
Forex market trading, the largest and most liquid financial market globally, involves buying and selling currencies to profit from exchange rate fluctuations. This dynamic marketplace, fueled by global economic forces, presents opportunities for both seasoned investors and newcomers to participate in the exciting world of currency trading.
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, providing a continuous flow of trading opportunities. Unlike traditional stock markets, forex trading allows traders to access a wide range of currency pairs, including major, minor, and exotic currencies, offering diverse trading strategies and risk management options.
Introduction to Forex Market Trading
The foreign exchange market, also known as Forex, is the largest and most liquid financial market globally. It facilitates the exchange of currencies, enabling businesses, individuals, and governments to conduct international transactions. Forex trading involves buying and selling currencies with the aim of profiting from fluctuations in their exchange rates.
The Forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, with trading activity occurring across different time zones. This continuous nature makes it a highly accessible market for traders worldwide.
Key Players in the Forex Market
The Forex market is characterized by a diverse range of participants, each playing a crucial role in its functioning.
- Central Banks: Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve (US) and the European Central Bank (EU), influence exchange rates through monetary policy decisions. They buy and sell currencies to manage inflation, interest rates, and economic growth.
- Commercial Banks: Commercial banks facilitate currency exchange for their clients, businesses, and individuals. They also participate in Forex trading to manage their foreign exchange exposures and generate profits.
- Investment Banks: Investment banks engage in Forex trading to facilitate international transactions for their clients, including mergers and acquisitions, and to speculate on currency movements.
- Hedge Funds: Hedge funds utilize sophisticated strategies to profit from short-term fluctuations in exchange rates. They often leverage high levels of debt to amplify their returns.
- Retail Traders: Individual traders participate in the Forex market through online brokerage platforms. They can trade currencies based on their own analysis and strategies.
Currency Pairs, Exchange Rates, and Pips
Understanding the basic concepts of currency pairs, exchange rates, and pips is essential for Forex trading.
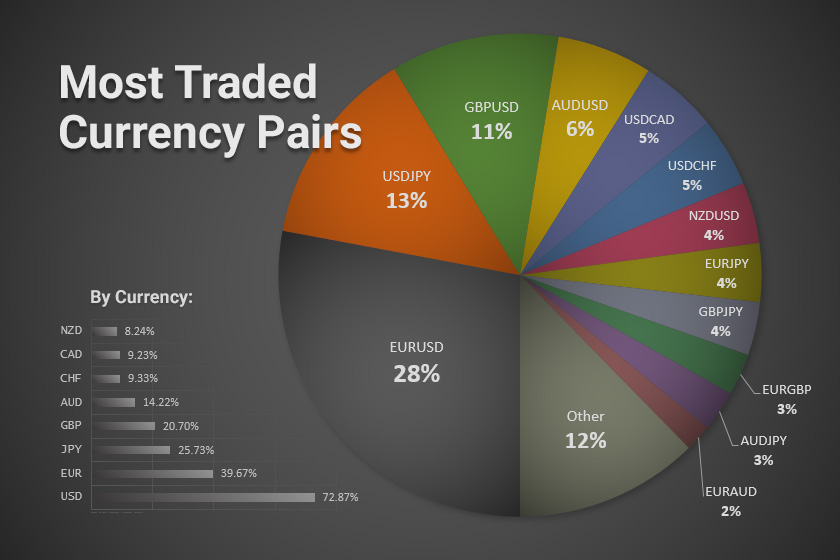
- Currency Pairs: Forex trading involves the simultaneous buying of one currency and selling of another. These pairs are typically quoted as a base currency and a quote currency. For example, the EUR/USD pair represents the exchange rate between the euro (EUR) and the US dollar (USD).
- Exchange Rates: Exchange rates reflect the value of one currency relative to another. They constantly fluctuate based on various factors, including economic data, political events, and market sentiment.
- Pips: A pip (point in percentage) is the smallest unit of change in an exchange rate. The value of a pip varies depending on the currency pair. For example, a pip in the EUR/USD pair is typically equivalent to 0.0001 USD.
For instance, if the EUR/USD exchange rate is 1.1200, a one-pip increase would result in a new rate of 1.1201.
Forex Trading Mechanics
Forex trading mechanics encompass the tools, strategies, and processes used to execute trades in the foreign exchange market. Understanding these mechanics is crucial for navigating the complexities of Forex trading and maximizing your chances of success.
