- What is a Bachelor of Accounting Degree?
- Career Paths with a Bachelor of Accounting Degree
- Benefits of Pursuing a Bachelor of Accounting Degree
- Skills and Qualities of Successful Accountants
- Accreditation and Professional Certifications
- The Role of Technology in Accounting: Bachelor Of Accounting Degree
- Choosing the Right Accounting Program
- Ultimate Conclusion
- Essential FAQs
A Bachelor of Accounting Degree is the cornerstone for a fulfilling career in finance, offering a solid foundation in financial principles, analysis, and reporting. This degree equips individuals with the essential knowledge and skills to navigate the complex world of accounting, opening doors to a wide range of opportunities in various industries.
From managing financial records and preparing tax returns to conducting audits and providing financial advice, accounting professionals play a vital role in the success of businesses and organizations. A Bachelor of Accounting Degree provides the necessary framework to understand financial statements, interpret financial data, and make informed financial decisions.
What is a Bachelor of Accounting Degree?
A Bachelor of Accounting degree is a highly sought-after undergraduate program that equips students with the essential knowledge and skills to navigate the complex world of finance and accounting. This degree is a gateway to various rewarding career paths in both the public and private sectors.
Nature and Scope of the Degree
A Bachelor of Accounting degree provides a comprehensive understanding of financial principles, accounting standards, and business operations. The curriculum covers a wide range of topics, including financial accounting, managerial accounting, auditing, taxation, and financial reporting. It also emphasizes the application of these concepts in real-world scenarios.
Core Knowledge and Skills
The program focuses on developing a strong foundation in accounting principles and their practical application. Students gain proficiency in:
- Financial Accounting: Recording, summarizing, and reporting financial transactions.
- Managerial Accounting: Using accounting information to support internal decision-making.
- Auditing: Evaluating and assessing the accuracy of financial statements.
- Taxation: Understanding tax laws and regulations and their impact on businesses.
- Financial Reporting: Preparing and analyzing financial statements for various stakeholders.
- Data Analysis and Interpretation: Utilizing data to identify trends, make informed decisions, and provide insights.
- Communication and Presentation Skills: Effectively communicating complex financial information to both technical and non-technical audiences.
- Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: Analyzing complex financial situations, identifying solutions, and making sound judgments.
- Ethics and Professionalism: Adhering to ethical principles and maintaining professional standards in the accounting profession.
Typical Coursework
A typical Bachelor of Accounting degree program includes a diverse range of courses, such as:
- Financial Accounting I & II: Introduces fundamental accounting principles and practices, covering topics like the accounting cycle, financial statements, and accounting standards.
- Managerial Accounting: Explores how accounting information is used to support internal decision-making, including cost accounting, budgeting, and performance analysis.
- Auditing: Covers the principles and practices of auditing, including audit planning, risk assessment, and audit procedures.
- Taxation: Provides an in-depth understanding of tax laws and regulations, including income tax, corporate tax, and sales tax.
- Financial Reporting: Focuses on the preparation and analysis of financial statements, including the statement of cash flows, statement of comprehensive income, and balance sheet.
- Business Law: Covers legal principles relevant to business operations, including contracts, torts, and corporate law.
- Statistics and Data Analysis: Develops skills in statistical analysis and data interpretation, essential for analyzing financial data and making informed decisions.
- Information Systems: Explores the use of technology in accounting and finance, including accounting software, databases, and data analytics tools.
- Ethics and Professionalism: Emphasizes ethical considerations and professional standards in the accounting profession.
Specialization Options
Many accounting programs offer specialization options to allow students to tailor their studies to their interests and career aspirations. Some common specialization areas include:
- Forensic Accounting: Investigating financial crimes and fraud, and providing expert testimony in legal proceedings.
- Management Accounting: Providing financial and operational support to businesses, including budgeting, cost analysis, and performance evaluation.
- Tax Accounting: Specializing in tax planning, preparation, and compliance for individuals and businesses.
- Auditing: Conducting independent audits of financial statements to ensure accuracy and compliance with accounting standards.
- Financial Analysis: Analyzing financial data to make investment recommendations, assess company performance, and evaluate risk.
Career Paths with a Bachelor of Accounting Degree
A Bachelor of Accounting degree opens doors to a wide range of career opportunities in various industries and organizations. Accounting graduates are highly sought after for their analytical, problem-solving, and communication skills, which are essential in today’s business world.
