
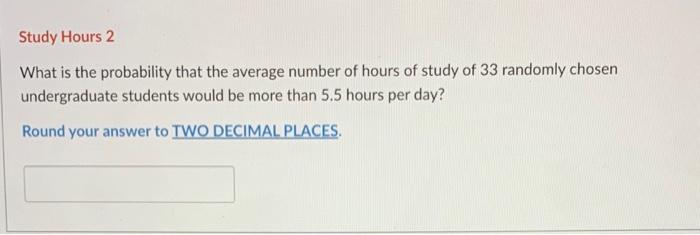
How many hours in a bachelor’s degree? It’s a question that often arises as prospective students embark on their academic journey. The answer, however, isn’t as straightforward as it might seem. A bachelor’s degree typically requires a significant commitment of time and effort, and the total number of hours can vary depending on a multitude of factors.
From the traditional four-year model to accelerated programs and part-time studies, the path to a bachelor’s degree can be customized to fit individual needs and circumstances. Understanding the factors that influence the duration of a bachelor’s degree, such as program intensity, course load, and credit hour systems, is crucial for making informed decisions and setting realistic expectations.
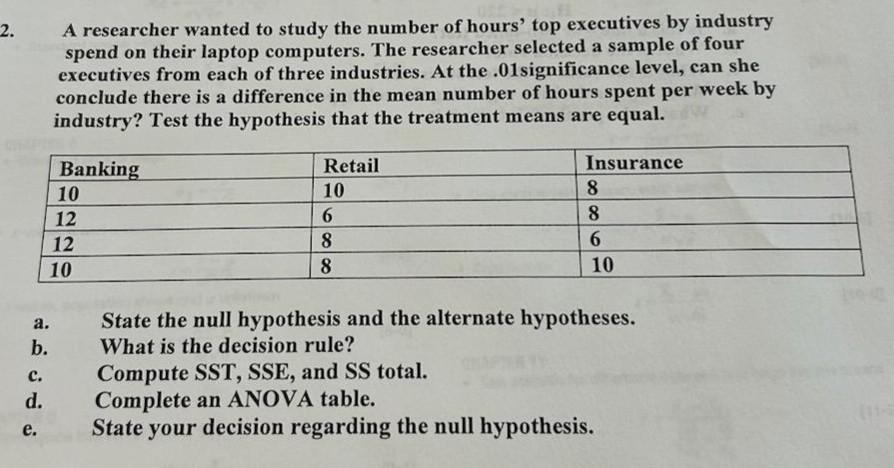
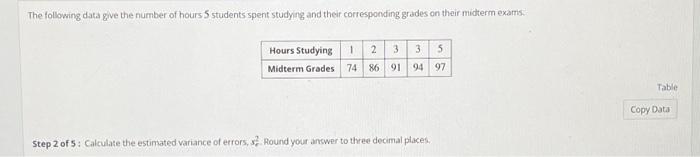
Bachelor’s Degree Duration: How Many Hours In A Bachelor’s Degree
A bachelor’s degree is a significant academic achievement, representing years of dedicated study and the acquisition of specialized knowledge and skills. Understanding the typical duration of a bachelor’s degree program is crucial for planning and navigating your educational journey.
Typical Duration of a Full-Time Bachelor’s Degree
A full-time bachelor’s degree program typically takes four years to complete. This duration is based on the standard course load, which usually involves taking 15 credit hours per semester, or 30 credit hours per year.
Factors Influencing Bachelor’s Degree Length
Several factors can influence the length of a bachelor’s degree program. These factors include:
Program Intensity
The intensity of a program can significantly impact its duration. Programs with a heavy course load, such as engineering or medicine, may require more time to complete. Conversely, programs with a lighter course load, such as liberal arts or humanities, may take less time.
Course Load
The number of courses taken each semester or year can affect the overall program duration. Students who take a heavier course load, such as 18 credit hours per semester, may be able to complete their degree in less than four years. However, it’s important to consider the potential impact on academic performance and overall well-being.