Types of Forex Orders, Forex market trading
Forex orders are instructions given to a broker to buy or sell a currency pair at a specific price or under certain conditions. Different types of orders offer varying levels of control and risk management.
- Market Orders: These orders are executed immediately at the best available market price. Market orders are ideal for traders seeking quick entry or exit points, but they may result in a less favorable price than anticipated, especially during volatile market conditions.
- Limit Orders: Limit orders allow traders to set a specific price at which they are willing to buy or sell a currency pair. The order will only be executed if the market price reaches the specified limit. Limit orders offer greater control over entry and exit points, but they may not be filled if the market price never reaches the limit.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders are designed to limit potential losses on a trade. These orders are placed at a predetermined price level below the entry price for a buy order or above the entry price for a sell order. When the market price reaches the stop-loss level, the order is automatically triggered, closing the position and minimizing further losses. Stop-loss orders are essential for risk management, but they should be set at a realistic level to avoid premature exits due to market fluctuations.
Leverage in Forex Trading
Leverage is a powerful tool that allows traders to control a larger position in the market with a smaller amount of capital. It essentially amplifies both potential profits and losses.
For example, a leverage ratio of 1:100 means that a trader can control $100,000 worth of currency with only $1,000 of their own capital.
While leverage can significantly enhance returns, it also magnifies the risk of losing capital.
- Risk Management: It is crucial to use leverage responsibly and implement appropriate risk management strategies. This includes setting stop-loss orders, diversifying trades, and carefully calculating position sizes.
- Margin Requirements: Brokers typically require traders to deposit a certain amount of margin as collateral to cover potential losses. This margin requirement varies depending on the leverage ratio and the specific currency pair being traded.
Trading Platforms, Charting Tools, and Technical Indicators
Forex trading platforms are software applications that provide traders with the tools necessary to execute trades, analyze market data, and manage their accounts.
- Popular Platforms: Some popular Forex trading platforms include MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), and cTrader. These platforms offer a wide range of features, including real-time market data, charting tools, technical indicators, and automated trading capabilities.
- Charting Tools: Charting tools are essential for analyzing price movements and identifying potential trading opportunities. These tools allow traders to visualize historical price data, draw trend lines, and apply technical indicators to identify patterns and trends.
- Technical Indicators: Technical indicators are mathematical formulas that analyze historical price data to generate buy or sell signals. Popular technical indicators include moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and MACD. These indicators can help traders identify overbought or oversold conditions, identify trends, and generate trading signals.
Forex Trading Strategies
Forex trading strategies are the blueprints that traders use to make informed decisions in the market. They provide a framework for analyzing market trends, identifying potential trading opportunities, and managing risk. Two main approaches to Forex trading are fundamental analysis and technical analysis.
Fundamental Analysis and Technical Analysis
Fundamental analysis focuses on economic factors that influence currency values. This approach examines economic data, such as interest rates, inflation, government policies, and global events, to predict future currency movements. For instance, if a country’s central bank raises interest rates, it can make its currency more attractive to foreign investors, potentially leading to an appreciation in its value.
Technical analysis, on the other hand, uses historical price data and chart patterns to identify trends and predict future price movements. Technical analysts believe that past price action provides insights into market sentiment and can be used to identify trading opportunities. They employ various tools and indicators, such as moving averages, MACD, and RSI, to analyze price patterns and generate trading signals.
Technical Indicators
Technical indicators are mathematical calculations based on historical price data. They help traders identify trends, overbought/oversold conditions, and potential reversal points.
Here are some popular technical indicators:
- Moving Averages (MA): Moving averages smooth out price fluctuations, highlighting trends. Traders use different types of MAs, such as simple moving averages (SMA) and exponential moving averages (EMA), to identify support and resistance levels, trend direction, and potential buy or sell signals.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. Values above 70 are considered overbought, suggesting a potential price reversal, while values below 30 indicate oversold conditions, potentially signaling a price rebound.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator that compares two moving averages to generate buy and sell signals. Crossovers between the MACD line and signal line can indicate potential trend changes, while divergences between price action and the MACD line can signal potential reversals.
Common Forex Trading Strategies
Forex trading strategies are categorized based on their timeframes and trading styles.
- Scalping: Scalpers aim to profit from small price fluctuations in the short term, typically holding trades for a few seconds or minutes. They use technical indicators and high leverage to maximize profits from small price movements.
