
Trade in the forex market is the largest and most liquid financial market globally, offering opportunities for both experienced traders and those new to the world of finance. It’s a decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded against each other, driven by a complex interplay of economic factors, political events, and market sentiment. The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, making it accessible to traders around the world.
Understanding the dynamics of the forex market is crucial for success. Currency pairs are the building blocks of forex trading, and their values fluctuate based on various factors. Traders utilize different strategies to profit from these fluctuations, including scalping, day trading, swing trading, and trend trading. Risk management is paramount, as forex trading involves inherent risks, but it also offers the potential for substantial rewards.
Introduction to Forex Trading
Forex trading, short for foreign exchange trading, is the simultaneous buying of one currency and selling of another. It is the largest and most liquid financial market globally, with trillions of dollars changing hands every day. The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, and is decentralized, meaning there is no single physical location for trading.
Forex trading is significant for several reasons. It enables businesses and individuals to exchange currencies for international transactions, such as importing and exporting goods and services. It also provides opportunities for investors to profit from fluctuations in exchange rates.
Key Participants in the Forex Market
The forex market is comprised of various participants, each playing a distinct role.
- Central Banks: Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve (US) and the European Central Bank, intervene in the forex market to influence exchange rates and manage their country’s monetary policy.
- Commercial Banks: Commercial banks facilitate foreign exchange transactions for their clients, including businesses and individuals, and also participate in the market for their own accounts.
- Investment Banks: Investment banks engage in forex trading to manage their own portfolios and provide financial services to clients, such as hedging currency risk.
- Hedge Funds: Hedge funds are investment funds that use various strategies, including forex trading, to generate returns for their investors.
- Retail Traders: Individuals who trade currencies through online brokers or platforms are known as retail traders. They typically use smaller amounts of capital compared to institutional investors.
History and Evolution of Forex Trading
The history of forex trading dates back centuries, with early forms of currency exchange taking place between merchants and traders. However, the modern forex market emerged in the 1970s, following the breakdown of the Bretton Woods system of fixed exchange rates. The introduction of floating exchange rates allowed currencies to fluctuate freely based on market forces.
The evolution of forex trading has been driven by several factors, including:
- Technological advancements: The development of electronic trading platforms and internet access has made forex trading more accessible and efficient.
- Globalization: The increasing interconnectedness of economies has led to greater demand for foreign exchange transactions.
- Deregulation: The deregulation of financial markets has allowed for greater participation and competition in forex trading.
Understanding Forex Market Dynamics
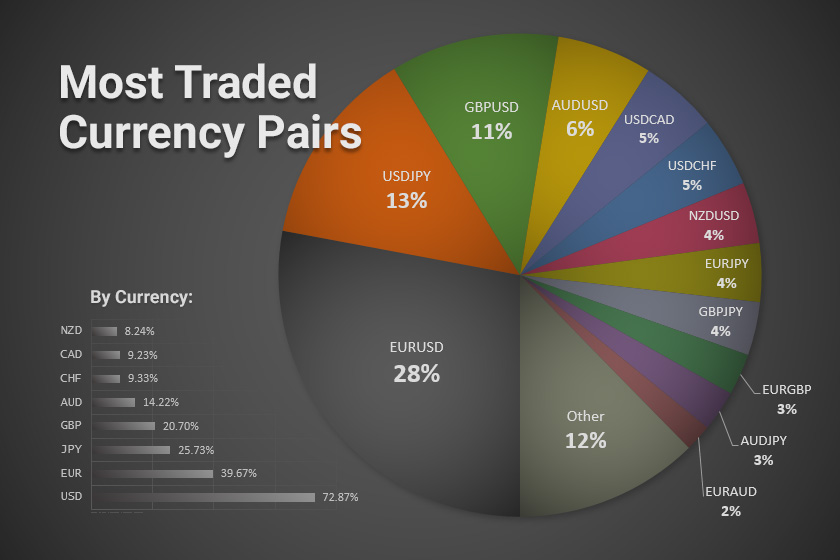
The forex market is a dynamic and complex environment where currencies are traded against each other. Understanding the forces that drive currency exchange rates is crucial for success in forex trading. This section will delve into the key factors that influence currency valuations and the mechanisms through which forex trading occurs.
Currency Pairs and Trading
Forex trading involves buying one currency while simultaneously selling another. This is done through currency pairs, which represent the exchange rate between two currencies. For example, the EUR/USD pair represents the exchange rate between the Euro and the US Dollar.
When trading a currency pair, you are essentially speculating on the future value of one currency relative to the other. If you believe the Euro will appreciate against the US Dollar, you would buy the EUR/USD pair. Conversely, if you anticipate a depreciation of the Euro, you would sell the pair.
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates
Several factors can influence currency exchange rates, including:
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators provide insights into the health of a country’s economy and can significantly impact currency valuations. Some key indicators include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Measures the total value of goods and services produced in a country. A strong GDP growth rate generally indicates a healthy economy and can lead to currency appreciation.
- Inflation: Measures the rate at which prices for goods and services rise. High inflation can erode the purchasing power of a currency, leading to depreciation.