Individual Learning Pace
Every student learns at their own pace. Some students may be able to complete their degree in less than four years, while others may need more time. Factors such as prior learning experiences, study habits, and personal commitments can all influence individual learning pace.
Examples of Bachelor’s Degree Programs and Durations
Here are some examples of different bachelor’s degree programs and their respective durations:
- Bachelor of Arts (BA) in English Literature: Typically 4 years
- Bachelor of Science (BS) in Computer Science: Typically 4 years
- Bachelor of Engineering (BE) in Mechanical Engineering: Typically 4-5 years
- Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS): Typically 5-7 years
Credit Hours and Course Load
Credit hours represent the units of academic work assigned to a specific course. These units reflect the time commitment, workload, and academic rigor expected of students enrolled in the course. The total credit hours required for a bachelor’s degree vary depending on the institution and program of study.
The number of credit hours required to complete a bachelor’s degree typically ranges from 120 to 130 credit hours. This represents the cumulative amount of academic work students need to successfully graduate. The specific credit hour requirements are Artikeld in the program’s curriculum and are often specified in the university’s catalog.
Credit Hour Systems, How many hours in a bachelor’s degree
Different universities use varying credit hour systems to define the workload associated with each course. Some common systems include:
- Semester System: In this system, academic year is divided into two semesters, usually fall and spring. Each semester typically consists of 15 weeks of instruction. Students usually take courses worth 3 or 4 credit hours each.
- Quarter System: The academic year is divided into three quarters, typically fall, winter, and spring. Each quarter usually consists of 10 weeks of instruction. Students typically take courses worth 3 or 4 credit hours each.
- Trimester System: This system divides the academic year into three trimesters, each lasting approximately 12 weeks. Students may take courses worth 3, 4, or 5 credit hours per trimester.
Course Load
The number of credit hours a student takes per semester or quarter is known as their course load. The typical course load for undergraduate students varies depending on individual factors such as academic ability, time commitment, and personal goals.
A common course load for full-time undergraduate students is 12 to 18 credit hours per semester or quarter.
- Full-time students typically take a course load of 12 to 18 credit hours per semester or quarter, depending on the credit hour system used by their institution.
- Part-time students may take fewer credit hours, typically ranging from 6 to 12 credit hours per semester or quarter, depending on their personal circumstances and academic goals.
Factors Affecting Completion Time
The duration of a bachelor’s degree is not fixed and can vary depending on several factors. While the standard duration is four years for full-time students, many factors can influence how long it takes to earn a degree.
Part-Time Enrollment
Part-time enrollment significantly impacts the time it takes to complete a bachelor’s degree. Students enrolled part-time typically take fewer courses per semester, which extends the overall duration of their studies. For instance, a student taking half the course load of a full-time student might take eight years to complete a four-year degree.
Transferring Credits
Transferring credits from previous institutions can significantly shorten the time needed to earn a bachelor’s degree. Students who have already completed courses at other colleges or universities can often transfer those credits to their new institution, reducing the number of courses they need to take. For example, if a student transfers 30 credits from a community college, they might only need to take an additional 90 credits to earn their bachelor’s degree, potentially reducing their time to completion by a year or more.
Internships, Research Projects, and Study Abroad Programs
Internships, research projects, and study abroad programs can all impact the duration of a bachelor’s degree. While these experiences can be valuable for career development and personal growth, they can also add time to the overall degree completion process. For example, a student who participates in a semester-long study abroad program will need an additional semester to complete their degree requirements. Similarly, students who engage in extensive research projects or internships might need to extend their studies to accommodate these commitments.
Importance of Time Management
Time management is crucial for success in a bachelor’s degree program. Balancing coursework, extracurricular activities, and personal life can be challenging, and without effective time management skills, students may struggle to meet deadlines, maintain a healthy work-life balance, and achieve their academic goals.
Time Management Strategies
Effective time management strategies are essential for students to allocate their time wisely and optimize their productivity. By implementing these strategies, students can effectively manage their academic workload, prioritize tasks, and ensure a balanced lifestyle.