- Day Trading: Day traders open and close trades within a single trading day, aiming to profit from intraday price swings. They use technical analysis, charting patterns, and various indicators to identify short-term trading opportunities.
- Swing Trading: Swing traders hold trades for a few days to a few weeks, capitalizing on larger price swings and market trends. They use technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and risk management techniques to identify potential entry and exit points for their trades.
Risk Management in Forex Trading: Forex Market Trading
Risk management is an essential aspect of Forex trading. It involves strategies and techniques to control potential losses and protect your capital. By implementing effective risk management practices, you can increase your chances of long-term profitability and avoid significant financial setbacks.
Setting Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are crucial for limiting potential losses on trades. They automatically close a position when the price reaches a predetermined level, preventing further losses.
The stop-loss order should be placed at a level that represents your maximum acceptable loss for the trade. This level is typically determined based on your risk tolerance, market volatility, and the specific trading strategy. For example, if you are trading a currency pair with a 100 pip stop-loss order, the trade will automatically close if the price moves against your position by 100 pips.
Managing Position Sizes
Managing position sizes is another critical aspect of risk management. It involves determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to each trade.
Position size should be calculated based on your risk tolerance, account balance, and the potential risk of the trade. A common approach is to use a risk percentage, which represents the maximum percentage of your account balance you are willing to risk on a single trade. For instance, if you have a $10,000 account and a 2% risk tolerance, your maximum risk per trade would be $200.
Risk Management Plan
A comprehensive risk management plan should encompass your risk tolerance, capital preservation, and profit targets.
- Risk Tolerance: Determine your maximum acceptable loss per trade and your overall risk appetite. This will guide your position sizing and stop-loss order placement.
- Capital Preservation: Prioritize capital preservation by setting appropriate stop-loss orders and managing position sizes. Aim to protect your capital from significant losses.
- Profit Targets: Define your profit targets for each trade based on your trading strategy and market analysis. Setting profit targets helps you manage expectations and take profits when they are achieved.
Forex Market Trends and Factors

The Forex market is influenced by a complex interplay of economic indicators, geopolitical events, and central bank policies. Understanding these factors is crucial for traders to make informed decisions and navigate the dynamic nature of currency valuations.
Economic Indicators and Geopolitical Events
Economic indicators and geopolitical events play a significant role in shaping Forex market trends. These factors can create volatility and influence currency valuations by affecting investor sentiment, economic growth prospects, and risk appetite.
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth typically leads to currency appreciation, as investors are attracted to economies with robust performance. Conversely, weak economic growth can lead to currency depreciation.
- Inflation: High inflation can erode purchasing power and weaken a currency, as investors seek investments that can preserve value. Low inflation, on the other hand, can support currency strength.
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates attract foreign investment, as investors seek higher returns. This can lead to currency appreciation. Conversely, lower interest rates can make a currency less attractive, potentially leading to depreciation.
- Government Debt: High levels of government debt can raise concerns about a country’s financial stability, potentially leading to currency depreciation. Conversely, lower debt levels can support currency strength.
- Political Stability: Political instability, such as elections, social unrest, or conflicts, can create uncertainty and lead to currency depreciation. Conversely, stable political environments tend to support currency valuations.
- Trade Relations: Trade disputes or sanctions can impact currency valuations. For example, if a country imposes tariffs on another country’s goods, it can lead to depreciation in the currency of the country imposing the tariffs.
Central Bank Policies
Central banks play a crucial role in influencing currency valuations through their monetary policies. These policies can impact interest rates, inflation, and economic growth, which in turn affect currency movements.
- Interest Rate Changes: When central banks raise interest rates, it can make a currency more attractive to foreign investors, leading to appreciation. Conversely, lowering interest rates can weaken a currency.
- Quantitative Easing (QE): QE involves central banks injecting money into the economy by buying government bonds or other assets. This can lead to currency depreciation, as it increases the money supply and can potentially lower interest rates.
- Currency Interventions: Central banks can intervene in the Forex market to influence currency valuations. This can involve buying or selling their own currency to stabilize its value or to achieve specific economic objectives.
Economic Data Releases
Economic data releases, such as GDP figures, inflation reports, and employment data, can provide insights into the health of an economy and influence currency valuations.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): GDP growth indicates the overall economic health of a country. Strong GDP growth can support currency appreciation, while weak growth can lead to depreciation.
- Inflation Rate: Inflation data can indicate price pressures within an economy. High inflation can weaken a currency, while low inflation can support currency strength.
