
Electric power companies in Texas play a vital role in powering the state’s booming economy and diverse population. From the sprawling urban centers to the vast rural landscapes, Texas relies heavily on a complex network of electricity generation, transmission, and distribution. This intricate system, governed by a unique regulatory framework, encompasses a variety of players, including investor-owned utilities, cooperatives, and municipal utilities, each contributing to the overall energy landscape.
The Texas electric power industry faces numerous challenges and opportunities, ranging from ensuring grid reliability and resilience in the face of extreme weather events to navigating the transition towards a more sustainable energy future. Understanding the dynamics of this sector is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers alike, as it directly impacts energy costs, environmental concerns, and the overall economic well-being of the state.
Overview of Electric Power Companies in Texas

Texas boasts a unique and dynamic electric power industry, characterized by a competitive market structure and a robust generation capacity. The state’s electricity sector is largely deregulated, allowing consumers to choose their electricity providers from a diverse range of companies. This competitive landscape has led to a variety of players vying for market share, resulting in a complex and multifaceted industry.
Key Players and Market Share
The Texas electric power industry is dominated by a few major players, with the largest being:
- Exelon Generation Company LLC: Exelon Generation is a subsidiary of Exelon Corporation, a Fortune 100 company, and one of the largest energy producers in the United States. It operates numerous power plants across Texas, including nuclear, natural gas, and coal-fired facilities. Exelon Generation holds a significant market share in the state, supplying electricity to millions of Texans.
- NRG Energy, Inc.: NRG Energy is a leading integrated power company with a diverse portfolio of power generation assets, including natural gas, coal, and renewable energy sources. NRG Energy operates several power plants in Texas, contributing significantly to the state’s electricity generation capacity.
- Vistra Energy Corp.: Vistra Energy is another major player in the Texas electric power market, operating a wide range of power generation assets, including coal, natural gas, and nuclear power plants. Vistra Energy is a major supplier of electricity to businesses and residential customers in Texas.
These companies, along with other smaller players, compete fiercely for customers in the deregulated Texas market. This competition has driven down electricity prices for consumers, leading to lower energy costs compared to other states with regulated markets.
Regulatory Framework, Electric power companies in texas
The Texas electric power industry is governed by the Public Utility Commission of Texas (PUCT), which is responsible for regulating the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity in the state. The PUCT plays a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and affordability of electricity for Texans. The regulatory framework in Texas emphasizes competition and consumer choice, allowing for a diverse range of electricity providers to operate in the market.
Types of Electric Power Companies
Texas is home to a variety of electric power companies, each with its own unique characteristics and operating model. These companies can be broadly classified into three main categories:
- Investor-Owned Utilities (IOUs): IOUs are privately owned companies that generate, transmit, and distribute electricity to customers. They are regulated by the PUCT and are required to provide reliable and affordable electricity to their customers. Examples of IOUs operating in Texas include:
- Oncor Electric Delivery Company LLC: Oncor is the largest electric transmission and distribution company in Texas, serving over 10 million customers.
- CenterPoint Energy, Inc.: CenterPoint Energy is a diversified energy company that operates in several states, including Texas. In Texas, CenterPoint Energy provides natural gas and electric service to customers in the Houston metropolitan area.
- Electric Cooperatives: Electric cooperatives are non-profit organizations owned and controlled by their members, who are also their customers. They are typically located in rural areas and provide electricity to their members at cost. Examples of electric cooperatives operating in Texas include:
- Brazos Electric Power Cooperative, Inc.: Brazos Electric is a generation and transmission cooperative that provides wholesale electricity to its member cooperatives.
- Pedernales Electric Cooperative, Inc.: Pedernales Electric is a distribution cooperative that provides retail electricity service to over 300,000 customers in central Texas.
- Municipal Utilities: Municipal utilities are owned and operated by cities or towns. They are typically regulated by local governments and provide electricity to residents within their jurisdiction. Examples of municipal utilities operating in Texas include:
- City of Austin Energy: Austin Energy is the municipally owned electric utility that serves the city of Austin and surrounding areas.
- City of San Antonio Public Service Board: CPS Energy is the municipally owned electric and gas utility that serves the city of San Antonio.