- Prioritize Tasks: Identifying and prioritizing tasks based on their urgency and importance is essential for efficient time allocation. Using methods like the Eisenhower Matrix, which categorizes tasks based on urgency and importance, can help students focus on high-priority tasks first.
- Create a Schedule: Developing a structured schedule that includes dedicated time slots for studying, attending classes, completing assignments, and personal activities can help students stay organized and on track.
- Set Realistic Goals: Setting achievable goals, breaking down large tasks into smaller, manageable steps, and setting realistic deadlines can enhance motivation and reduce procrastination.
- Eliminate Distractions: Identifying and minimizing distractions, such as social media, phone calls, or excessive socializing, is essential for maintaining focus and productivity.
- Take Breaks: Regular breaks throughout the day can improve concentration and prevent burnout. Short breaks for physical activity, relaxation, or social interaction can help students recharge and return to their studies with renewed focus.
- Utilize Time-Saving Techniques: Techniques like batching similar tasks together, using time-blocking methods, and implementing the Pomodoro Technique, which involves working in focused intervals with short breaks, can significantly improve efficiency.
Time Management Tools and Techniques
Various tools and techniques can assist students in managing their time effectively and staying organized. These tools provide a structured framework for planning, scheduling, and tracking progress, ultimately contributing to academic success.
- Digital Calendars: Digital calendars, such as Google Calendar or Outlook Calendar, allow students to schedule appointments, set reminders, and visualize their daily, weekly, or monthly commitments.
- To-Do List Apps: To-do list apps, such as Todoist or Asana, enable students to create, organize, and prioritize tasks, track progress, and set deadlines.
- Time Tracking Software: Time tracking software, such as Toggl or Clockify, allows students to monitor how they spend their time, identify time-consuming activities, and optimize their workflow.
- Pomodoro Technique: The Pomodoro Technique is a time management method that involves working in focused intervals of 25 minutes, separated by short breaks, to enhance concentration and productivity.
- Eisenhower Matrix: The Eisenhower Matrix is a prioritization tool that categorizes tasks based on their urgency and importance, helping students focus on high-priority tasks first.
Sample Weekly Schedule
A sample weekly schedule for a typical bachelor’s degree student can provide a framework for organizing time effectively. This schedule includes dedicated time slots for coursework, studying, extracurricular activities, and personal time.
| Day | Time | Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | 8:00 AM – 9:00 AM | Class: Introduction to Psychology |
| 9:00 AM – 10:00 AM | Study: Review Psychology notes | |
| 10:00 AM – 12:00 PM | Class: Calculus I | |
| 12:00 PM – 1:00 PM | Lunch | |
| 1:00 PM – 2:00 PM | Study: Complete Calculus homework | |
| 2:00 PM – 4:00 PM | Work: Part-time job | |
| 4:00 PM – 5:00 PM | Gym/Exercise | |
| 5:00 PM – 7:00 PM | Dinner/Social time | |
| 7:00 PM – 9:00 PM | Study: Prepare for upcoming exam | |
| Tuesday | 8:00 AM – 9:00 AM | Class: English Composition |
| 9:00 AM – 10:00 AM | Study: Review English essay writing techniques | |
| 10:00 AM – 12:00 PM | Class: History of Art | |
| 12:00 PM – 1:00 PM | Lunch | |
| 1:00 PM – 2:00 PM | Study: Complete History of Art reading assignment | |
| 2:00 PM – 4:00 PM | Work: Part-time job | |
| 4:00 PM – 5:00 PM | Student club meeting | |
| 5:00 PM – 7:00 PM | Dinner/Social time | |
| 7:00 PM – 9:00 PM | Study: Prepare for upcoming presentation | |
| Wednesday | 8:00 AM – 9:00 AM | Class: Introduction to Sociology |
| 9:00 AM – 10:00 AM | Study: Review Sociology notes | |
| 10:00 AM – 12:00 PM | Class: Biology I | |
