
Trade forex, the global marketplace for exchanging currencies, offers exciting opportunities for investors and traders alike. It’s a dynamic world where economic forces, political events, and market sentiment constantly influence currency values. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or a curious beginner, understanding the fundamentals of forex trading is essential to navigating this complex but rewarding landscape.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of forex trading, covering everything from basic concepts to advanced strategies. We’ll explore the mechanics of buying and selling currencies, analyze factors that drive price movements, and equip you with the knowledge and tools to make informed trading decisions.
What is Forex Trading?
Forex trading, short for foreign exchange trading, is the act of buying and selling currencies in the global marketplace. It’s like exchanging one type of money for another, but on a much larger scale. Imagine you’re traveling to another country and need to convert your dollars to euros. That’s essentially what forex trading is, except it’s done electronically and involves large amounts of money.
The Difference Between Forex Trading and Other Types of Trading
Forex trading is distinct from other types of trading, such as stock trading or commodity trading. Here’s why:
- Decentralized Market: Unlike stock markets, which operate through exchanges, the forex market is decentralized. This means there’s no single location or authority that controls trading. Instead, transactions occur directly between participants, typically through banks, brokers, or other financial institutions.
- High Liquidity: The forex market is the most liquid financial market globally. This means there’s always a buyer and seller for any currency, making it easy to enter and exit trades. This high liquidity also contributes to the market’s volatility.
- Trading Pairs: Forex trading involves trading currency pairs, such as the EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar) or GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen). The value of one currency is expressed relative to the other, and traders profit from fluctuations in the exchange rate.
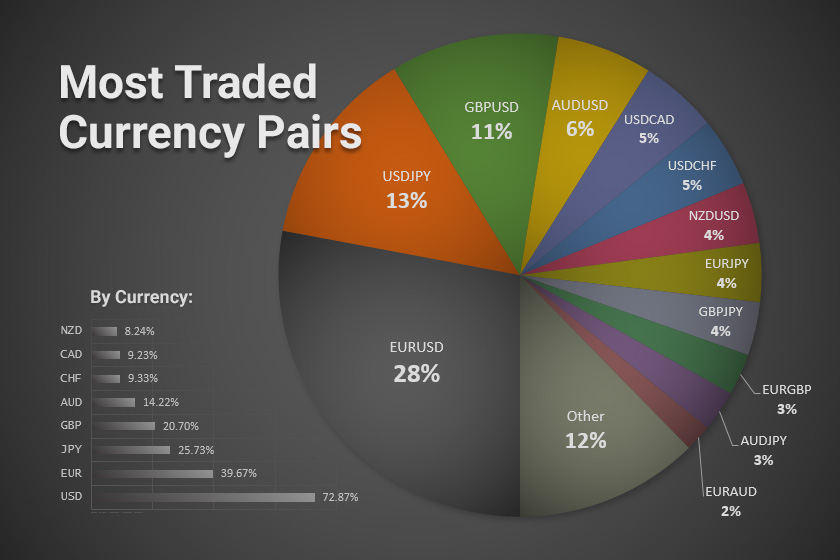
Examples of Major Currency Pairs
The forex market offers a wide range of currency pairs to trade. Here are some of the most popular and widely traded pairs:
- EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar): This is the most traded currency pair globally, representing about 25% of all forex transactions. It’s considered a highly liquid and volatile pair, often influenced by economic events in the Eurozone and the United States.
- USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen): This pair is known for its sensitivity to global risk appetite. When investors are risk-averse, they tend to buy the Japanese Yen, considered a safe-haven currency. This often leads to a decline in the USD/JPY exchange rate.
- GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar): The GBP/USD pair is influenced by economic developments in the UK and the US. It’s also impacted by Brexit-related news and events.
- AUD/USD (Australian Dollar/US Dollar): This pair is often seen as a proxy for commodity prices, particularly gold and iron ore, as Australia is a major exporter of these commodities.
How Forex Trading Works: Trade Forex
The forex market is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with trillions of dollars changing hands every day. To understand how forex trading works, it’s crucial to grasp the basic mechanics of buying and selling currencies, the role of leverage, and the different types of orders available.
Buying and Selling Currencies
Forex trading involves exchanging one currency for another. Each currency pair is quoted as a rate, with the first currency being the base currency and the second currency being the quote currency. For example, the EUR/USD currency pair represents the exchange rate between the euro (EUR) and the US dollar (USD).