Public Accounting
Public accounting firms provide accounting services to a diverse range of clients, including businesses, individuals, and government agencies. These firms offer a variety of services, including auditing, tax preparation, financial advisory, and consulting. Public accounting roles often involve working with clients directly, analyzing their financial statements, and providing recommendations to improve their financial performance.
- Auditing: Auditors examine a company’s financial records to ensure they are accurate and compliant with accounting standards. They provide an independent opinion on the company’s financial statements, which is crucial for investors and other stakeholders.
- Taxation: Tax accountants specialize in helping clients comply with tax laws and regulations. They prepare tax returns, advise clients on tax planning strategies, and represent clients in tax audits.
- Advisory: Advisory services involve providing financial advice to clients on a wide range of issues, such as mergers and acquisitions, business valuations, and risk management.
Corporate Accounting
Corporate accounting roles are found within companies of all sizes, from small businesses to multinational corporations. Corporate accountants are responsible for managing the company’s financial records, preparing financial statements, and ensuring compliance with accounting standards. They work closely with other departments, such as sales, marketing, and operations, to provide financial information and support decision-making.
- Financial Accounting: Financial accountants are responsible for preparing financial statements, which are used by investors, creditors, and other stakeholders to assess the company’s financial performance.
- Cost Accounting: Cost accountants track the costs associated with producing goods or services. They help companies identify areas where they can reduce costs and improve profitability.
- Management Accounting: Management accountants provide financial information and analysis to managers to help them make informed decisions. They develop budgets, analyze financial performance, and identify opportunities for improvement.
Government and Non-profit Accounting
Government and non-profit organizations also employ accountants to manage their finances and ensure accountability. These roles may involve managing budgets, preparing financial reports, and conducting audits.
- Government Accounting: Government accountants work for federal, state, and local governments. They manage the government’s finances, prepare financial statements, and ensure compliance with accounting standards.
- Non-profit Accounting: Non-profit accountants work for organizations that provide public benefit, such as charities, hospitals, and educational institutions. They manage the organization’s finances, prepare financial statements, and ensure compliance with accounting standards.
Other Accounting Careers
A Bachelor of Accounting degree can also lead to careers in other fields, such as finance, investment banking, and consulting.
- Financial Analyst: Financial analysts analyze financial data to make investment recommendations. They may work for investment banks, hedge funds, or mutual funds.
- Investment Banker: Investment bankers advise companies on mergers and acquisitions, debt and equity financing, and other financial transactions.
- Management Consultant: Management consultants help businesses improve their operations and financial performance. They may specialize in accounting, finance, or other areas.
Benefits of Pursuing a Bachelor of Accounting Degree
A Bachelor of Accounting degree is a valuable investment that opens doors to numerous opportunities. The knowledge and skills gained from this program are highly sought after in the job market, leading to promising career paths and financial stability.
Financial Benefits of an Accounting Degree