| 12:00 PM – 1:00 PM | Lunch | |
| 1:00 PM – 2:00 PM | Study: Complete Biology lab report | |
| 2:00 PM – 4:00 PM | Work: Part-time job | |
| 4:00 PM – 5:00 PM | Free time | |
| 5:00 PM – 7:00 PM | Dinner/Social time | |
| 7:00 PM – 9:00 PM | Study: Prepare for upcoming quiz | |
| Thursday | 8:00 AM – 9:00 AM | Class: Introduction to Philosophy |
| 9:00 AM – 10:00 AM | Study: Review Philosophy concepts | |
| 10:00 AM – 12:00 PM | Class: Statistics | |
| 12:00 PM – 1:00 PM | Lunch | |
| 1:00 PM – 2:00 PM | Study: Complete Statistics practice problems | |
| 2:00 PM – 4:00 PM | Work: Part-time job | |
| 4:00 PM – 5:00 PM | Volunteer activity | |
| 5:00 PM – 7:00 PM | Dinner/Social time | |
| 7:00 PM – 9:00 PM | Study: Prepare for upcoming group project | |
| Friday | 8:00 AM – 9:00 AM | Class: Introduction to Economics |
| 9:00 AM – 10:00 AM | Study: Review Economics notes | |
| 10:00 AM – 12:00 PM | Class: Physics I | |
| 12:00 PM – 1:00 PM | Lunch | |
| 1:00 PM – 2:00 PM | Study: Complete Physics homework | |
| 2:00 PM – 4:00 PM | Free time | |
| 4:00 PM – 5:00 PM | Free time | |
| 5:00 PM – 7:00 PM | Dinner/Social time | |
| 7:00 PM – 9:00 PM | Relax/Personal time | |
| Saturday | 9:00 AM – 12:00 PM | Study: Review course material for upcoming exams |
| 12:00 PM – 1:00 PM | Lunch | |
| 1:00 PM – 5:00 PM | Free time/Personal errands | |
| 5:00 PM – 7:00 PM | Dinner/Social time | |
| 7:00 PM – 9:00 PM | Relax/Personal time | |
| Sunday | 9:00 AM – 12:00 PM | Study: Complete assignments and prepare for the upcoming week |
| 12:00 PM – 1:00 PM | Lunch | |
| 1:00 PM – 5:00 PM | Free time/Personal errands | |
| 5:00 PM – 7:00 PM | Dinner/Social time | |
| 7:00 PM – 9:00 PM | Relax/Personal time |
Real-World Implications of Time to Degree Completion
The duration of a bachelor’s degree can significantly impact an individual’s job prospects and career advancement, as well as their financial well-being. It’s crucial to understand how the time spent pursuing a degree can influence these real-world factors.
Impact on Job Prospects and Career Advancement
The time it takes to complete a bachelor’s degree can influence an individual’s competitiveness in the job market. Employers often consider the time to degree completion as a proxy for an individual’s work ethic, dedication, and ability to meet deadlines. A shorter time to degree completion can signal to potential employers that an individual is efficient, organized, and able to manage their time effectively.
End of Discussion
Navigating the complexities of a bachelor’s degree requires a clear understanding of the time commitment involved. By exploring the various factors that influence the duration of a degree, from credit hours and course load to individual learning pace and program choices, students can gain valuable insights into their academic journey. Ultimately, achieving a bachelor’s degree is a testament to dedication, perseverance, and a commitment to lifelong learning.
FAQ Resource
What is the average time to complete a bachelor’s degree?
The average time to complete a full-time bachelor’s degree is four years, or eight semesters. However, this can vary depending on factors such as program intensity, course load, and individual learning pace.
How many credit hours are required for a bachelor’s degree?
The number of credit hours required for a bachelor’s degree varies by institution and program. Generally, students need to earn around 120-130 credit hours to graduate.
Can I earn a bachelor’s degree in less than four years?
Yes, it is possible to earn a bachelor’s degree in less than four years through accelerated programs, taking a heavier course load, or transferring credits from previous institutions.
What are the financial implications of extending the duration of a bachelor’s degree?
Extending the duration of a bachelor’s degree can lead to higher tuition costs and potential lost income. It’s important to consider these financial implications when making academic decisions.