To buy a currency pair, you are essentially buying the base currency and selling the quote currency. Conversely, to sell a currency pair, you are selling the base currency and buying the quote currency. The profit or loss on a forex trade is determined by the difference between the entry price and the exit price, taking into account the exchange rate fluctuations.
Leverage in Forex Trading
Leverage is a powerful tool that allows traders to control a larger position in the market with a smaller amount of capital. It essentially magnifies both potential profits and losses. Forex brokers typically offer leverage ratios, which represent the amount of money a trader can control for every dollar they invest.
For example, a leverage ratio of 1:100 means that a trader can control $100,000 worth of currency with an initial investment of only $1,000. While leverage can amplify profits, it can also amplify losses, making risk management crucial.
Forex Orders
Forex traders can place different types of orders to execute trades. Here are some common order types:
- Market Order: A market order is executed immediately at the best available price in the market. It is used when traders want to enter or exit a trade quickly, but they may not get the exact price they want.
- Limit Order: A limit order is an order to buy or sell a currency pair at a specific price or better. This type of order is used when traders want to enter or exit a trade at a particular price level. If the market price reaches the limit price, the order will be executed.
- Stop-Loss Order: A stop-loss order is an order to automatically sell or buy a currency pair when the market price reaches a specific level. This type of order is used to limit potential losses on a trade. When the market price hits the stop-loss price, the order is triggered, and the trade is closed, regardless of the current market conditions.
Factors Influencing Forex Rates
Forex rates, also known as exchange rates, are constantly fluctuating due to a complex interplay of economic, political, and social factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for traders to make informed decisions and potentially profit from currency movements.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators provide valuable insights into the health of a country’s economy, which directly influences its currency’s value. Key indicators that impact forex rates include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): GDP measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders. A strong GDP growth rate typically indicates a healthy economy and can lead to a stronger currency. For example, a country with a high GDP growth rate might attract foreign investment, increasing demand for its currency and pushing its value higher.
- Inflation: Inflation refers to the rate at which prices for goods and services rise over time. High inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, making it less attractive to investors and potentially weakening its value. For instance, if a country experiences high inflation, its currency may depreciate against currencies with lower inflation rates.
- Interest Rates: Central banks often adjust interest rates to control inflation and stimulate economic growth. Higher interest rates generally attract foreign investment, as investors seek higher returns. This increased demand for the currency can lead to appreciation. Conversely, lower interest rates can make a currency less attractive, potentially causing depreciation.
- Unemployment Rate: A low unemployment rate indicates a strong economy, as more people are employed and contributing to economic activity. This can lead to a stronger currency, as it signals a healthy labor market and potential for future growth. Conversely, a high unemployment rate can indicate economic weakness, potentially weakening the currency.
- Trade Balance: The trade balance reflects the difference between a country’s exports and imports. A trade surplus (exports exceeding imports) suggests a strong economy and can boost currency value. Conversely, a trade deficit (imports exceeding exports) can weaken the currency.
Political Events and News
Political events and news can significantly influence forex rates by impacting investor sentiment and economic stability. Here are some examples:
- Government Policies: Changes in government policies, such as tax reforms, trade agreements, or regulatory changes, can impact a country’s economic outlook and currency value. For instance, a government’s decision to implement stricter regulations on foreign investment might discourage investors, leading to a weaker currency.
- Political Instability: Political instability, such as riots, protests, or elections, can create uncertainty and volatility in the market, impacting investor confidence and potentially weakening the currency. For example, a country facing political unrest might experience a decline in its currency value as investors seek safer investments.
- Geopolitical Events: Global events, such as wars, natural disasters, or international sanctions, can significantly impact forex rates. For example, a major geopolitical conflict could lead to increased demand for safe-haven currencies like the US dollar, causing other currencies to depreciate.
Interest Rates and Currency Exchange Rates
There is a strong relationship between interest rates and currency exchange rates. Higher interest rates generally attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the currency and pushing its value higher. This is because investors seek higher returns on their investments, and a country with higher interest rates offers a more attractive opportunity.
