
Electric companies Texas play a vital role in powering the Lone Star State, a state known for its vast energy resources and booming economy. From the bustling cities to the sprawling ranches, electricity is the lifeblood of Texas, and the companies that provide it are integral to the state’s success.
The Texas electric market is unique in its structure and operates differently from many other states. It’s a deregulated market, meaning that consumers have the freedom to choose their electricity provider, leading to a competitive landscape with a diverse range of options. This article will delve into the complexities of the Texas electric industry, exploring the major players, generation sources, pricing models, and the future of electricity in the state.
Texas Electric Company Landscape: Electric Companies Texas

The Texas electric market is a complex and dynamic landscape, characterized by a diverse mix of electric providers and a unique regulatory framework. Understanding the key players, regulatory environment, and different provider types is crucial for navigating this intricate system.
Major Electric Companies in Texas
Texas is home to several major electric companies that serve millions of customers across the state. These companies are responsible for generating, transmitting, and distributing electricity to homes, businesses, and industries.
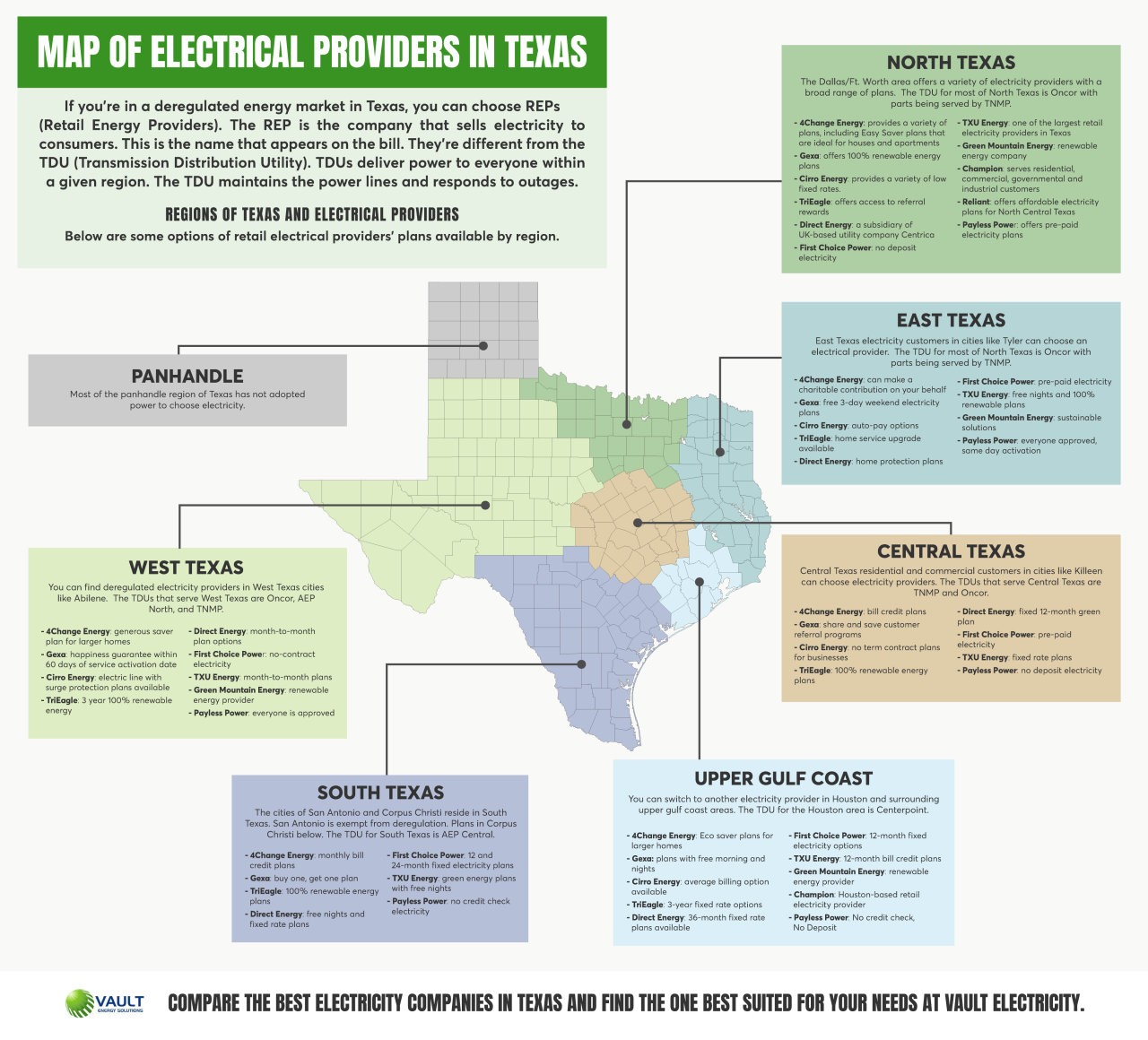
- Oncor Electric Delivery Company: Oncor is the largest electric transmission and distribution company in Texas, serving over 10 million customers in North and Central Texas. It is a subsidiary of Energy Future Holdings Corp. and operates under a regulated monopoly model.
