
- Overview of a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology
- Career Paths with a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology
- Benefits of Pursuing a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology
- The Importance of Research in Psychology: Bachelor Of Arts Degree In Psychology
- The Impact of Psychology on Society
- The Future of Psychology
- Wrap-Up
- Frequently Asked Questions
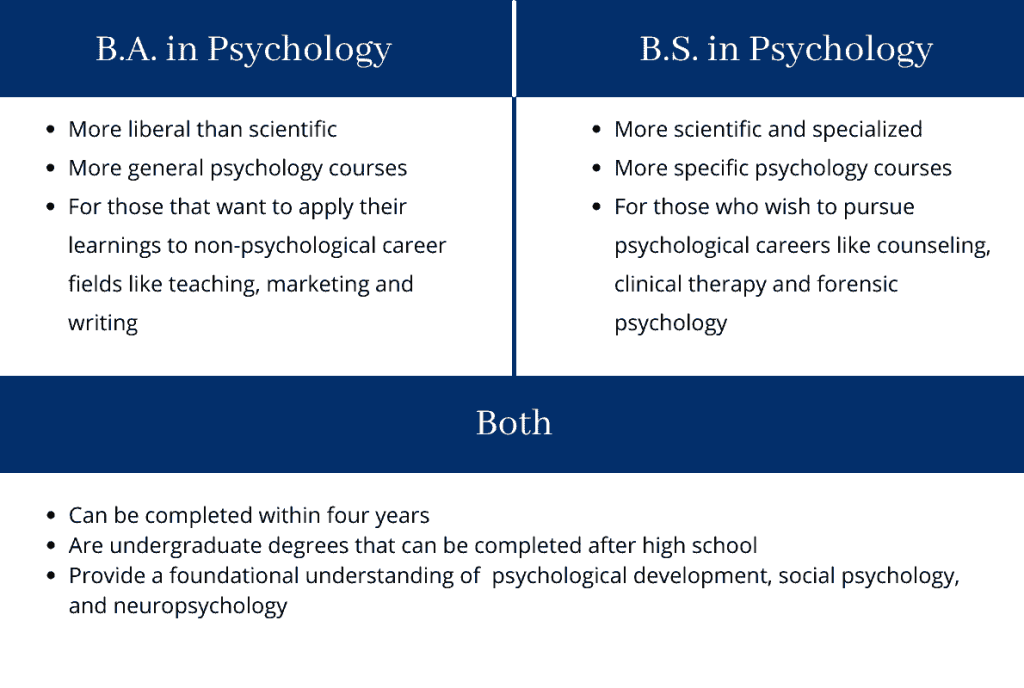
A Bachelor of Arts degree in Psychology opens doors to a world of understanding human behavior and mental processes. It’s more than just studying the mind; it’s about delving into the intricacies of emotions, thoughts, and actions, unraveling the complexities of human experience.
This program equips individuals with a diverse skillset, from critical thinking and communication to research methods and data analysis. It’s a journey of personal and professional growth, providing a foundation for a wide range of careers that impact lives and communities.
Overview of a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology

A Bachelor of Arts (BA) in Psychology is a versatile undergraduate degree that provides a comprehensive understanding of human behavior, cognition, and emotions. It equips students with the skills and knowledge to explore the complexities of the human mind and apply their insights to various fields.
Core Principles and Concepts
The core principles and concepts of psychology form the foundation of the field, providing a framework for understanding human behavior. These principles include:
- Scientific Method: Psychology relies on the scientific method to systematically investigate and understand human behavior. This involves formulating hypotheses, conducting experiments, analyzing data, and drawing conclusions.
- Biological Bases of Behavior: This area explores the physiological processes that underlie behavior, such as the role of the brain, nervous system, and hormones.
- Cognitive Processes: This area focuses on how people think, learn, remember, and solve problems.
- Social Influences: This area examines the impact of social factors on behavior, including group dynamics, social norms, and cultural influences.
- Personality and Individual Differences: This area explores the unique characteristics and traits that make each individual different, including personality theories, motivation, and emotion.
- Developmental Psychology: This area examines how people change and develop throughout their lifespan, from infancy to adulthood.
Areas of Specialization
Within psychology, there are various areas of specialization, each focusing on a specific aspect of human behavior. These specializations include:
- Clinical Psychology: This area focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental disorders. Clinical psychologists work with individuals, families, and communities to address mental health concerns.
- Developmental Psychology: This area explores the physical, cognitive, social, and emotional changes that occur throughout the lifespan. Developmental psychologists often work with children, adolescents, and families.
- Cognitive Psychology: This area investigates how people think, learn, remember, and solve problems. Cognitive psychologists often work in research settings or in applied fields such as education or human-computer interaction.
- Social Psychology: This area examines the impact of social factors on behavior, including group dynamics, social norms, and cultural influences. Social psychologists often work in research settings or in applied fields such as marketing or advertising.
Curriculum of a Psychology Program
A typical psychology program includes a combination of required courses and elective options. Required courses provide a broad foundation in the core principles and concepts of psychology, while elective courses allow students to specialize in areas of interest.