Generation and Transmission of Electricity
Texas’s electric power system is vast and complex, encompassing various sources of electricity generation and a robust transmission infrastructure. Understanding the intricacies of this system is crucial to appreciating the challenges and opportunities associated with supplying electricity to the state’s rapidly growing population.
Sources of Electricity Generation
Texas boasts a diverse portfolio of electricity generation sources, including fossil fuels, renewable energy, and nuclear power.
- Fossil Fuels: Fossil fuels remain the dominant source of electricity generation in Texas, accounting for the majority of the state’s energy mix. Natural gas, coal, and oil are the primary fossil fuels used in power plants. Natural gas is particularly prominent, fueled by the state’s abundant natural gas reserves.
- Renewable Energy: Texas is rapidly expanding its renewable energy capacity, with solar and wind energy playing significant roles.
- Solar Energy: The state’s abundant sunshine makes solar energy a highly viable option. Large-scale solar farms are increasingly being constructed across Texas, contributing to the state’s renewable energy goals.
- Wind Energy: Texas is a leader in wind energy generation, with vast stretches of open land ideal for wind turbines. The state’s wind farms generate significant amounts of electricity, contributing to a cleaner energy mix.
- Nuclear Power: Nuclear power plants play a role in Texas’s energy mix, providing a reliable and baseload source of electricity.
Transmission Infrastructure
Texas’s electric grid is vast and complex, encompassing a network of high-voltage transmission lines that transport electricity from power plants to consumers across the state.
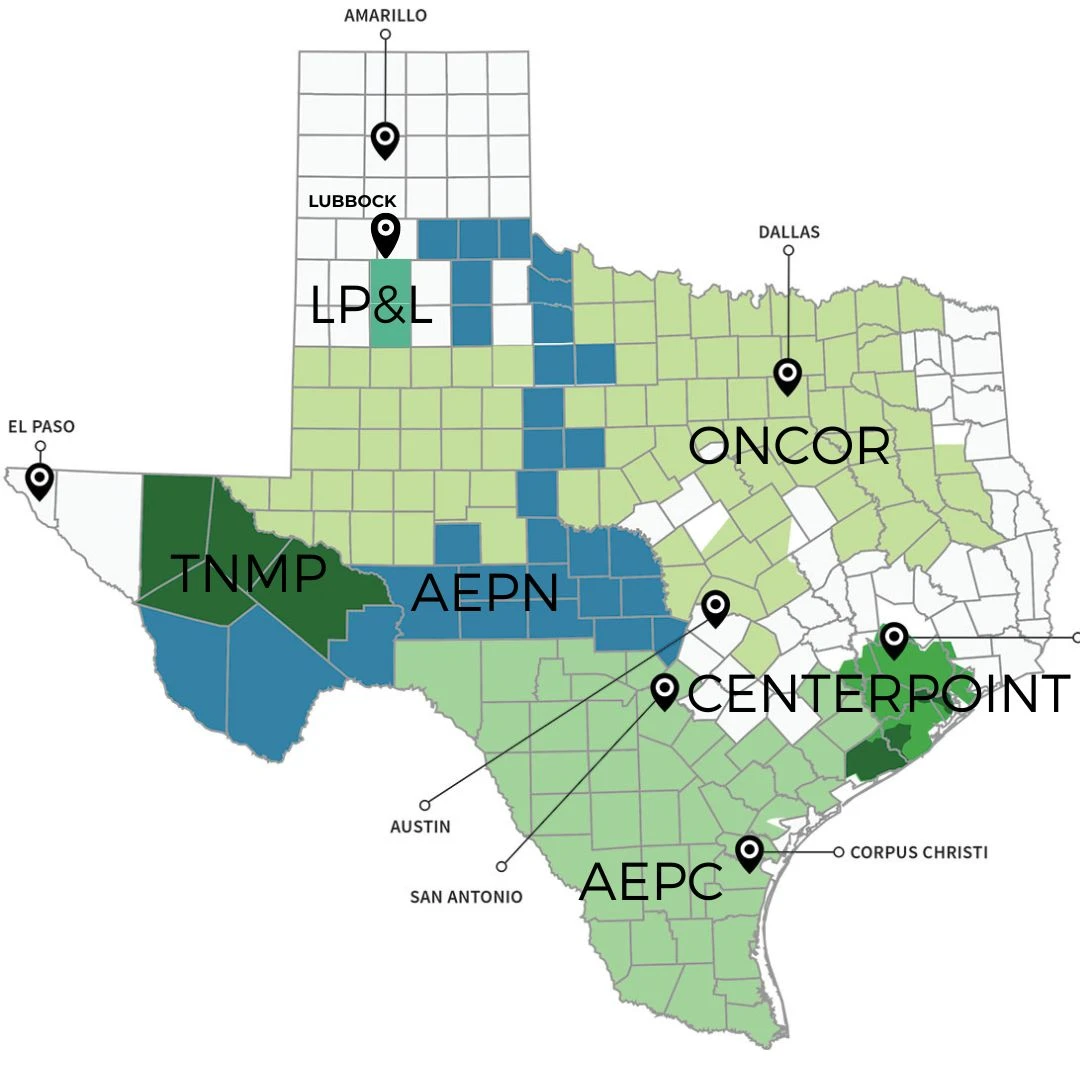
- Major Transmission Lines: The Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT), the independent system operator for most of Texas, manages a network of major transmission lines that connect power plants to load centers.
