
- Overview of a Bachelor’s Degree in Nursing
- Career Paths for Registered Nurses (RNs)
- Skills and Qualities of Successful Nurses
- The Nursing Profession and Its Impact
- Admission Requirements and Considerations
- The Nursing School Experience: Bachelor Degree In Nursing
- Continuing Education and Professional Development
- Final Conclusion
- FAQ Section
Bachelor degree in nursing – A bachelor’s degree in nursing is a gateway to a fulfilling and impactful career in healthcare. This comprehensive program equips aspiring nurses with the knowledge, skills, and clinical experience necessary to provide compassionate and effective patient care.
The curriculum encompasses a wide range of subjects, including anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and nursing theory. Students gain hands-on experience through clinical rotations in various healthcare settings, allowing them to apply their knowledge and develop critical thinking skills.
Overview of a Bachelor’s Degree in Nursing
A Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) is a comprehensive program that prepares graduates for a rewarding career as a registered nurse. This degree provides a solid foundation in nursing theory, practice, and research, equipping students with the skills and knowledge necessary to provide high-quality patient care.
Core Curriculum
The core curriculum of a BSN program encompasses a wide range of subjects, including:
- Nursing Fundamentals: This foundational course introduces students to the nursing profession, its history, and the essential principles of patient care. Topics covered include the nursing process, patient assessment, vital signs, and basic nursing skills.
- Medical-Surgical Nursing: This course focuses on the care of adult patients with a variety of medical and surgical conditions. Students learn about common illnesses, surgical procedures, and the management of chronic diseases.
- Maternal-Newborn Nursing: This course covers the care of pregnant women, newborns, and their families. Students learn about the stages of labor and delivery, postpartum care, and common complications of pregnancy.
- Pediatric Nursing: This course focuses on the care of children from birth to adolescence. Students learn about childhood illnesses, developmental milestones, and the unique needs of children.
- Mental Health Nursing: This course explores the care of patients with mental health disorders. Students learn about various psychiatric conditions, therapeutic interventions, and the principles of mental health care.
- Community Health Nursing: This course examines the role of nurses in promoting health and preventing disease within communities. Students learn about public health principles, community health assessment, and health education strategies.
- Nursing Informatics: This course focuses on the use of technology in nursing practice. Students learn about electronic health records, data management, and the application of technology to improve patient care.
- Nursing Research: This course introduces students to the principles of research methodology and the application of research findings to nursing practice. Students learn how to critically evaluate research studies and conduct their own research projects.
Course Load and Structure
A BSN program typically takes four years to complete, with each year consisting of two semesters. The course load is generally demanding, with students taking a combination of theoretical and clinical courses. The structure of the program is designed to build upon previous knowledge and skills, with courses progressing in complexity and scope.
Clinical Experiences and Practicum Hours
A significant component of a BSN program is clinical experience. Students are required to complete a certain number of hours in various clinical settings, such as hospitals, clinics, and community health centers. These experiences provide students with hands-on training and the opportunity to apply their knowledge in real-world settings.
Specializations in Nursing
Nursing offers a wide range of specializations, allowing individuals to focus on specific areas of interest. Some common specializations include:
- Critical Care Nursing: This specialization focuses on the care of critically ill patients in intensive care units (ICUs). Critical care nurses possess advanced skills in managing life-threatening conditions and providing complex medical interventions.
- Emergency Nursing: This specialization involves the care of patients presenting with acute medical or traumatic conditions in emergency departments. Emergency nurses must be able to assess patients quickly, prioritize care, and make critical decisions under pressure.
- Oncology Nursing: This specialization focuses on the care of patients with cancer. Oncology nurses provide support and education to patients and their families, manage side effects of treatment, and advocate for their well-being.
- Pediatric Nursing: This specialization focuses on the care of children from birth to adolescence. Pediatric nurses possess specialized knowledge of child development, common childhood illnesses, and the unique needs of children.
- Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing: This specialization focuses on the care of patients with mental health disorders. Psychiatric-mental health nurses provide therapy, medication management, and support to patients and their families.
Career Paths for Registered Nurses (RNs)
A Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) degree opens doors to a wide range of career paths in the dynamic and rewarding field of nursing. Registered Nurses (RNs) are highly sought-after professionals who play a vital role in providing quality healthcare to individuals and communities.
