
Most volatile forex pairs take center stage, presenting both thrilling opportunities and significant risks. This journey into the world of high-risk trading delves into the dynamics of volatility, exploring its causes, impacts, and strategies for navigating these turbulent waters.
Understanding forex volatility is crucial for any trader, as it can lead to substantial profits or devastating losses. This guide provides insights into identifying the most volatile currency pairs, analyzing their movements, and developing effective risk management strategies. We’ll explore the factors that contribute to volatility, examine the advantages and disadvantages of trading these pairs, and learn from real-world case studies of both successful and unsuccessful trades.
Introduction to Forex Volatility
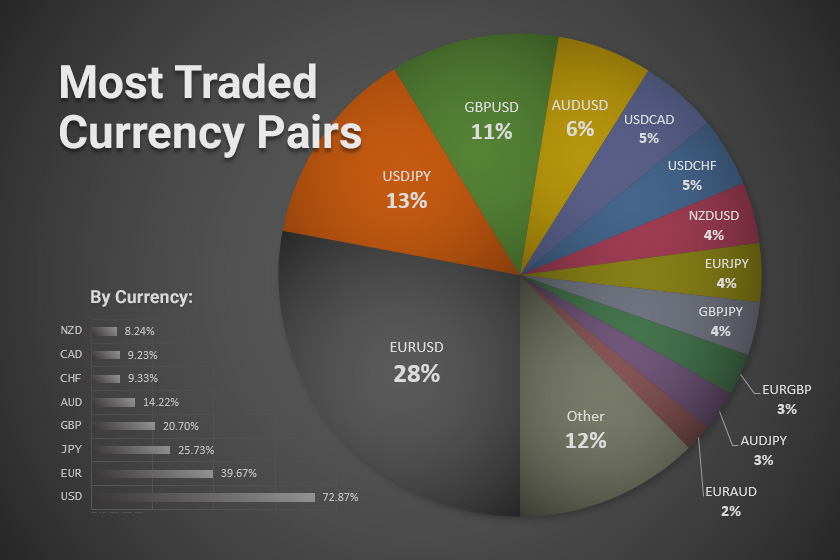
Forex volatility refers to the rate at which currency exchange rates fluctuate. It is a crucial aspect of forex trading, as it influences the potential for both profits and losses. Understanding volatility is essential for forex traders to make informed decisions and manage their risk effectively.
Forex volatility is driven by various factors, both internal and external to the financial markets. These factors can influence the supply and demand for currencies, leading to price fluctuations.
Economic Events and News, Most volatile forex pairs
Economic events and news releases have a significant impact on forex volatility. These events can be macroeconomic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation rates, interest rate decisions, and employment data. They can also include political events, natural disasters, and global economic trends.
For example, a surprise announcement of an interest rate hike by a central bank can lead to a sharp appreciation of the corresponding currency, as investors anticipate higher returns. Similarly, a negative news report about a country’s economic performance can trigger a depreciation of its currency.
Forex volatility is a double-edged sword. While it can create opportunities for traders to profit from price fluctuations, it also increases the risk of losses.
Identifying the Most Volatile Forex Pairs
Volatility in forex trading is a crucial factor that traders need to consider. Highly volatile currency pairs offer the potential for significant profits, but also come with increased risk. Understanding which currency pairs are the most volatile can help traders make informed decisions about their trading strategies.
Average Daily Volatility of Major Currency Pairs
This table showcases the average daily volatility of major currency pairs over a specific period, calculated using the standard deviation of daily price changes.
| Currency Pair | Average Daily Volatility |
|---|---|
| EUR/USD | 0.65% |
| USD/JPY | 0.58% |
| GBP/USD | 0.72% |
| AUD/USD | 0.81% |
| NZD/USD | 0.85% |
| USD/CHF | 0.52% |
| EUR/GBP | 0.54% |
| USD/CAD | 0.61% |
Calculating Volatility
Volatility is typically measured using statistical methods like standard deviation and Average True Range (ATR).
Standard Deviation
Standard deviation measures the dispersion of data points around the mean. A higher standard deviation indicates greater volatility.
Standard Deviation = √(∑(x – μ)2 / (n – 1))
where:
– x is the price of the currency pair at a given time
– μ is the mean price of the currency pair
– n is the number of data points
Average True Range (ATR)
ATR measures the average price movement of a currency pair over a specified period, typically 14 days. It takes into account the true range of price fluctuations, which is the greatest of the following:
– Current High – Current Low
– Absolute value of (Current High – Previous Close)
– Absolute value of (Current Low – Previous Close)
ATR = (TR1 + TR2 + … + TRn) / n
where:
– TRi is the true range for the i-th period
– n is the number of periods (typically 14)
Currency Pair Overview and Economic Factors
Each currency pair’s volatility is influenced by various economic factors, including:
EUR/USD
– The Euro is the official currency of the Eurozone, which includes 19 European countries.
