity to experience a different culture, broaden your horizons, and develop valuable global skills.
- Networking: International students have the opportunity to build relationships with students and faculty from around the world, which can be beneficial for their future careers.
Conclusive Thoughts: Bachelor’s Degree Meaning
In conclusion, understanding the meaning of a bachelor’s degree is paramount for individuals seeking to navigate the complexities of higher education and career development. This academic achievement represents a commitment to learning, a catalyst for personal and professional advancement, and a testament to the power of knowledge in shaping a successful future.
Detailed FAQs
What is the difference between a Bachelor of Arts (BA) and a Bachelor of Science (BS)?
A BA typically focuses on humanities, social sciences, and liberal arts, while a BS emphasizes science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
How long does it take to earn a bachelor’s degree?
A traditional bachelor’s degree typically takes four years of full-time study.
Is a bachelor’s degree required for all jobs?
While some professions require a bachelor’s degree, others may accept equivalent experience or certifications.
Can I earn a bachelor’s degree online?
Yes, many universities offer online bachelor’s degree programs.