Common Nursing Roles and Responsibilities
RNs work in diverse settings, from hospitals and clinics to schools and home health agencies. Their responsibilities vary depending on their specialization and work environment. Here are some common nursing roles:
- Medical-Surgical Nursing: These nurses provide care to patients with a wide range of medical and surgical conditions, managing their medications, monitoring their vital signs, and assisting with daily living activities.
- Critical Care Nursing: RNs in critical care units provide specialized care to patients with life-threatening conditions, such as heart attacks, strokes, and respiratory failure. They monitor patients closely, administer medications, and work closely with physicians to ensure optimal patient outcomes.
- Emergency Room Nursing: Emergency room nurses are skilled in handling emergencies and providing immediate care to patients with various injuries and illnesses. They triage patients, stabilize their conditions, and work under pressure to provide timely and effective treatment.
- Pediatric Nursing: Pediatric nurses specialize in caring for infants, children, and adolescents. They provide age-appropriate care, administer medications, educate parents, and promote the well-being of their young patients.
- Obstetric Nursing: Obstetric nurses assist women during pregnancy, labor, and delivery. They monitor mothers and babies, provide education and support, and help with postpartum recovery.
- Psychiatric Nursing: Psychiatric nurses work with individuals experiencing mental health conditions. They provide counseling, medication management, and support to help patients manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Career Advancement Opportunities in Nursing
Nursing offers a clear path for career advancement. RNs can pursue specialized certifications, master’s degrees, and doctoral degrees to enhance their skills and knowledge, opening up opportunities for leadership and research roles.
Benefits of a Bachelor’s Degree in Nursing for Career Progression
A BSN degree provides a solid foundation for a successful nursing career. It equips nurses with advanced clinical skills, critical thinking abilities, and leadership qualities. Furthermore, a BSN degree is often a requirement for advanced nursing roles, such as nurse manager, nurse educator, and advanced practice registered nurse (APRN).
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook for RNs with Different Levels of Education
The salary and job outlook for RNs can vary depending on their education, experience, and location. RNs with a BSN degree generally earn higher salaries and have better job prospects than those with an associate’s degree in nursing (ADN).
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 7% growth in employment for registered nurses from 2020 to 2030, which is faster than the average for all occupations.
For example, a BSN-prepared nurse working in a hospital setting might earn a starting salary of $70,000 to $80,000 per year, while an ADN-prepared nurse might earn a starting salary of $55,000 to $65,000 per year. However, these figures can vary depending on factors such as location, experience, and specialization.
Skills and Qualities of Successful Nurses
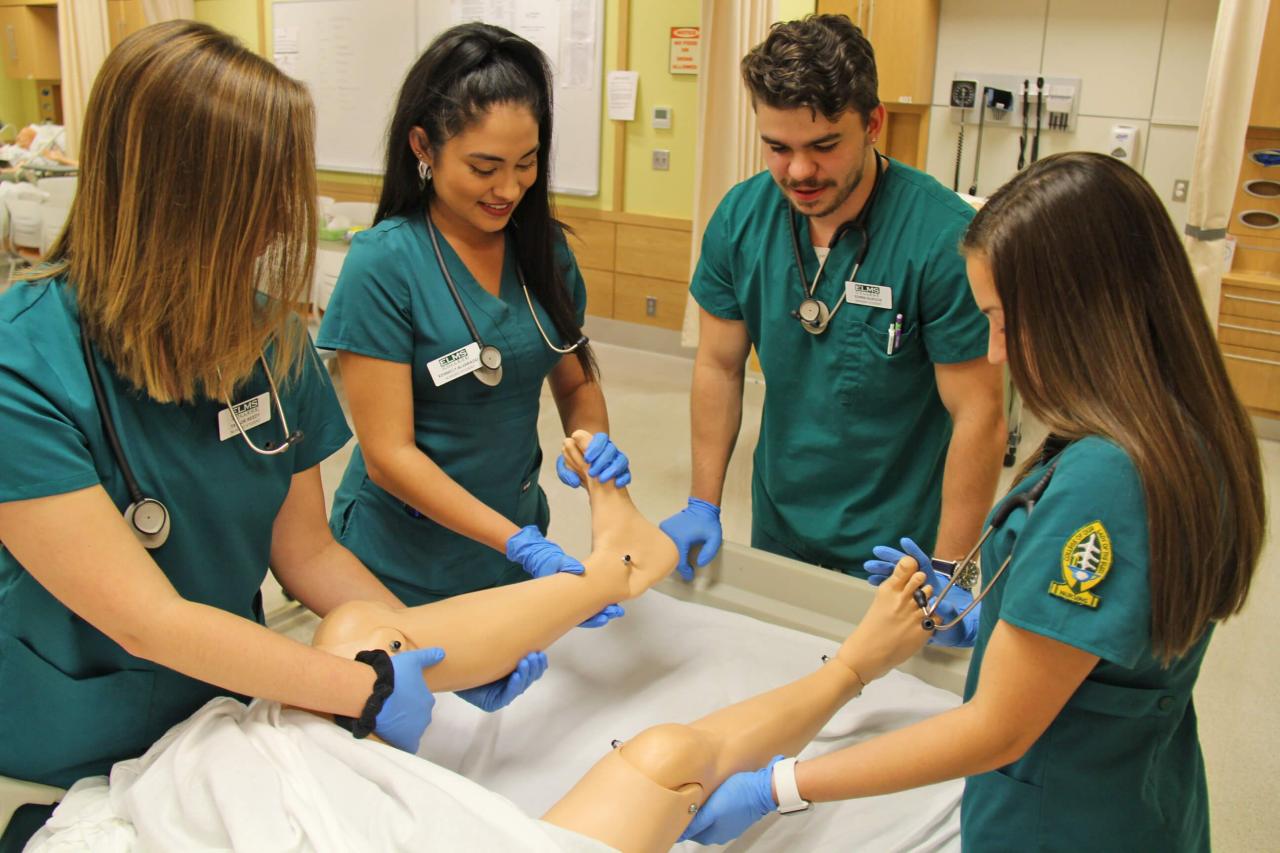