– The US Dollar is the official currency of the United States.
– Economic factors affecting EUR/USD volatility include:
– Interest rate differentials between the Eurozone and the United States
– Economic growth and inflation in both regions
– Political stability in Europe
USD/JPY
– The US Dollar is the official currency of the United States.
– The Japanese Yen is the official currency of Japan.
– Economic factors affecting USD/JPY volatility include:
– Interest rate differentials between the United States and Japan
– Safe-haven demand for the Japanese Yen during times of global uncertainty
– Japan’s trade balance and economic growth
GBP/USD
– The British Pound Sterling is the official currency of the United Kingdom.
– The US Dollar is the official currency of the United States.
– Economic factors affecting GBP/USD volatility include:
– Interest rate differentials between the United Kingdom and the United States
– The UK’s economic growth and Brexit-related uncertainties
– The performance of the UK’s financial sector
AUD/USD
– The Australian Dollar is the official currency of Australia.
– The US Dollar is the official currency of the United States.
– Economic factors affecting AUD/USD volatility include:
– Australia’s commodity prices, particularly iron ore and coal
– Interest rate differentials between Australia and the United States
– China’s economic growth, as Australia is a major exporter to China
NZD/USD
– The New Zealand Dollar is the official currency of New Zealand.
– The US Dollar is the official currency of the United States.
– Economic factors affecting NZD/USD volatility include:
– New Zealand’s dairy and tourism industries
– Interest rate differentials between New Zealand and the United States
– China’s economic growth, as New Zealand is a major exporter to China
USD/CHF
– The US Dollar is the official currency of the United States.
– The Swiss Franc is the official currency of Switzerland.
– Economic factors affecting USD/CHF volatility include:
– Safe-haven demand for the Swiss Franc during times of global uncertainty
– Interest rate differentials between the United States and Switzerland
– Switzerland’s economic growth and inflation
EUR/GBP
– The Euro is the official currency of the Eurozone, which includes 19 European countries.
– The British Pound Sterling is the official currency of the United Kingdom.
– Economic factors affecting EUR/GBP volatility include:
– Interest rate differentials between the Eurozone and the United Kingdom
– Economic growth and inflation in both regions
– Brexit-related uncertainties
USD/CAD
– The US Dollar is the official currency of the United States.
– The Canadian Dollar is the official currency of Canada.
– Economic factors affecting USD/CAD volatility include:
– Oil prices, as Canada is a major oil producer
– Interest rate differentials between the United States and Canada
– The Canadian economy’s performance, particularly in the manufacturing and housing sectors
Understanding the Dynamics of Volatility
Volatility is a key aspect of the forex market and directly impacts trading opportunities. It refers to the degree of price fluctuations in a currency pair over a specific period. Understanding volatility is crucial for traders because it influences risk and potential profit.
Volatility can be influenced by various factors, including economic news releases, political events, and market sentiment. High volatility can lead to significant price swings, offering traders the chance to capitalize on quick and substantial movements. However, it also comes with increased risk, as losses can be just as substantial as profits.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Trading High-Volatility Pairs
Trading high-volatility pairs can offer significant advantages and disadvantages. It’s important to understand both sides before engaging in such trading.
- Advantages:
- Greater profit potential: High volatility creates opportunities for quick and significant price movements, allowing traders to potentially realize larger profits.
- Faster trading: The rapid price fluctuations allow for shorter-term trading strategies, enabling traders to enter and exit positions quickly.
- Increased trading opportunities: High volatility generates more trading signals and opportunities, allowing traders to participate in the market more frequently.
- Disadvantages:
- Higher risk: The rapid price swings in high-volatility pairs can lead to significant losses, especially if trades are not managed properly.
- Increased stress: The fast-paced nature of trading high-volatility pairs can be stressful, requiring constant monitoring and quick decision-making.
- Higher trading costs: Frequent trading can lead to higher trading costs, including commissions and spreads.
Trading Strategies that Exploit Volatility
Several trading strategies can be employed to capitalize on high volatility in the forex market.
- Scalping: This strategy involves taking advantage of small price fluctuations by entering and exiting trades quickly, aiming to profit from minor price movements.
- News Trading: This strategy involves trading based on the release of economic news data, which can significantly impact currency prices.
- Breakout Trading: This strategy focuses on identifying and trading breakouts from price consolidation patterns, which can occur during periods of high volatility.