Earning an accounting degree can significantly improve your financial well-being. The knowledge and skills gained in this program are highly sought after in the job market, leading to promising career paths and financial stability.
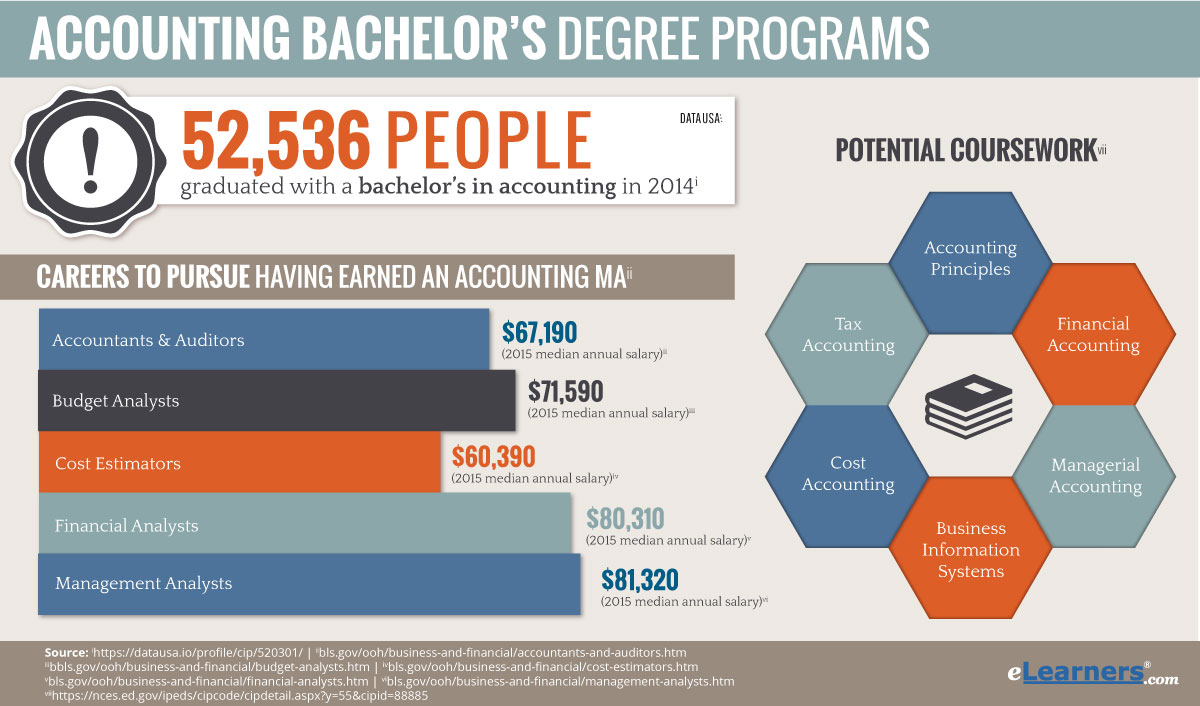
- Higher Starting Salaries: Accountants with a bachelor’s degree typically earn higher starting salaries compared to those with only a high school diploma or associate’s degree. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for accountants and auditors in 2022 was $77,250.
- Career Advancement Potential: An accounting degree provides a strong foundation for career advancement. With experience and additional certifications, you can progress into management roles, such as financial controller, chief financial officer (CFO), or even become a Certified Public Accountant (CPA). These positions often come with higher salaries and greater responsibilities.
- Job Security: The accounting profession is known for its job security. Even during economic downturns, businesses still need accountants to manage their finances. The demand for qualified accountants is expected to remain strong in the coming years, as businesses continue to rely on their expertise to navigate complex financial matters.
Skills and Qualities of Successful Accountants
Becoming a successful accountant requires a blend of technical expertise and personal attributes. While a strong foundation in accounting principles is essential, it’s the combination of hard and soft skills that truly sets successful accountants apart.
Essential Hard Skills
These are the technical skills that form the bedrock of accounting expertise.
- Financial Accounting: Understanding financial statements, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, is fundamental. Accountants analyze and interpret these statements to provide insights into a company’s financial health.
- Taxation: Accountants must navigate complex tax laws and regulations, ensuring compliance for individuals and businesses. This involves preparing tax returns, understanding tax implications of transactions, and advising clients on tax strategies.
- Auditing: This skill involves examining financial records to ensure accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. Auditors evaluate internal controls, identify potential risks, and provide assurance on the reliability of financial information.
- Accounting Software Proficiency: Familiarity with accounting software programs like QuickBooks, Xero, or SAP is crucial for efficient record-keeping, data analysis, and reporting.
- Analytical Skills: Accountants are problem solvers who use their analytical skills to identify trends, analyze financial data, and interpret complex information. They must be able to sift through large amounts of data to draw meaningful conclusions.
- Data Management: Effective data management is essential for accountants. This involves organizing, storing, and retrieving financial data efficiently, ensuring accuracy and integrity.
Importance of Soft Skills, Bachelor of accounting degree
While hard skills provide the technical foundation, soft skills are equally crucial for success in accounting.
- Communication: Accountants must be able to communicate financial information clearly and concisely, both verbally and in writing. They need to explain complex financial concepts to clients, colleagues, and stakeholders in a way that is easily understood.
- Problem-Solving: Accountants often face complex financial challenges. Strong problem-solving skills are essential for identifying issues, analyzing potential solutions, and implementing effective strategies.
- Teamwork: Accountants frequently collaborate with other professionals, such as lawyers, financial advisors, and business managers. Effective teamwork skills are crucial for working together to achieve common goals.
- Interpersonal Skills: Building strong relationships with clients, colleagues, and stakeholders is essential for an accountant’s success. Interpersonal skills, such as empathy, active listening, and diplomacy, help foster trust and cooperation.