Nurses are the backbone of the healthcare system, providing compassionate care and expert medical knowledge to patients. To excel in this demanding profession, nurses need a unique blend of technical skills, personal qualities, and cognitive abilities.
Essential Hard Skills for Nursing Practice
Nurses require a solid foundation of technical skills to deliver safe and effective care. These skills are learned through formal education and practical training.
- Medical Knowledge: Nurses must have a deep understanding of anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and common medical conditions. This knowledge allows them to assess patients, interpret medical orders, and administer medications safely.
- Clinical Skills: Nurses perform a wide range of clinical procedures, including taking vital signs, administering medications, wound care, and assisting with surgery. Proficiency in these skills is essential for providing quality care.
- Patient Assessment: Nurses need to be skilled at gathering patient information, including medical history, symptoms, and physical findings. This information helps them develop individualized care plans.
- Documentation: Nurses meticulously document patient care, including assessments, interventions, and outcomes. Accurate and complete documentation is crucial for communication and legal purposes.
- Technology Proficiency: The healthcare industry relies heavily on technology, and nurses need to be comfortable using electronic health records, medical devices, and telehealth platforms.
Soft Skills and Personal Qualities
While technical skills are essential, soft skills and personal qualities are equally important for success in nursing. These traits contribute to effective communication, strong relationships with patients and colleagues, and overall job satisfaction.
- Communication Skills: Nurses must communicate effectively with patients, families, and other healthcare professionals. This includes active listening, clear explanations, and empathy in conveying information.
- Empathy and Compassion: Nurses are expected to show genuine care and concern for their patients. This involves understanding and responding to their emotional needs, offering support, and advocating for their well-being.
- Emotional Intelligence: Nurses need to be aware of their own emotions and how they impact their interactions with patients. Emotional intelligence helps them manage stress, build rapport, and provide sensitive care.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Nurses often face complex situations that require quick thinking and creative solutions. They need to analyze problems, gather information, and develop effective interventions.
- Teamwork and Collaboration: Nursing is a collaborative profession. Nurses work closely with doctors, other nurses, and healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care. Strong teamwork skills are essential for successful outcomes.
- Time Management: Nurses work in fast-paced environments with demanding schedules. Effective time management skills are crucial for prioritizing tasks, managing workloads, and providing timely care.
- Resilience: Nursing can be emotionally and physically challenging. Nurses need to be resilient, able to cope with stress, and maintain a positive attitude even in difficult situations.
Importance of Critical Thinking, Problem-Solving, and Communication Skills
Critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills are interconnected and fundamental to nursing practice.