- Interest Rates: Central banks set interest rates to control inflation and economic growth. Higher interest rates can attract foreign investment, boosting demand for the currency and leading to appreciation.
- Unemployment Rate: Reflects the percentage of the workforce that is unemployed. A low unemployment rate suggests a strong economy and can support currency appreciation.
Political Events
Political events, such as elections, changes in government policies, and geopolitical tensions, can significantly impact currency exchange rates. Political instability or uncertainty can lead to currency depreciation as investors seek safer havens.
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment refers to the overall feeling or attitude of traders towards a particular currency. Positive sentiment can lead to currency appreciation, while negative sentiment can result in depreciation. Market sentiment is often influenced by news events, economic data releases, and speculation.
Types of Forex Orders
Forex traders use various types of orders to execute their trades. Understanding these orders is crucial for effectively managing risk and maximizing profits. Some common types of forex orders include:
- Market Order: This order is executed immediately at the best available price in the market. Market orders are suitable for traders who want to enter a trade quickly but may not get the desired price.
- Limit Order: A limit order is placed at a specific price or better. This order will only be executed if the desired price is reached. Limit orders allow traders to control their entry and exit points but may not be filled if the price does not reach the specified level.
- Stop-Loss Order: A stop-loss order is placed at a specific price level below the current market price for a buy order or above the current market price for a sell order. This order automatically executes when the market reaches the specified price, limiting potential losses.
- Take-Profit Order: A take-profit order is placed at a specific price level above the current market price for a buy order or below the current market price for a sell order. This order automatically executes when the market reaches the specified price, locking in profits.
Forex Trading Strategies
Forex trading strategies are the methods and techniques employed by traders to identify and capitalize on profitable opportunities in the foreign exchange market. These strategies involve a combination of technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and risk management to guide trading decisions.
Scalping
Scalping is a high-frequency trading strategy that aims to profit from small price fluctuations in the market. Scalpers typically hold trades for a short period, often just a few seconds or minutes. This strategy requires quick reflexes, a high level of technical analysis skills, and a robust trading platform.
Advantages of Scalping
- Potential for high profits: Scalpers can generate substantial profits by taking advantage of small price movements, even if the market is relatively stable.
- Flexibility: Scalping allows traders to enter and exit trades quickly, making it adaptable to various market conditions.
Disadvantages of Scalping
- High risk: Scalping involves high trading frequency and the potential for rapid losses if the market moves against the trader.
- High trading costs: The high trading volume associated with scalping can result in significant transaction fees and slippage.
- Requires constant monitoring: Scalpers must constantly monitor the market and be ready to act quickly, which can be demanding and stressful.
Day Trading
Day trading involves opening and closing trades within the same trading day, aiming to profit from short-term price fluctuations. Day traders typically focus on technical analysis and use various indicators to identify potential trading opportunities.
Advantages of Day Trading
- Flexibility: Day traders can adjust their trading strategy based on market conditions throughout the day.
- Lower risk than scalping: Day traders generally hold trades for a longer duration than scalpers, reducing the risk of rapid losses.
Disadvantages of Day Trading
- Requires significant time commitment: Day trading demands constant monitoring of the market and active participation in trading activities.
- High stress levels: The fast-paced nature of day trading can lead to significant stress and emotional fatigue.
Swing Trading
Swing trading involves holding trades for a few days to a few weeks, aiming to capture larger price swings in the market. Swing traders often use technical analysis and fundamental analysis to identify potential trends and support/resistance levels.
Advantages of Swing Trading
- Lower risk than day trading: Swing traders hold trades for a longer period, reducing the impact of short-term market fluctuations.
- Less time commitment: Swing traders can monitor the market less frequently than day traders, allowing for more flexibility in their schedule.
Disadvantages of Swing Trading
- Lower profit potential than day trading: Swing traders typically aim for larger price movements, which may take longer to materialize, resulting in lower profits.
- Requires a deeper understanding of market dynamics: Swing traders need to analyze both technical and fundamental factors to identify long-term trends.
Trend Trading
Trend trading involves identifying and following the prevailing market trends, aiming to capitalize on long-term price movements. Trend traders typically use technical analysis and fundamental analysis to identify trends and potential breakout points.
Advantages of Trend Trading
- Lower risk: Trend trading focuses on capturing long-term trends, reducing the impact of short-term market volatility.
- Higher profit potential: Trend trading allows traders to profit from significant price movements over extended periods.
Disadvantages of Trend Trading
- Requires patience: Trend trading involves holding trades for a longer duration, requiring patience and discipline to wait for profitable exits.
- Difficult to identify trends accurately: Identifying the correct trend and timing entries and exits can be challenging, requiring experience and a deep understanding of market dynamics.
Technical Analysis in Forex Trading
Technical analysis involves using charts and indicators to identify patterns and trends in the market. It focuses on the historical price movements of a currency pair, assuming that past price action can predict future price movements. Technical analysis tools include:
- Moving averages: These indicators smooth out price fluctuations and identify trends.
- Relative strength index (RSI): This indicator measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): This indicator identifies trend changes and potential buy or sell signals.