Higher interest rates = Increased demand for currency = Currency appreciation
Conversely, lower interest rates can make a currency less attractive, potentially causing depreciation. Investors may choose to invest in countries with higher interest rates, reducing demand for the currency with lower rates.
Lower interest rates = Decreased demand for currency = Currency depreciation
However, it’s important to note that other factors, such as economic growth, inflation, and political stability, can also influence the relationship between interest rates and currency exchange rates.
Forex Trading Strategies

Forex trading strategies are the plans and methods that traders use to identify potential trading opportunities and execute trades in the foreign exchange market. These strategies can range from simple to complex, and each one is designed to capitalize on different market conditions and trader preferences.
Comparison of Forex Trading Strategies
Different forex trading strategies cater to varying risk appetites, time commitments, and market analysis approaches. Here’s a comparison of three popular strategies:
- Scalping: This strategy involves making numerous small profits from small price fluctuations in a short period. Scalpers typically hold trades for seconds or minutes, aiming to capitalize on short-term market movements. This strategy requires high levels of technical analysis and fast execution speed. Scalping is suitable for traders with a high risk tolerance and who can dedicate significant time to monitoring the market.
- Day Trading: Day traders aim to profit from intraday price movements by opening and closing positions within the same trading day. They analyze charts and news events to identify trading opportunities and typically use technical indicators and analysis tools to guide their decisions. Day trading requires active monitoring of the market and can involve higher risk due to the potential for rapid price fluctuations. It is suitable for traders who have the time and resources to dedicate to active trading during market hours.
- Swing Trading: Swing traders hold positions for longer periods, typically days or weeks, aiming to capture larger price swings in the market. They analyze trends and use technical indicators to identify potential entry and exit points. Swing trading is less demanding on time commitment compared to scalping and day trading but requires a deeper understanding of market dynamics and risk management. It is suitable for traders who prefer a more relaxed trading style and are comfortable with holding positions for extended periods.
Simple Forex Trading Strategy for Beginners
A simple forex trading strategy for beginners can be based on trend following, using moving averages to identify market direction. This strategy can be applied to any currency pair and can be adapted to different timeframes.
A moving average is a technical indicator that smooths out price data by calculating the average price over a specific period.
Here’s a basic example:
1. Choose a currency pair, for example, EUR/USD.
2. Select a timeframe, for example, a 4-hour chart.
3. Apply a 20-period moving average to the chart.
4. Buy when the price crosses above the moving average, indicating an upward trend.
5. Sell when the price crosses below the moving average, indicating a downward trend.
6. Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and take-profit orders to lock in profits.
This strategy is relatively straightforward and can be a good starting point for beginners. However, it is essential to remember that no trading strategy guarantees success.
Importance of Risk Management in Forex Trading
Risk management is crucial for any forex trader, regardless of their experience level. It involves strategies and techniques designed to protect capital and limit potential losses.
- Stop-loss orders: Stop-loss orders are essential for limiting potential losses on trades. They automatically close a position when the price reaches a predetermined level, preventing further losses.
- Position sizing: Position sizing refers to determining the amount of capital to allocate to each trade. It is important to risk only a small percentage of your capital on each trade to avoid significant losses.
- Diversification: Diversification involves spreading your trades across multiple currency pairs or trading strategies to reduce risk. It helps to mitigate the impact of losses on any single trade.
- Risk-reward ratio: The risk-reward ratio measures the potential profit compared to the potential loss on a trade. A favorable risk-reward ratio ensures that potential profits outweigh potential losses.
By implementing effective risk management techniques, traders can significantly reduce their exposure to losses and improve their overall trading performance.
Tools and Resources for Forex Traders

Forex trading is a complex endeavor, requiring a combination of technical and fundamental analysis to make informed trading decisions. To navigate the intricacies of the forex market, traders rely on a range of tools and resources that provide valuable insights and support their trading strategies.
Technical Analysis Tools
Technical analysis involves studying past price movements and trading patterns to identify trends and predict future price action. Technical analysts use various tools and indicators to interpret market data and generate trading signals.
- Charting Software: Charting software is essential for visualizing price data and analyzing market trends. These platforms offer various chart types, drawing tools, and indicators that allow traders to identify patterns, support and resistance levels, and generate buy or sell signals. Popular charting software includes TradingView, MetaTrader 4 (MT4), and MetaTrader 5 (MT5).