- Critical Thinking: Nurses use critical thinking to analyze patient information, identify potential problems, and develop evidence-based solutions. This involves evaluating information, considering multiple perspectives, and making informed decisions.
- Problem-Solving: Nurses frequently encounter complex situations that require problem-solving skills. They need to identify the root cause of a problem, develop a plan of action, and evaluate the effectiveness of their interventions.
- Communication Skills: Effective communication is essential for all aspects of nursing care. Nurses use communication to gather patient information, explain procedures, provide instructions, and collaborate with other healthcare professionals.
Role of Empathy, Compassion, and Emotional Intelligence in Providing Patient Care
Empathy, compassion, and emotional intelligence are crucial for providing patient-centered care.
- Empathy: Empathy allows nurses to understand and share the feelings of their patients. This involves actively listening, acknowledging their emotions, and showing genuine concern.
- Compassion: Compassion involves acting on empathy by providing comfort, support, and care to patients. It is about showing kindness, understanding, and a desire to alleviate suffering.
- Emotional Intelligence: Nurses with high emotional intelligence are better equipped to manage their own emotions and understand the emotions of others. This helps them build rapport with patients, handle challenging situations, and provide compassionate care.
The Nursing Profession and Its Impact

Nurses play a pivotal role in healthcare delivery, serving as essential members of the medical team and providing direct patient care. Their impact extends beyond individual patients, influencing public health and shaping the future of healthcare.
The Evolving Role of Nurses in Healthcare Delivery
The nursing profession has undergone significant transformations, adapting to the changing needs of healthcare systems and evolving patient demands. Nurses are no longer solely focused on providing bedside care; they are now actively involved in patient education, health promotion, disease prevention, and interdisciplinary collaboration.
- Increased Focus on Patient Education: Nurses are increasingly recognized as vital educators, empowering patients to manage their health conditions effectively. They provide comprehensive instructions on medication management, lifestyle modifications, and disease prevention strategies.
- Health Promotion and Disease Prevention: Nurses actively participate in health promotion programs, educating the public about healthy habits and disease prevention strategies. They conduct screenings, administer vaccinations, and provide guidance on risk reduction behaviors.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: The modern healthcare landscape emphasizes collaborative care, and nurses are integral members of interdisciplinary teams. They work closely with physicians, pharmacists, therapists, and other healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive and coordinated patient care.
- Technological Advancements: Advances in technology have significantly impacted the nursing profession. Nurses utilize electronic health records (EHRs) to document patient care, access medical information, and communicate with other healthcare providers. They also leverage telehealth platforms to provide remote patient monitoring and virtual consultations.
Challenges and Opportunities Facing the Nursing Profession
The nursing profession faces a number of challenges and opportunities that influence its future direction. These factors require ongoing attention and proactive solutions to ensure a thriving and sustainable nursing workforce.
- Nurse Shortages: The increasing demand for healthcare services coupled with an aging nursing workforce has resulted in persistent nurse shortages in many regions. This shortage can lead to increased workloads, burnout, and compromised patient care.
- Burnout and Stress: The demanding nature of nursing can lead to burnout and stress. Nurses often work long hours, deal with complex patient needs, and face emotionally challenging situations.
- Technological Advancements: While technology offers opportunities, it also presents challenges. Nurses must adapt to new technologies, maintain proficiency in using electronic health records, and ensure that technology enhances rather than hinders patient care.
- Aging Population: As the population ages, the demand for healthcare services, particularly those related to chronic diseases, will continue to rise. This trend necessitates a robust and well-prepared nursing workforce to meet the growing needs of older adults.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Creating a diverse and inclusive nursing workforce is essential to reflect the diverse patient populations they serve. Promoting diversity and inclusion in nursing education and practice can improve patient care outcomes and enhance the overall health of communities.
Impact of Nursing on Patient Outcomes and Healthcare Quality
Nurses play a critical role in improving patient outcomes and enhancing healthcare quality. Their contributions extend beyond direct patient care to encompass quality improvement initiatives, patient safety measures, and advocacy for optimal healthcare practices.
- Reduced Hospital Readmissions: Nurses actively participate in programs designed to reduce hospital readmissions. They provide comprehensive discharge planning, educate patients about their medications and follow-up care, and address any potential barriers to adherence.
- Improved Patient Safety: Nurses are on the front lines of patient safety, vigilantly monitoring patients for signs of complications, implementing protocols to prevent infections, and advocating for safe medication practices.