- Fibonacci retracement levels: These levels are based on the Fibonacci sequence and are used to identify potential support and resistance levels.
Fundamental Analysis in Forex Trading, Trade in the forex market
Fundamental analysis involves examining economic, political, and social factors that influence currency values. It focuses on understanding the underlying forces that drive currency movements, such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth. Fundamental analysis tools include:
- Economic data releases: These releases, such as GDP figures, inflation rates, and unemployment data, can provide insights into the health of an economy and its impact on currency values.
- Central bank policies: Central bank decisions on interest rates, monetary policy, and intervention can significantly influence currency movements.
- Political events: Political events, such as elections, wars, and policy changes, can create volatility in the market and impact currency values.
Forex Trading Tools and Resources

Forex trading requires a range of tools and resources to effectively analyze the market, execute trades, and manage risk. Understanding these tools and their applications is crucial for success in the forex market.
Trading Platforms
Trading platforms are software applications that provide traders with access to the forex market. They offer a variety of features, including real-time quotes, charting tools, order execution capabilities, and analytical indicators. Some popular trading platforms include:
- MetaTrader 4 (MT4): One of the most widely used platforms, known for its advanced charting tools and customizable indicators.
- MetaTrader 5 (MT5): The newer version of MT4, offering more advanced features, such as hedging capabilities and improved order types.
- cTrader: A platform designed for scalping and high-frequency trading, featuring advanced order execution and real-time market depth.
Charting Software
Charting software is essential for analyzing price trends and identifying trading opportunities. It allows traders to visualize price movements, identify patterns, and apply technical indicators. Popular charting software includes:
- TradingView: A web-based platform offering real-time charts, technical indicators, and drawing tools, with a user-friendly interface.
- NinjaTrader: A platform known for its advanced charting capabilities, customizable indicators, and automated trading features.
- ProRealTime: A platform designed for professional traders, offering a wide range of charting tools, real-time market data, and advanced analytical features.
Economic Calendars
Economic calendars are essential tools for staying informed about upcoming economic events that can influence forex prices. These calendars provide details on events like interest rate decisions, employment reports, and inflation data.
- Investing.com: A popular website offering a comprehensive economic calendar with details on various economic events and their impact on forex markets.
- FXStreet: Another reputable website providing a detailed economic calendar, along with news and analysis related to upcoming economic events.
- DailyFX: A website offering a user-friendly economic calendar, along with forex market analysis and educational resources.
Risk Management Tools and Techniques
Risk management is crucial in forex trading, as losses can occur due to market volatility and unpredictable price movements. Effective risk management tools and techniques help traders limit potential losses and protect their capital.
- Stop-Loss Orders: These orders automatically close a trade when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.
- Take-Profit Orders: These orders automatically close a trade when the price reaches a predetermined profit target, securing profits.
- Position Sizing: This technique involves determining the appropriate size of a trade based on risk tolerance and account balance.
Reputable Forex Brokers and Educational Resources
Choosing a reputable forex broker is essential for safe and reliable trading. It is important to research and select a broker with a good track record, strong regulation, and competitive trading conditions.
- FXTM: A regulated broker offering a wide range of trading instruments, competitive spreads, and educational resources.
- XM: Another regulated broker known for its competitive spreads, fast order execution, and educational materials.
- AvaTrade: A broker offering a user-friendly platform, a wide range of trading instruments, and educational resources for beginners.
- Babypips: A popular website offering free educational resources for forex traders, including tutorials, articles, and interactive courses.
- FXCM: A broker providing a comprehensive range of educational resources, including webinars, trading guides, and market analysis.
- DailyFX: A website offering educational content, market analysis, and trading strategies for forex traders.
Conclusion

The forex market is a dynamic and complex environment, demanding a combination of knowledge, skill, and discipline. By understanding the fundamentals of forex trading, employing effective strategies, and managing risk responsibly, traders can navigate this exciting market and potentially achieve their financial goals. However, it’s crucial to remember that forex trading is not without risk, and losses are possible. Thorough research, continuous learning, and a disciplined approach are essential for success in this challenging yet rewarding market.
Detailed FAQs: Trade In The Forex Market
What is the minimum amount I need to start trading forex?
The minimum amount required to start trading forex varies depending on the broker and account type. Some brokers offer micro accounts with as little as $5 or $10, while others may require a higher minimum deposit.
Is forex trading legal?
Yes, forex trading is legal in most countries. However, it’s essential to choose a regulated broker and ensure that you comply with all applicable laws and regulations.
How do I choose a forex broker?
When selecting a forex broker, consider factors such as regulation, trading platform, fees, customer support, and educational resources. It’s advisable to research and compare different brokers before making a decision.
What are the risks of forex trading?
Forex trading involves significant risks, including leverage, volatility, and market liquidity. Leverage can amplify both profits and losses, while volatility can lead to rapid price fluctuations. Market liquidity can also impact trading opportunities.
How can I learn more about forex trading?
There are numerous resources available to learn about forex trading, including online courses, books, articles, and webinars. Many brokers also offer educational materials and tutorials for their clients.