Risk Management in Volatile Markets
Navigating the turbulent waters of volatile Forex pairs requires a robust risk management strategy. This strategy should be tailored to the unique characteristics of these high-fluctuation markets, emphasizing control and minimizing potential losses.
Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are essential for managing risk in volatile markets. They act as automatic safeguards, exiting a trade when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.
- Setting Appropriate Levels: Stop-loss levels should be strategically placed, taking into account the volatility of the pair and the trader’s risk tolerance.
- Trailing Stop-Loss Orders: Trailing stop-loss orders dynamically adjust the stop-loss level as the price moves in the trader’s favor, protecting profits while allowing for potential upside movement.
Position Sizing
Position sizing is the art of determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to a trade. It plays a crucial role in risk management, ensuring that potential losses remain within acceptable limits.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: A common approach is to calculate the risk-reward ratio, which compares the potential profit to the potential loss. A favorable risk-reward ratio, such as 1:2 or 1:3, suggests that the potential reward outweighs the potential risk.
- Percentage of Account: Another approach is to allocate a specific percentage of the trading account to each trade, typically 1-2%. This ensures that even if a trade goes against the trader, the overall account balance is not significantly impacted.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis provides valuable insights into price movements, helping traders identify potential entry and exit points in volatile markets.
- Trend Lines: Trend lines connect a series of price points, revealing the direction of the underlying trend. Breakouts from established trend lines can signal significant price movements.
- Moving Averages: Moving averages smooth out price fluctuations, providing a clearer view of the underlying trend. Crossovers between different moving averages can indicate potential trend reversals.
- Oscillators: Oscillators measure the momentum of price movements, helping traders identify overbought or oversold conditions.
Case Studies of High-Volatility Trading
Understanding the dynamics of volatile markets is essential, but real-world examples provide valuable insights into the complexities and potential outcomes of high-volatility trading. Analyzing successful and unsuccessful trades allows traders to learn from past experiences and refine their strategies.
Successful Trade Case Study
This case study examines a successful trade during the 2020 US Presidential Election.
The trader identified a potential opportunity in the GBP/USD pair due to the high volatility expected during the election results. The trader anticipated that a Biden victory would weaken the US dollar and strengthen the British pound, based on the potential impact on trade relations and global economic sentiment.
The trader executed a long position in GBP/USD, buying at 1.3000 and setting a take-profit order at 1.3200 and a stop-loss order at 1.2800.
The election results, as anticipated, led to a surge in the GBP/USD pair, reaching a high of 1.3150 before settling at 1.3200. The trader’s take-profit order was triggered, resulting in a successful trade.
The key factors contributing to the success of this trade include:
- Accurate market analysis and identification of a potential opportunity
- Well-defined risk management strategies with stop-loss orders
- Understanding the potential impact of the election results on the currency pair
Unsuccessful Trade Case Study
This case study explores an unsuccessful trade during the 2015 Swiss National Bank (SNB) decision to remove the euro-franc floor.
The trader believed that the SNB would maintain the floor and entered a long position in EUR/CHF, anticipating a strengthening of the euro against the Swiss franc.
The SNB’s unexpected decision to remove the floor led to a sharp decline in the EUR/CHF pair, resulting in a significant loss for the trader.
The factors contributing to the unsuccessful trade include:
- Lack of understanding of the potential impact of the SNB’s decision on the currency pair
- Insufficient risk management strategies, with no stop-loss orders in place
- Underestimating the potential for unexpected market events
Final Conclusion: Most Volatile Forex Pairs
Mastering the art of trading volatile forex pairs requires a blend of knowledge, discipline, and a keen understanding of market dynamics. By combining a thorough analysis of economic indicators, technical patterns, and risk management principles, traders can navigate the complexities of volatile markets and potentially capitalize on the opportunities they present. Remember, trading volatile pairs is not for the faint of heart, but with careful planning and execution, it can be a rewarding endeavor.
Questions and Answers
What are the most volatile forex pairs?
The most volatile forex pairs typically include those involving emerging market currencies like the Turkish Lira (TRY), South African Rand (ZAR), and Mexican Peso (MXN). However, volatility can fluctuate based on economic events and market sentiment.
How can I manage risk when trading volatile forex pairs?
Implementing a robust risk management strategy is essential. This includes using stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, setting appropriate position sizes, and diversifying your portfolio across different assets.
What are some trading strategies for volatile forex pairs?
Popular strategies include scalping, day trading, and swing trading. Scalping involves taking advantage of small price fluctuations, while day trading focuses on intraday movements. Swing trading involves holding positions for longer periods, capturing larger price swings.