- Unemployment Rate: Low unemployment rates indicate a strong labor market, which can support currency appreciation. High unemployment rates can signal economic weakness and lead to depreciation.
Forex Market Trends
Forex markets exhibit various trends, which can provide valuable insights for traders. Understanding these trends can help traders identify potential trading opportunities and manage risk.
- Bull Markets: Bull markets are characterized by sustained price increases. In Forex, a bull market for a specific currency indicates that its value is rising against other currencies.
- Bear Markets: Bear markets are characterized by sustained price declines. In Forex, a bear market for a specific currency indicates that its value is falling against other currencies.
- Consolidation Periods: Consolidation periods occur when prices trade within a defined range, indicating a period of indecision or a lack of clear direction in the market. These periods can offer opportunities for traders to enter positions when a breakout or breakdown occurs.
Forex Trading Resources and Education
Navigating the Forex market can be overwhelming, especially for beginners. Accessing reliable resources and education is crucial for building a solid foundation in Forex trading. This section will guide you through finding reputable brokers, platforms, and educational materials to enhance your trading journey.
Choosing a Forex Broker
Selecting the right Forex broker is paramount for a successful trading experience. Here’s a breakdown of factors to consider:
- Regulation: Choose a broker regulated by a reputable financial authority, such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK, the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) in Australia, or the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the United States. Regulation ensures the broker adheres to specific standards, protecting your funds and ensuring fair trading practices.
- Trading Conditions: Examine the broker’s spreads, commissions, leverage, and trading platform features. Lower spreads and commissions can improve profitability, while leverage allows you to control larger positions with a smaller deposit. A user-friendly trading platform with advanced charting tools and order execution capabilities is essential.
- Customer Support: Reliable customer support is vital. Assess the broker’s availability, response time, and channels of communication (phone, email, live chat). Prompt and helpful support can resolve issues quickly and provide guidance when needed.
- Demo Account: Many brokers offer demo accounts, allowing you to practice trading in a risk-free environment. This is an excellent opportunity to test different trading strategies, familiarize yourself with the platform, and gain confidence before risking real capital.
Educational Resources
The Forex market is constantly evolving, so continuous learning is essential. Here are some resources to enhance your understanding of Forex trading:
- Books: Several reputable books delve into Forex trading strategies, risk management, and market analysis. Some popular choices include “Trading in the Zone” by Mark Douglas, “The Disciplined Trader” by Mark Douglas, and “Japanese Candlestick Charting Techniques” by Steve Nison.
- Articles: Numerous websites and financial publications offer insightful articles on Forex trading. Look for articles from established financial institutions, experienced traders, and reputable financial analysts. Websites like Investopedia, DailyFX, and ForexFactory provide valuable content.
- Online Courses: Online courses offer structured learning paths, often with interactive elements and expert guidance. Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and Babypips provide a range of Forex trading courses catering to different skill levels.
- Webinars and Podcasts: Webinars and podcasts provide valuable insights from experienced traders and industry experts. Look for webinars and podcasts hosted by reputable brokers, financial institutions, and educational platforms.
Last Word
Navigating the forex market requires a blend of knowledge, strategy, and discipline. Understanding fundamental and technical analysis, mastering risk management techniques, and choosing the right trading platform are crucial steps toward successful forex trading. By carefully evaluating market trends, economic indicators, and personal risk tolerance, traders can make informed decisions and potentially capitalize on the opportunities presented by the global currency exchange market.
Expert Answers
What is the minimum amount I need to start forex trading?
The minimum deposit requirement varies depending on the forex broker you choose. Some brokers offer micro accounts with as little as $10, while others may require a higher minimum deposit.
Is forex trading legal?
Yes, forex trading is legal in most countries. However, it is essential to choose a regulated broker to ensure your funds are protected and you are trading within a legal framework.
How much money can I make trading forex?
There is no guaranteed return on investment in forex trading. Profits depend on your trading skills, risk management, and market conditions. It’s important to approach forex trading with realistic expectations and understand that losses are possible.
Is forex trading risky?
Yes, forex trading involves significant risk. Leverage can amplify both profits and losses, making it crucial to manage risk effectively to protect your capital.
What are the best resources for learning about forex trading?
There are numerous resources available for learning forex trading, including online courses, books, articles, and educational websites. Look for reputable sources that provide comprehensive information on fundamental and technical analysis, risk management, and trading strategies.