- Interconnections with Other States: Texas’s electric grid is interconnected with neighboring states, allowing for the exchange of electricity during periods of high demand or low generation. These interconnections provide flexibility and enhance grid reliability.
Challenges and Opportunities
The Texas electric power system faces a number of challenges and opportunities:
- Reliability and Resilience: Maintaining a reliable and resilient electric grid is crucial for Texas’s economic and social well-being. The state’s grid has faced challenges in recent years, including extreme weather events and grid overloads.
- Growing Energy Demand: Texas’s population and economy are growing, driving an increasing demand for electricity. Meeting this demand while ensuring grid reliability and environmental sustainability is a key challenge.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Integrating increasing amounts of renewable energy into the grid presents challenges related to intermittency and grid stability. However, it also offers opportunities for a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
- Grid Modernization: Modernizing the electric grid through investments in advanced technologies and infrastructure is crucial to enhance grid reliability, resilience, and efficiency.
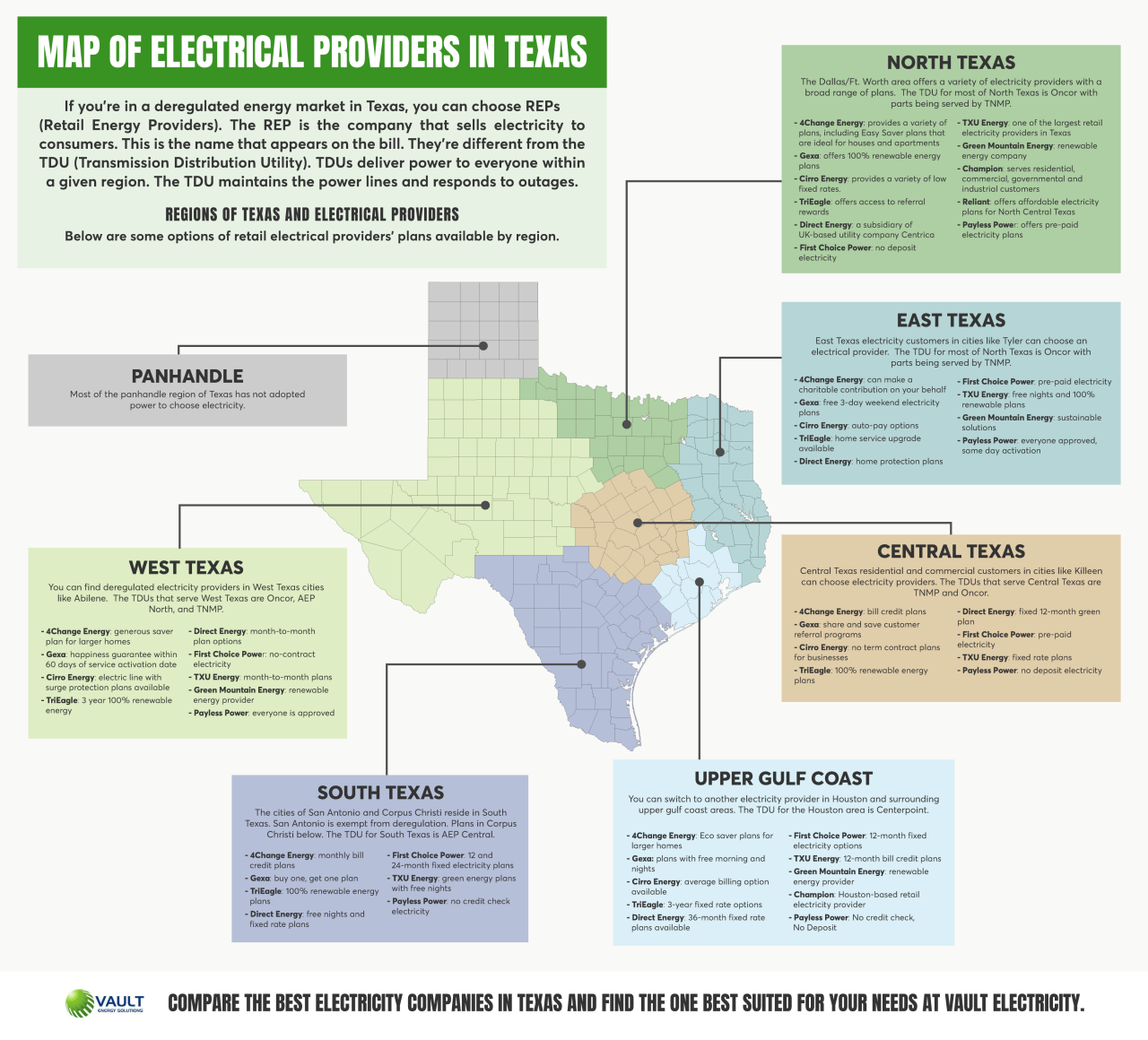
Retail Electricity Market: Electric Power Companies In Texas
Texas has a deregulated electricity market, meaning consumers have the freedom to choose their electricity provider. This competitive environment offers a variety of plans and rates, empowering consumers to make informed decisions about their energy needs.
Structure of the Retail Electricity Market
The Texas retail electricity market is structured to allow consumers to choose their electricity provider. This structure involves two primary players:
- Electricity Providers: These companies generate, transmit, and distribute electricity to consumers. They offer various electricity plans with different pricing structures and features.
- Retail Electric Providers (REPs): These companies act as intermediaries, purchasing electricity from electricity providers and selling it to consumers. They offer various plans and rates, often competing with each other to attract customers.