- Enhanced Communication: Nurses act as crucial communicators between patients and physicians, ensuring that patients’ needs are understood and addressed. They also play a vital role in coordinating care among different healthcare providers.
- Patient Satisfaction: Nurses’ compassion, empathy, and dedication to patient care contribute significantly to patient satisfaction. They provide emotional support, comfort, and a sense of well-being to patients and their families.
Impact of Nursing on Public Health and Community Well-being
Nurses’ impact extends beyond individual patients to the broader community, contributing to public health initiatives and improving the overall well-being of society.
- Community Health Programs: Nurses are actively involved in community health programs, providing health education, screenings, vaccinations, and other essential services. They work to address health disparities and promote health equity within communities.
- Disease Prevention and Control: Nurses play a vital role in disease prevention and control efforts. They administer vaccinations, conduct screenings, and educate the public about healthy behaviors and risk factors.
- Disaster Response: Nurses are often on the front lines during natural disasters and other emergencies. They provide immediate medical care, support evacuation efforts, and assist with public health interventions.
- Advocacy for Health Policy: Nurses advocate for health policies that promote public health, improve access to care, and ensure the well-being of communities. They engage with policymakers, participate in public forums, and raise awareness about critical health issues.
Admission Requirements and Considerations
Embarking on a nursing career requires careful planning and meeting specific academic requirements. Admission to nursing programs is competitive, and understanding the criteria is crucial for successful application.
Nursing schools typically have a comprehensive set of admission requirements designed to assess applicants’ academic preparedness, personal qualities, and suitability for the profession. These requirements are aimed at ensuring that students have the necessary foundation and skills to succeed in a rigorous nursing curriculum.
Prerequisite Courses
Prerequisite courses serve as the foundation for your nursing education. They provide the essential knowledge and skills required to understand complex medical concepts and clinical practices. These courses typically include:
- Biology
- Chemistry
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Microbiology
- Psychology
- Sociology
- Statistics
- English Composition
Successfully completing these prerequisite courses with a strong GPA demonstrates your academic ability and commitment to the nursing profession. Many programs require a minimum GPA for consideration.
Standardized Test Scores
Standardized tests, such as the Test of Essential Academic Skills (TEAS) or the Health Education Systems, Inc. (HESI) exam, are commonly used to evaluate your knowledge and readiness for nursing school. These tests assess your understanding of fundamental concepts in math, science, reading, and critical thinking.
- Preparing adequately for these exams is crucial. Many programs have minimum score requirements for admission.
- Reviewing relevant content, practicing with sample questions, and taking practice tests can improve your scores.
Personal Statements and Letters of Recommendation
Personal statements and letters of recommendation offer an opportunity to showcase your passion for nursing, your experiences, and your suitability for the program.
- Your personal statement should highlight your motivations for pursuing a nursing career, your relevant experiences, and your understanding of the nursing profession.
- Letters of recommendation from professors, employers, or healthcare professionals who can attest to your skills, work ethic, and potential as a nurse are essential.
- Choose recommenders who know you well and can provide insightful and positive evaluations.
Preparing for Nursing School
To ensure a successful application and a smooth transition into nursing school, consider these tips:
- Maintain a strong academic record: Focus on your studies and strive for high grades in your prerequisite courses.
- Gain relevant experience: Volunteer in healthcare settings, shadow nurses, or participate in community health initiatives to gain practical experience and enhance your understanding of the profession.
- Develop strong communication skills: Nursing requires effective communication with patients, families, and colleagues. Practice your communication skills and seek opportunities to improve them.
- Develop time management skills: Nursing school is demanding, so it’s essential to be organized, prioritize tasks, and manage your time effectively.
- Seek guidance and support: Connect with current nursing students, faculty, or advisors for advice and support throughout the application process.