Personal Qualities
Beyond hard and soft skills, certain personal qualities contribute significantly to a successful accounting career.
- Attention to Detail: Accountants work with numbers and financial data, requiring a high level of accuracy and attention to detail. Errors in accounting can have serious consequences, so meticulousness is essential.
- Integrity: Accountants are entrusted with sensitive financial information. Integrity is paramount, ensuring ethical conduct and upholding professional standards.
- Adaptability: The accounting field is constantly evolving, with new regulations, technologies, and industry trends emerging. Adaptable accountants are able to learn and adjust to these changes, staying ahead of the curve.
- Time Management: Accountants often face tight deadlines and manage multiple tasks simultaneously. Effective time management skills are crucial for prioritizing work, meeting deadlines, and avoiding burnout.
Accreditation and Professional Certifications

Earning a Bachelor of Accounting degree is a significant step towards a successful career in the field. However, to enhance your credentials and increase your job prospects, it’s crucial to understand the importance of accreditation and professional certifications. These elements can significantly impact your career path and open doors to new opportunities.
Accreditation of Accounting Programs
Accreditation ensures that accounting programs meet high standards of quality and prepare students for the demands of the profession. Accreditation is a process by which an external organization evaluates an academic program and determines whether it meets specific standards. The primary accrediting body for accounting programs in the United States is the Accreditation Council for Business Schools and Programs (ACBSP). Accreditation by ACBSP indicates that a program has met rigorous standards in areas such as curriculum, faculty qualifications, and resources.
Benefits of Professional Certifications
Professional certifications, such as the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or the Certified Management Accountant (CMA), demonstrate a commitment to professional development and enhance your credibility in the accounting field. These certifications require a combination of education, experience, and examination, ensuring that holders possess a high level of knowledge and skills.
CPA (Certified Public Accountant)
- Enhanced credibility and marketability: The CPA designation is widely recognized and respected in the accounting profession, signifying a high level of competency and professionalism.
- Increased earning potential: Studies have shown that CPAs earn significantly more than their non-certified counterparts.
- Broader career opportunities: The CPA credential opens doors to a wide range of career paths, including public accounting, corporate accounting, and government accounting.
CMA (Certified Management Accountant)
- Specialized expertise in management accounting: The CMA certification focuses on the management and analysis of financial information for internal decision-making.
- Strong demand in the corporate sector: CMAs are highly sought after by companies seeking professionals with expertise in cost accounting, budgeting, and financial forecasting.
- Competitive advantage in the job market: Holding a CMA certification can make you a more attractive candidate for management accounting roles.
Steps to Obtain Professional Certifications
The process of obtaining professional certifications typically involves the following steps:
- Meet the eligibility requirements: This usually includes a bachelor’s degree in accounting, a minimum number of work experience hours, and passing the Uniform CPA Examination or CMA Examination.
- Prepare for the exam: There are various study materials and courses available to help you prepare for the certification exams.
- Pass the exam: The CPA and CMA exams are rigorous and require a strong understanding of accounting principles and practices.
- Complete the required continuing education: Once certified, you must maintain your credentials by completing continuing education requirements.
The Role of Technology in Accounting: Bachelor Of Accounting Degree
Technology has revolutionized the accounting profession, transforming how accountants work and the services they offer. From automating routine tasks to enabling real-time data analysis, technology has significantly enhanced efficiency, accuracy, and insights in accounting.
Accounting Software and Tools
Accounting software and tools have become indispensable for accountants, automating tasks and streamlining processes. These tools help manage financial data, generate reports, and perform complex calculations, freeing up accountants to focus on higher-level analysis and strategic decision-making.
- General Ledger Software: Software like QuickBooks, Xero, and Sage Intacct helps businesses manage their financial records, track transactions, and generate financial statements. These programs are widely used by small and medium-sized businesses.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: Large organizations often utilize ERP systems like SAP and Oracle, which integrate various business functions, including accounting, finance, supply chain management, and human resources. These systems provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s operations and facilitate real-time data analysis.
- Spreadsheet Software: Microsoft Excel remains a powerful tool for accountants, enabling them to perform calculations, create financial models, and analyze data. Its flexibility and extensive functionality make it a versatile tool for various accounting tasks.
- Tax Preparation Software: Programs like TurboTax and H&R Block simplify tax preparation by guiding users through the process, calculating deductions, and generating tax forms. These tools are widely used by individuals and businesses for tax filing.