The Texas Electricity Reliability Council (ERCOT) manages the state’s power grid and ensures the reliable delivery of electricity to consumers. ERCOT does not provide electricity directly to consumers; instead, it acts as a market operator, coordinating the flow of electricity across the grid.
Types of Electricity Plans
Consumers in Texas have access to a variety of electricity plans, each with its own unique features and pricing structure.
- Fixed-Rate Plans: These plans offer a set price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) for a specific period, typically 12 months. This provides price certainty, allowing consumers to budget their electricity expenses.
- Variable-Rate Plans: These plans offer a price per kWh that fluctuates based on wholesale market prices. This can result in lower prices during periods of low demand but higher prices during periods of high demand.
- Renewable Energy Plans: These plans allow consumers to purchase electricity generated from renewable sources, such as wind or solar. These plans often come with a premium price, reflecting the higher cost of renewable energy production.
Factors Influencing Consumer Choice
Consumers in Texas consider several factors when choosing an electricity provider and plan. These factors include:
- Price: The cost of electricity is a major factor for most consumers. They often compare prices from different providers and plans to find the most affordable option.
- Contract Length: Consumers consider the length of the contract offered by different providers, balancing the benefits of a longer contract with the potential for price fluctuations.
- Renewable Energy Options: Consumers who prioritize sustainability often choose plans that include renewable energy sources.
- Customer Service: The reputation of the provider’s customer service is crucial, as consumers want reliable support in case of billing issues or outages.
Reliability and Resilience
The reliability of the Texas electric grid has been a subject of much debate, particularly after the severe winter storms of 2021, which resulted in widespread power outages and a humanitarian crisis. While the Texas grid is generally considered reliable, it faces unique challenges due to its independence from the national grid and its vulnerability to extreme weather events.