The Nursing School Experience: Bachelor Degree In Nursing
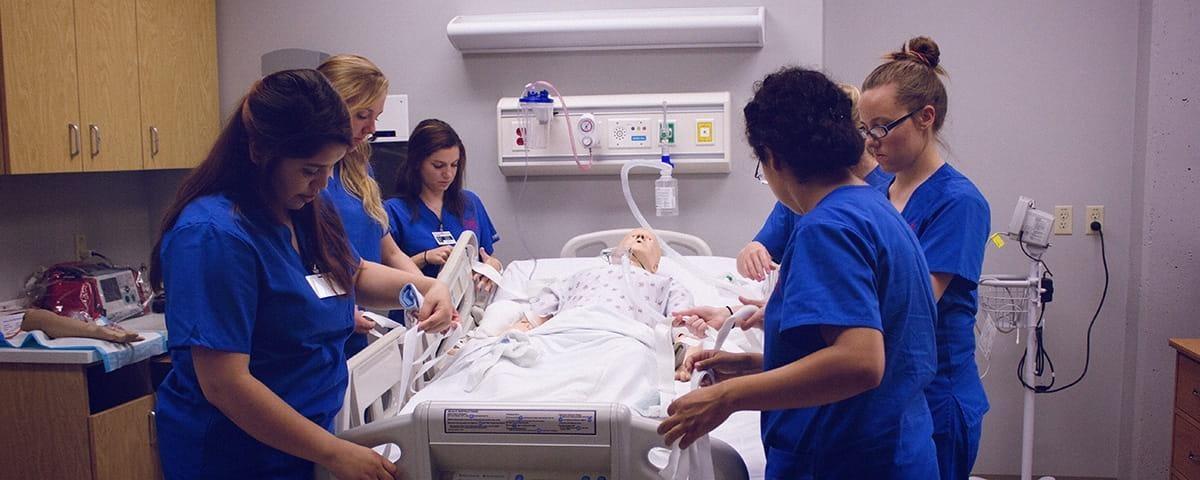
Nursing school is a demanding but rewarding journey that prepares aspiring nurses for a fulfilling career in healthcare. The curriculum covers a wide range of theoretical and practical knowledge, while clinical experiences provide hands-on training in real-world settings.
Types of Nursing Programs
The path to becoming a registered nurse (RN) can be taken through various types of nursing programs, each with its own unique structure and requirements. Here’s a comparison of three common program types:
| Program Type | Duration | Structure | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional BSN | 4 years | Full-time, on-campus | – Comprehensive curriculum – Strong foundation in nursing theory and practice – Extensive clinical experiences |
– Time-consuming – Can be expensive – Limited flexibility |
| Accelerated BSN | 12-18 months | Intensive, full-time, on-campus | – Shorter time commitment – Designed for students with prior college credits – Fast track to RN licensure |
– Demanding workload – May require prerequisites – Limited time for clinical experiences |
| Online BSN | 2-4 years | Part-time or full-time, online and on-campus | – Flexibility and convenience – Access to online resources and support – Can be completed while working |
– May require on-campus clinical experiences – Limited interaction with faculty and peers – Requires self-discipline and time management |
Challenges and Rewards of Nursing School
Nursing school is a challenging experience that requires dedication, resilience, and a strong commitment to learning. Students face a demanding workload, intense clinical experiences, and the constant pressure to succeed. However, the rewards of becoming a nurse are immeasurable.
Challenges
- Heavy workload: Nursing school involves a significant amount of coursework, exams, and clinical assignments.
- Clinical experiences: Students are exposed to various healthcare settings and patient populations, which can be emotionally and physically demanding.
- Time management: Balancing academics, clinical experiences, and personal life can be challenging.
- Financial burden: Nursing school can be expensive, with tuition fees, books, and other expenses.
- Stress and burnout: The intense workload and emotional demands of nursing school can lead to stress and burnout.
Rewards
- Making a difference: Nurses play a vital role in improving the lives of patients and their families.
- Personal growth: Nursing school fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills.
- Job security: The demand for nurses is high, and job prospects are excellent.
- Variety of career paths: Nursing offers a wide range of specializations and career paths.
- Sense of purpose: Nurses find deep satisfaction in helping others and making a positive impact on their lives.
Balancing Academics, Clinical Experiences, and Personal Life
Maintaining a healthy balance between academics, clinical experiences, and personal life is crucial for nursing students’ well-being and success. Here are some tips:
- Prioritize time management: Create a schedule that allocates time for studying, clinicals, and personal activities.
- Set realistic goals: Break down large tasks into smaller, manageable steps.
- Seek support from peers and faculty: Don’t hesitate to ask for help when needed.
- Take care of your physical and mental health: Get enough sleep, eat a healthy diet, and exercise regularly.
- Make time for relaxation and hobbies: Engage in activities that help you de-stress and recharge.