- Technical Indicators: Technical indicators are mathematical formulas that are applied to price data to generate buy or sell signals. These indicators can help traders identify overbought or oversold conditions, momentum shifts, and trend changes. Some commonly used technical indicators include:
- Moving Averages (MAs): MAs smooth out price fluctuations and identify trend direction.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): RSI measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions.
- Bollinger Bands: Bollinger Bands are volatility indicators that show the range of price fluctuations.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): MACD identifies trend changes and potential reversals.
Fundamental Analysis Resources
Fundamental analysis focuses on economic factors and events that influence currency values. Fundamental analysts study economic data, political developments, and other macroeconomic factors to assess the health of an economy and its impact on currency exchange rates.
- Economic Calendars: Economic calendars list upcoming economic releases, such as inflation reports, interest rate decisions, and employment data. These releases can significantly impact currency values and provide trading opportunities.
- News Websites: Staying informed about global economic events is crucial for fundamental analysis. News websites such as Bloomberg, Reuters, and Financial Times provide real-time news updates and expert analysis on economic developments.
- Central Bank Statements: Central banks play a significant role in influencing currency values through interest rate decisions and monetary policy announcements. Monitoring central bank statements and press conferences can provide valuable insights into future currency movements.
Forex Broker Comparison
Forex brokers facilitate trading in the forex market by providing platforms, tools, and execution services. Choosing the right forex broker is essential for successful forex trading. Here’s a table comparing different forex brokers based on their features:
| Broker | Minimum Deposit | Spreads | Trading Platforms | Regulation | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FXTM | $10 | Variable | MT4, MT5 | CySEC, FCA | Educational resources, demo account, copy trading |
| XM | $5 | Variable | MT4, MT5 | CySEC, ASIC | Welcome bonus, zero commission, multiple account types |
| Exness | $1 | Variable | MT4, MT5 | CySEC, FCA | High leverage, fast execution, low spreads |
| AvaTrade | $100 | Variable | MT4, MT5, AvaTradeGO | Central Bank of Ireland, ASIC | Copy trading, social trading, multiple account types |
Risks and Rewards of Forex Trading
Forex trading, while potentially lucrative, comes with inherent risks. Understanding these risks and implementing proper risk management strategies is crucial for successful and sustainable trading.
Understanding Forex Trading Risks
Forex trading involves the exchange of currencies, and the value of these currencies constantly fluctuates. This volatility creates opportunities for profit but also exposes traders to significant losses. The following are some of the key risks associated with forex trading:
- Market Volatility: Currency prices can move rapidly and unpredictably, leading to sudden and substantial losses. This is particularly true during periods of economic uncertainty, political instability, or major news events.
- Leverage: Forex trading often involves leverage, which amplifies both profits and losses. While leverage can enhance returns, it also increases the potential for significant losses if the market moves against the trader’s position.
- Liquidity Risk: In some currency pairs, liquidity can be limited, especially during periods of high volatility. This can make it difficult to enter or exit trades at desired prices, potentially resulting in slippage or missed opportunities.
- Counterparty Risk: Forex trading typically involves dealing with brokers or other financial institutions. If these entities become insolvent, traders may lose their investments.
Importance of Risk Management
Risk management is an essential aspect of forex trading. It involves strategies and techniques designed to minimize potential losses and protect trading capital.
- Defining Risk Tolerance: Before engaging in forex trading, traders should determine their risk tolerance. This involves assessing how much potential loss they are comfortable with.
- Setting Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders automatically exit a trade when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.
- Position Sizing: Proper position sizing involves determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to each trade, based on risk tolerance and account size.
- Diversification: Diversifying trading across multiple currency pairs can help to mitigate risk by reducing exposure to any single market.
Mitigating Losses in Forex Trading, Trade forex
While forex trading involves risks, there are strategies that traders can implement to mitigate potential losses:
- Thorough Research and Analysis: Understanding market fundamentals, economic indicators, and technical analysis can help traders make informed trading decisions.
- Developing a Trading Plan: Having a well-defined trading plan that Artikels entry and exit strategies, risk management measures, and profit targets can help traders stay disciplined and avoid emotional trading.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: The forex market is constantly evolving. Traders should continuously learn and adapt their strategies to stay ahead of market trends and changes.
- Seeking Professional Guidance: Consulting with experienced forex traders or financial advisors can provide valuable insights and guidance.