Extreme Weather Events and Reliability
Extreme weather events, such as winter storms and heat waves, pose significant challenges to the reliability of the Texas electric grid. During the February 2021 winter storm, freezing temperatures caused widespread power outages across the state, affecting millions of residents. The grid’s infrastructure, including power plants and transmission lines, was ill-prepared for such extreme conditions. For example, natural gas pipelines froze, leading to a shortage of fuel for power plants. Additionally, wind turbines froze, further reducing power generation capacity. The lack of adequate winterization measures for critical infrastructure contributed significantly to the grid’s failure.
Similarly, during extreme heat waves, the demand for electricity surges, straining the grid’s capacity. The Texas grid has experienced several heat waves in recent years, leading to rolling blackouts to prevent system collapse. These events highlight the importance of investing in grid infrastructure and ensuring its resilience against extreme weather events.
Measures to Improve Grid Resilience
The Texas legislature has passed several laws and regulations aimed at improving the reliability and resilience of the Texas electric grid. These measures include:
- Winterization Requirements: New regulations require power plants and transmission lines to be winterized to withstand extreme cold temperatures. These regulations aim to prevent a repeat of the widespread outages experienced during the 2021 winter storm.
- Investment in Renewable Energy: The state is actively promoting investments in renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power. These sources are less susceptible to extreme weather events than fossil fuel-based power plants. For example, the Texas wind power industry has grown significantly in recent years, contributing to the state’s energy independence.
- Grid Modernization: The Texas grid is undergoing modernization efforts to improve its efficiency and reliability. These efforts include upgrading transmission lines, integrating new technologies, and enhancing grid management systems. The modernization of the grid is crucial to ensure its ability to withstand extreme weather events and meet the growing demand for electricity.
- Enhanced Emergency Response: The state is strengthening its emergency response capabilities to ensure a coordinated and effective response to grid disruptions caused by extreme weather events. This includes improving communication channels, establishing backup power sources, and developing better disaster preparedness plans.
Comparison with Other States
The reliability of the Texas electric grid has been compared to other states, with varying results. While Texas boasts a generally reliable grid, it faces unique challenges due to its independence from the national grid. This independence allows for greater flexibility in energy policy, but it also limits the ability to share resources and capacity during extreme weather events.
The Texas grid is often praised for its reliability and affordability. However, the 2021 winter storm exposed its vulnerabilities to extreme weather events.
The reliability of the Texas grid is a complex issue with no easy solutions. The state is actively working to improve its resilience and prepare for future extreme weather events. The ongoing efforts to modernize the grid, promote renewable energy sources, and enhance emergency response capabilities are crucial steps in ensuring a more reliable and resilient energy system for Texas.
Environmental Impact
Texas’s electricity generation significantly impacts the environment, raising concerns about greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. However, the state is actively exploring and implementing renewable energy sources to mitigate these effects and achieve environmental sustainability.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from power generation are a significant contributor to climate change. Texas, with its reliance on fossil fuels, faces challenges in reducing these emissions.
- Texas is the leading producer of electricity from natural gas, contributing to significant methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas.
- The state’s coal-fired power plants contribute to substantial carbon dioxide emissions, a major driver of global warming.
- Texas’s electric power sector is a major source of carbon dioxide emissions, accounting for approximately 30% of the state’s total emissions.
Air Pollution
Air pollution from power generation poses health risks to Texans.
- Fossil fuel-based power plants emit pollutants like sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, contributing to respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and other health issues.
- Air pollution from power plants disproportionately affects low-income communities and communities of color, exacerbating existing health disparities.
- Texas’s air quality has been impacted by emissions from power plants, leading to violations of federal air quality standards in some areas.
Role of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, play a crucial role in reducing the environmental impact of Texas’s electric power industry.
- Texas is a leader in wind energy, with vast wind resources generating a significant portion of the state’s electricity.
- Solar energy is rapidly growing in Texas, contributing to a cleaner energy mix and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- The integration of renewable energy sources into the Texas grid helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, improving air quality and public health.
Challenges and Opportunities
Achieving environmental sustainability in the Texas electric power sector presents challenges and opportunities.
- Balancing the need for reliable and affordable electricity with environmental concerns is a key challenge.