- Required Courses: These courses cover fundamental topics in psychology, such as introductory psychology, research methods, statistics, and biological psychology.
- Elective Courses: These courses offer students the opportunity to delve deeper into specific areas of psychology, such as clinical psychology, developmental psychology, cognitive psychology, or social psychology.
Career Paths with a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology

A Bachelor of Arts in Psychology opens doors to a diverse range of career paths, as the skills and knowledge acquired through this degree are highly transferable to various industries.
Psychology graduates can pursue careers in research, counseling, education, business, and many other fields.
Research
A psychology degree equips individuals with the research skills needed to conduct studies, analyze data, and interpret findings. These skills are valuable in various research settings, including:
- Academic Research: Psychology graduates can work as research assistants or conduct independent research in universities and research institutions.
- Market Research: The principles of psychology are applied in market research to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and motivations.
- Healthcare Research: Psychology graduates can contribute to healthcare research by studying the effectiveness of treatments, understanding patient experiences, and improving healthcare delivery.
Counseling, Bachelor of arts degree in psychology
Psychology graduates are well-prepared for careers in counseling, where they use their knowledge of human behavior and mental health to provide support and guidance to individuals, families, and groups. Some common counseling roles include:
- Mental Health Counselor: Provide therapy and support to individuals experiencing mental health challenges, such as anxiety, depression, or trauma.
- School Counselor: Support students’ academic, social, and emotional well-being, providing guidance on academic planning, career exploration, and personal development.
- Marriage and Family Therapist: Help couples and families address relationship issues, communication breakdowns, and conflict resolution.
Education
Psychology graduates can apply their knowledge of learning, motivation, and development to careers in education, working with students of all ages.
- Teacher: Psychology graduates can teach various subjects, incorporating principles of learning and motivation to create engaging and effective learning environments.
- Educational Psychologist: Work in schools or educational institutions to assess students’ learning needs, develop interventions, and provide support to students and educators.
- Curriculum Developer: Develop and design educational materials and programs based on psychological principles of learning and development.
Business
The skills and knowledge gained in a psychology degree are highly valuable in business settings, where understanding human behavior and motivation is crucial for success.
- Human Resources: Psychology graduates can work in human resources, applying their knowledge of motivation, leadership, and team dynamics to recruit, train, and manage employees.
- Marketing: Psychology principles are used in marketing to understand consumer behavior, develop effective advertising campaigns, and design products that meet customer needs.
- Sales: Psychology graduates can excel in sales by understanding customer motivations, building rapport, and effectively communicating product value.
Benefits of Pursuing a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology
A Bachelor of Arts in Psychology offers a unique blend of academic rigor and personal growth, equipping graduates with valuable skills and knowledge that can open doors to diverse career paths.
Personal Growth and Development
Studying psychology provides a profound opportunity for self-discovery and personal development. By exploring the complexities of human behavior, students gain a deeper understanding of themselves, their motivations, and their interactions with others. This knowledge fosters self-awareness, empathy, and a more nuanced perspective on the world.
Enhanced Critical Thinking, Communication, and Problem-Solving Skills
Psychology is a discipline that emphasizes critical thinking, analysis, and the ability to draw sound conclusions from complex information. Students learn to identify patterns, evaluate evidence, and formulate logical arguments. Furthermore, psychology courses often involve group discussions and presentations, enhancing communication skills and the ability to articulate ideas effectively.
Potential for Personal and Professional Fulfillment
A career in psychology offers the opportunity to make a meaningful difference in the lives of others. Whether working as a therapist, researcher, or in a related field, psychology professionals have the chance to apply their knowledge to help individuals, families, and communities. The potential for personal and professional fulfillment is high in a field that focuses on improving well-being and understanding human behavior.
The Importance of Research in Psychology: Bachelor Of Arts Degree In Psychology
Psychology is a scientific discipline that aims to understand human behavior and mental processes. Research is at the heart of this pursuit, providing the foundation for developing theories, testing hypotheses, and ultimately, improving our understanding of the human mind.
Different Research Methodologies
Research methodologies in psychology are diverse, each offering unique insights into the complexities of human behavior. These methods are carefully chosen based on the research question and the type of data being sought.
- Experiments are designed to establish cause-and-effect relationships. Researchers manipulate an independent variable (the cause) and observe its effect on a dependent variable (the outcome). For example, a study might investigate the impact of sleep deprivation on memory performance. Participants would be randomly assigned to sleep-deprived or control groups, and their memory would be tested.
- Surveys are used to gather data from a large sample of individuals. Researchers ask participants to answer questions about their attitudes, beliefs, behaviors, or experiences. This method is particularly useful for exploring trends and patterns within a population. For instance, a survey might be conducted to assess the prevalence of anxiety disorders among college students.
- Case studies provide in-depth examinations of a single individual or a small group. This method is valuable for understanding unique cases, exploring complex phenomena, or developing new theories. A famous case study in psychology is that of Phineas Gage, who survived a traumatic brain injury that significantly altered his personality.