Getting Started with Forex Trading
Ready to dive into the world of Forex trading? This section will guide you through the initial steps to open a trading account and begin your journey. We’ll cover essential aspects like choosing a reputable broker and placing your first trade.
Opening a Forex Trading Account
Opening a Forex trading account is your gateway to the global currency market. This process is relatively straightforward and can be completed online. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Choose a Forex Broker: The first step is selecting a reputable Forex broker. This broker acts as your intermediary, providing you with a platform to execute trades. We’ll delve into choosing a broker in the next section.
- Fill Out an Application: Once you’ve chosen a broker, you’ll need to fill out an application form. This typically involves providing personal information, such as your name, address, and contact details. You may also be asked for your financial background and trading experience.
- Fund Your Account: After your application is approved, you’ll need to deposit funds into your trading account. The minimum deposit requirement varies depending on the broker.
- Verify Your Identity: For security and regulatory compliance, you’ll need to verify your identity by providing documents like a passport or driver’s license.
- Start Trading: Once your account is funded and verified, you’re ready to start trading Forex. Your broker will provide you with a trading platform, which allows you to access real-time market data, place orders, and manage your trades.
Choosing a Reputable Forex Broker
Selecting the right Forex broker is crucial for your success. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Regulation: Ensure your chosen broker is regulated by a reputable financial authority. This provides an extra layer of protection for your funds and ensures the broker adheres to industry standards.
- Trading Platform: The trading platform should be user-friendly, provide real-time market data, and offer a range of order types. Look for platforms that offer advanced charting tools and analytical features.
- Spreads and Commissions: Spreads are the difference between the buy and sell price of a currency pair. Lower spreads mean lower trading costs. Also, consider any commissions charged by the broker.
- Customer Support: Reliable customer support is essential, especially when you’re new to Forex trading. Look for brokers with responsive and knowledgeable support teams available via phone, email, or live chat.
- Education and Resources: A good broker should provide educational resources, including tutorials, webinars, and market analysis, to help you improve your trading skills.
Placing Your First Forex Trade
Ready to take the plunge? Placing your first Forex trade is simple once you’ve opened an account and understand the basics. Here’s a breakdown:
- Choose a Currency Pair: Forex trading involves buying one currency and selling another. Each pair is represented by a three-letter code, such as EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar). Choose a currency pair you want to trade based on your analysis and strategy.
- Set Your Order Type: There are two main types of orders: market orders and limit orders. A market order executes immediately at the current market price. A limit order specifies a price you’re willing to buy or sell at.
- Determine Your Trade Size: The trade size is the amount of currency you want to buy or sell. This should be based on your risk tolerance and capital.
- Set Your Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels: Stop-loss orders automatically close your trade if the price moves against you, limiting your potential losses. Take-profit orders automatically close your trade when the price reaches a predetermined profit target.
- Place Your Order: Once you’ve set your order parameters, you can place your trade through your broker’s platform.
Example: Let’s say you believe the Euro is going to strengthen against the US Dollar. You decide to buy EUR/USD. You place a market order to buy 1,000 Euros at the current market price. You also set a stop-loss order at 1.1000 and a take-profit order at 1.1200. If the Euro strengthens, your take-profit order will be triggered, and your trade will close automatically. If the Euro weakens, your stop-loss order will trigger, limiting your potential losses.
Summary
Mastering the art of forex trading requires a blend of knowledge, discipline, and risk management. By understanding the underlying principles, analyzing market trends, and employing effective strategies, you can navigate the world of currency trading with confidence. This guide has provided you with a solid foundation, but remember that continuous learning and adaptation are key to success in this ever-evolving market.
Popular Questions
What is the minimum amount I need to start trading forex?
The minimum deposit required to start trading forex varies depending on the broker you choose. Some brokers may offer micro-accounts with as little as $5 or $10, while others may require a higher minimum deposit. It’s essential to research and compare different brokers before making a decision.
How can I learn more about forex trading after reading this guide?
There are numerous resources available for further learning, including online courses, books, webinars, and trading communities. You can also find valuable information on reputable forex websites and blogs.
Is forex trading legal?
Forex trading is legal in most countries, but it’s important to ensure that the broker you choose is regulated and licensed by the appropriate authorities.