Data Analytics and Financial Modeling
Data analytics and financial modeling skills are becoming increasingly important for accountants. These skills enable accountants to analyze large datasets, identify trends, and make informed financial decisions.
- Data Analytics: Accountants use data analytics to uncover patterns and insights in financial data, helping them identify areas for improvement, mitigate risks, and optimize business performance. Tools like Tableau and Power BI provide powerful visualization and analysis capabilities for financial data.
- Financial Modeling: Financial modeling involves creating spreadsheets or using specialized software to simulate different financial scenarios. This allows accountants to assess the potential impact of various decisions, such as investment strategies, pricing changes, or expansion plans.
Choosing the Right Accounting Program
Selecting the right accounting program is a crucial step in your journey to becoming a successful accountant. With diverse options available, it’s essential to carefully consider your individual needs, goals, and preferences.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Accounting Program
When evaluating different accounting programs, it’s important to consider several factors to ensure you choose a program that aligns with your aspirations.
- Reputation and Accreditation: Look for programs accredited by reputable organizations such as the Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business (AACSB) or the Accreditation Council for Business Schools and Programs (ACBSP). Accreditation signifies that the program meets high quality standards and prepares graduates for professional success.
- Faculty Expertise: Choose a program with experienced and qualified faculty who possess industry knowledge and can provide valuable guidance and mentorship. Consider their academic credentials, professional experience, and teaching styles.
- Curriculum and Course Offerings: The program’s curriculum should align with your career goals and provide a strong foundation in core accounting principles and concepts. Look for programs that offer specialized courses in areas such as financial accounting, managerial accounting, auditing, and taxation.
- Career Services and Placement Rates: A good accounting program will offer career services that can help you connect with potential employers and secure internships or full-time positions. Investigate the program’s placement rates and alumni success stories.
- Flexibility and Convenience: Consider the program’s format, scheduling, and location. Traditional, online, and accelerated programs offer different levels of flexibility and convenience. Choose a program that fits your lifestyle and learning preferences.
- Cost and Financial Aid: Evaluate the program’s tuition fees, living expenses, and financial aid options. Consider scholarships, grants, and student loans to make the program financially feasible.
Types of Accounting Programs
The accounting field offers various program formats to accommodate diverse learning styles and preferences. Here’s a comparison of common program types:
| Program Type | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional | Full-time, on-campus program with in-person classes. | Strong student-faculty interaction, access to campus resources, and structured learning environment. | Less flexibility in scheduling and location, potentially higher cost. |
| Online | Flexible, remote learning program with virtual classes and coursework. | Convenience, accessibility, and flexibility in scheduling. | Limited interaction with faculty and peers, potential for technical difficulties. |
| Accelerated | Fast-paced program designed for students who want to complete their degree in a shorter timeframe. | Quick completion time, potential for career advancement. | Intense workload, less time for networking and professional development. |
Reputable Accounting Schools
Numerous institutions offer highly regarded accounting programs. Here are a few examples:
- University of Texas at Austin (McCombs School of Business): Known for its strong academic reputation, comprehensive curriculum, and dedicated faculty.
- Indiana University (Kelley School of Business): Renowned for its emphasis on practical skills, career services, and industry connections.
- University of Pennsylvania (Wharton School): Prestigious business school with a rigorous accounting program and strong alumni network.
Ultimate Conclusion
Pursuing a Bachelor of Accounting Degree is an investment in your future, providing you with the skills and knowledge to thrive in a dynamic and rewarding field. Whether you aspire to work in public accounting, corporate finance, or government, an accounting degree can unlock a world of possibilities and pave the way for a successful and fulfilling career.
Essential FAQs
What are the typical job titles for accounting graduates?
Accounting graduates can find employment in various roles such as Staff Accountant, Cost Accountant, Financial Analyst, Auditor, Tax Accountant, and Controller.
Is an accounting degree worth it?
Yes, an accounting degree is a valuable investment. It opens doors to high-demand careers with strong earning potential and excellent job security.
What are the admission requirements for accounting programs?
Admission requirements vary depending on the institution. Generally, you will need a high school diploma or equivalent, with a strong academic record, particularly in math and business courses.
What are the benefits of pursuing a CPA certification?
The CPA certification is a highly respected credential that demonstrates advanced accounting knowledge and professional competency, enhancing earning potential and career advancement opportunities.