Ethical Considerations in Psychological Research
Conducting ethical research is paramount in psychology. Researchers must adhere to strict guidelines to ensure the well-being and rights of participants. These ethical principles include:
- Informed consent: Participants must be fully informed about the nature of the research, its potential risks and benefits, and their right to withdraw at any time.
- Confidentiality: Participants’ data and identities must be kept confidential, ensuring their privacy is protected.
- Beneficence: Research should aim to benefit participants or society as a whole, minimizing potential harm.
- Justice: Participants should be selected fairly, and the benefits and risks of the research should be distributed equitably.
The Impact of Psychology on Society
Psychology’s influence extends far beyond the confines of a therapist’s office, permeating various aspects of society and shaping our understanding of human behavior. From healthcare to education and the legal system, psychological principles are applied to address critical social issues, improve individual well-being, and drive societal progress.
Psychology’s Influence on Healthcare
The application of psychological principles in healthcare has revolutionized patient care and treatment. Psychologists contribute to the development and implementation of effective treatment strategies for mental health disorders, chronic illnesses, and substance abuse. For instance, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is widely used to manage anxiety, depression, and other mental health conditions. Moreover, psychological interventions like stress management techniques and relaxation therapies are incorporated into treatment plans for chronic illnesses to improve patient outcomes.
The Future of Psychology
The field of psychology is constantly evolving, adapting to new discoveries, societal shifts, and technological advancements. As we move forward, the future of psychology holds both exciting possibilities and significant challenges.
The Integration of Technology
Technology is revolutionizing how we understand and interact with the human mind. The integration of technology in psychology offers numerous opportunities for innovation and advancement.
- Digital Mental Health Tools: Apps and online platforms are becoming increasingly popular for providing mental health services, offering accessibility, affordability, and personalized care. These tools can help with tracking moods, managing anxiety, and accessing therapy sessions remotely.
- Brain-Computer Interfaces: BCIs are emerging technologies that allow direct communication between the brain and external devices. These interfaces have the potential to revolutionize the treatment of neurological disorders, enhance cognitive abilities, and even provide new ways to interact with the world.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI algorithms are being used to analyze large datasets of psychological information, identify patterns, and develop personalized interventions. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are also being used to provide support and guidance to individuals struggling with mental health issues.
The Growing Importance of Cultural Diversity
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, it is crucial to recognize the diversity of human experiences and how culture shapes our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. The field of psychology is increasingly recognizing the importance of cultural sensitivity and inclusivity in research and practice.
- Cultural Influences on Mental Health: Cultural factors can influence the expression and understanding of mental health conditions. For example, the stigma associated with mental illness can vary significantly across cultures.
- Diversity in Research: It is essential to include diverse populations in psychological research to ensure that findings are generalizable and applicable across different cultures.
- Culturally Competent Practice: Psychologists need to be culturally competent, meaning they understand and respect the values, beliefs, and experiences of individuals from diverse backgrounds.
The Focus on Positive Psychology
While traditional psychology has often focused on addressing mental health problems, positive psychology emphasizes the study of human strengths, well-being, and flourishing. This field explores factors that contribute to happiness, resilience, and meaning in life.
- Building Resilience: Positive psychology research helps us understand how to cultivate resilience, the ability to bounce back from adversity and thrive in challenging situations.
- Promoting Well-Being: Positive psychology interventions aim to promote well-being by fostering positive emotions, building meaningful relationships, and encouraging engagement in activities that provide a sense of purpose.
- Focus on Strengths: Positive psychology emphasizes identifying and developing individual strengths, rather than solely focusing on weaknesses or deficits.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities
The future of psychology presents both challenges and opportunities.
- Ethical Considerations: As technology advances, it is crucial to address ethical considerations related to privacy, data security, and the potential for bias in AI algorithms.
- Access to Mental Health Services: Despite advancements in digital mental health, disparities in access to mental health services persist. Ensuring equitable access to care for all individuals is a critical challenge.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: The future of psychology requires collaboration with other disciplines, such as neuroscience, computer science, and sociology, to address complex societal issues.
Wrap-Up
A Bachelor of Arts in Psychology is a gateway to a fulfilling career, empowering individuals to make a positive impact on the world. Whether you’re drawn to research, counseling, education, or business, this degree provides the knowledge and skills to navigate complex challenges and contribute to a better understanding of the human experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the admission requirements for a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology?
Admission requirements vary depending on the university. Typically, they include a high school diploma or equivalent, a minimum GPA, and standardized test scores (SAT or ACT).
What are the job prospects for psychology graduates?
Psychology graduates have a wide range of career options, including research, counseling, education, marketing, human resources, and social work.
Is a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology a good choice for someone interested in clinical psychology?
A Bachelor of Arts in Psychology is a good starting point for a career in clinical psychology. However, it typically requires further education, such as a Master’s or Doctoral degree.
What are some popular specializations within psychology?
Some popular specializations include clinical psychology, developmental psychology, cognitive psychology, social psychology, and industrial-organizational psychology.