- CenterPoint Energy: CenterPoint Energy serves over 2.5 million electric customers in Houston and surrounding areas. It is an investor-owned utility that also provides natural gas service.
- AEP Texas: AEP Texas, a subsidiary of American Electric Power, serves over 1.5 million customers in West Texas and the Panhandle. It is a regulated utility that focuses on generating and transmitting electricity.
- Texas-New Mexico Power Company: TNMP, a subsidiary of NRG Energy, serves over 500,000 customers in North Texas and New Mexico. It operates under a regulated monopoly model.
- Luminant: Luminant is a large power generation company in Texas, owned by Vistra Energy. It owns and operates several coal-fired and natural gas power plants, supplying electricity to various parts of the state.
Regulatory Framework
The Texas electric market operates under a deregulated model, with the Public Utility Commission of Texas (PUCT) as the primary regulatory body. The PUCT oversees the wholesale and retail electric markets, ensuring fair competition and consumer protection.
- Public Utility Commission of Texas (PUCT): The PUCT is responsible for setting rates, approving new power plants, and ensuring the reliability of the electric grid. It also oversees the activities of retail electric providers (REPs).
- Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT): ERCOT is an independent system operator that manages the flow of electricity across the Texas grid. It ensures the reliability and stability of the power system, coordinating with power plants and transmission lines.
- Texas Legislature: The Texas Legislature plays a crucial role in shaping the regulatory environment by passing laws that impact the electric market. It sets policy directives for the PUCT and other agencies.
Types of Electric Providers, Electric companies texas
The Texas electric market features a diverse range of electric providers, each with its own operating model and customer base.
- Investor-Owned Utilities (IOUs): IOUs are privately owned companies that generate, transmit, and distribute electricity to customers. They are regulated by the PUCT and earn a return on their investment through regulated rates. Examples include Oncor, CenterPoint Energy, and AEP Texas.
- Municipally-Owned Utilities (MOUs): MOUs are electric utilities owned and operated by cities or towns. They are typically regulated by the city council or a separate board of directors. MOUs often offer lower rates and prioritize local economic development.
- Electric Cooperatives: Electric cooperatives are non-profit organizations owned and controlled by their members. They serve rural areas and are regulated by the Texas Electric Cooperative Rural Electric Cooperative Association (TRECA). Cooperatives often focus on community service and providing affordable electricity.
- Retail Electric Providers (REPs): REPs are private companies that sell electricity to customers in deregulated areas. They compete with each other on price, service, and other factors. REPs do not own power plants or transmission lines but purchase electricity from wholesale providers. Examples include TXU Energy, Reliant Energy, and Ambit Energy.
Closing Summary
As Texas continues to grow and evolve, the electric industry is poised for significant change. The adoption of renewable energy sources, advancements in smart grid technology, and the increasing demand for reliable and affordable electricity present both challenges and opportunities for electric companies in Texas. Navigating these trends will require innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to providing sustainable and efficient energy solutions for the state’s future.
FAQ Overview
What are the biggest electric companies in Texas?
Some of the largest electric companies in Texas include Oncor, TXU Energy, Reliant Energy, and CenterPoint Energy.
How do I choose the best electricity plan for my needs?
To find the best electricity plan, consider your energy consumption, budget, and preferred energy sources. Use online comparison tools and consult with energy experts to make an informed decision.
What are the benefits of using a renewable energy provider?
Renewable energy providers offer cleaner and more sustainable energy options, reducing your carbon footprint and supporting a greener future.
What are the challenges facing the Texas electric grid?
The Texas electric grid faces challenges such as extreme weather events, growing energy demand, and the need to integrate more renewable energy sources.