- Integrating large-scale renewable energy sources into the grid requires significant infrastructure investments and technological advancements.
- Policy and regulatory frameworks need to be adapted to encourage and facilitate the transition to a cleaner energy future.
Future Trends
The Texas electric power industry is on the cusp of significant change, driven by a confluence of factors including environmental concerns, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences. This section will delve into the future trends shaping the Texas electric power landscape, focusing on the growth of renewable energy, the adoption of smart grid technologies, and the increasing importance of energy storage.
Growth of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are experiencing rapid growth in Texas, fueled by factors like falling costs, favorable government policies, and increasing consumer demand for cleaner energy. The Texas legislature has set ambitious goals for renewable energy development, aiming to significantly increase the state’s reliance on these resources in the coming years. This trend is expected to have a profound impact on the Texas electric power landscape, leading to:
- Increased Generation Capacity: The state is witnessing a surge in the construction of new solar and wind farms, adding substantial renewable energy generation capacity to the grid. This will increase the overall electricity supply and diversify the energy mix.
- Shifting Power Dynamics: As renewable energy sources become more prominent, traditional power plants, primarily fueled by natural gas and coal, will face increased competition. This shift in power dynamics could lead to the retirement of older, less efficient power plants and the emergence of new business models for electric power companies.
- Job Creation: The renewable energy sector is creating new jobs in Texas, from manufacturing and construction to operation and maintenance. This growth is contributing to the state’s economic development and providing employment opportunities in emerging industries.
Adoption of Smart Grid Technologies
Smart grid technologies are transforming the way electricity is generated, transmitted, and consumed. These technologies, including advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), distributed energy resources (DER), and communication networks, are enhancing grid efficiency, reliability, and responsiveness. The adoption of smart grid technologies in Texas is expected to:
- Improve Grid Reliability: Smart grid technologies enable real-time monitoring and control of the grid, allowing utilities to identify and respond to disruptions more effectively. This can reduce the frequency and duration of power outages, enhancing grid reliability and resilience.
- Enable Integration of Renewable Energy: Smart grid technologies facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, which are often intermittent and distributed. By providing greater flexibility and control, smart grids enable utilities to manage the flow of renewable energy more efficiently.
- Empower Consumers: Smart grid technologies provide consumers with greater control over their energy usage, enabling them to monitor their consumption, adjust their usage patterns, and even participate in demand response programs. This empowers consumers to make informed energy decisions and potentially reduce their energy costs.
Increasing Importance of Energy Storage
Energy storage is becoming increasingly crucial for ensuring grid reliability and integrating renewable energy sources. Battery storage, pumped hydro, and other storage technologies can help address the intermittency of renewable energy, store excess energy generated during peak production periods, and provide backup power during outages. The growing importance of energy storage in Texas is likely to:
- Enhance Grid Resilience: Energy storage systems can provide backup power during outages, ensuring the continued operation of critical infrastructure and reducing the impact of disruptions on consumers.
- Optimize Renewable Energy Integration: Energy storage can help manage the intermittency of renewable energy sources, allowing utilities to store excess energy generated during periods of high wind or solar output and release it when demand is high.
- Promote Grid Flexibility: Energy storage systems can provide ancillary services to the grid, such as voltage support and frequency regulation, enhancing grid flexibility and stability.
Final Thoughts
As Texas continues to grow and evolve, the electric power industry will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the state’s future. The ongoing pursuit of clean energy, the development of innovative technologies, and the ongoing efforts to ensure grid reliability and resilience will be key factors in determining the success of the Texas electric power sector. With its unique market structure and diverse energy sources, Texas offers a fascinating case study for understanding the challenges and opportunities facing the electricity industry in the 21st century.
User Queries
What are the major electric power companies in Texas?
Some of the major electric power companies in Texas include Exelon, NRG Energy, and Vistra Energy.
What are the different types of electricity plans available in Texas?
Texas offers a variety of electricity plans, including fixed-rate plans, variable-rate plans, and renewable energy plans.
How does the Texas electric grid compare to other states?
The Texas electric grid is unique in that it is not interconnected with the national grid. This can make it more vulnerable to extreme weather events, but it also provides greater flexibility and independence.