Support Systems and Resources, Bachelor degree in nursing
Nursing schools offer a variety of support systems and resources to help students succeed.
- Academic advisors: Provide guidance on course selection, academic planning, and career goals.
- Faculty mentors: Offer support and guidance throughout the program.
- Student support services: Provide tutoring, counseling, and other resources to help students cope with the challenges of nursing school.
- Professional organizations: Offer networking opportunities, professional development resources, and advocacy for nursing students and professionals.
- Online resources: Provide access to a wealth of information, including textbooks, journals, and other learning materials.
Continuing Education and Professional Development
In the dynamic and ever-evolving field of nursing, lifelong learning is not merely an option, but a necessity. Continuing education and professional development are crucial for nurses to maintain their competence, expand their skills, and advance their careers.
Nurses are responsible for providing safe and effective care to patients, which requires them to stay abreast of the latest advancements in medical knowledge, treatment modalities, and best practices. Furthermore, the healthcare landscape is constantly changing, with new technologies, regulations, and patient needs emerging regularly. Continuing education empowers nurses to adapt to these changes, ensuring they can deliver the highest quality of care.
Professional Certifications and Advanced Degrees
Nurses have various opportunities to enhance their credentials and expertise through professional certifications and advanced degrees.
Professional certifications demonstrate specialized knowledge and skills in specific areas of nursing practice. For example, a Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA) provides anesthesia care, while a Certified Wound Ostomy Continence Nurse (CWOCN) specializes in wound care, ostomy management, and continence issues. These certifications often require specific educational requirements, clinical experience, and passing an exam.
Advanced degrees, such as a Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) or a Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP), offer nurses the opportunity to deepen their knowledge and develop leadership skills. These degrees prepare nurses for advanced practice roles, such as nurse practitioners, clinical nurse specialists, and nurse educators. Advanced degrees often focus on specialized areas of nursing practice, such as adult-gerontology, pediatrics, or mental health.
Professional Organizations and Networking
Professional organizations play a vital role in supporting the professional development of nurses.
These organizations offer numerous resources, including continuing education opportunities, networking events, and advocacy efforts. Membership in professional organizations allows nurses to connect with colleagues, share best practices, and stay informed about current trends in the field. Networking with other nurses can open doors to new career opportunities and provide valuable mentorship.
For example, the American Nurses Association (ANA) is the largest professional organization for registered nurses in the United States. The ANA offers a wide range of resources, including continuing education courses, certification programs, and advocacy initiatives. Other professional organizations, such as the National League for Nursing (NLN) and the American Academy of Nursing (AAN), also provide valuable resources and support for nurses.
Benefits of Lifelong Learning
Lifelong learning in nursing offers numerous benefits for both individual nurses and the healthcare system as a whole.
For nurses, continuing education can lead to career advancement, increased earning potential, and greater job satisfaction. By staying current with the latest developments in nursing practice, nurses can enhance their skills and knowledge, making them more valuable assets to their employers. Furthermore, continuing education can provide nurses with the confidence and expertise to take on new challenges and leadership roles.
For the healthcare system, a workforce of well-educated and highly skilled nurses is essential for providing high-quality patient care. Continuing education ensures that nurses have the knowledge and skills to deliver safe and effective care, leading to improved patient outcomes and increased patient satisfaction.
Final Conclusion
A bachelor’s degree in nursing opens doors to a diverse array of career paths, offering opportunities for professional growth and personal fulfillment. From providing direct patient care to leading healthcare teams, nurses play a vital role in improving the health and well-being of individuals and communities.
FAQ Section
What are the job prospects for nurses with a bachelor’s degree?
Nurses with a bachelor’s degree enjoy excellent job prospects, with high demand across various healthcare settings. They are qualified for a wider range of roles and have greater opportunities for career advancement.
How long does it take to complete a bachelor’s degree in nursing?
A traditional bachelor’s degree in nursing typically takes four years to complete. Accelerated programs may offer faster completion options for students with prior college credit.
What are the admission requirements for nursing programs?
Admission requirements vary by program, but typically include a high school diploma or equivalent, prerequisite courses in science and math, and a minimum GPA. Some programs may also require standardized test scores like the TEAS or the SAT/ACT.
What are the challenges of nursing school?
Nursing school is demanding, requiring a high level of commitment and dedication. Students face challenges such as a rigorous curriculum, demanding clinical experiences, and balancing academics with personal life.




