How many credit hours for a bachelor degree – How many credit hours for a bachelor’s degree? This question arises for many aspiring college graduates, as it’s a crucial factor in understanding the journey ahead. The standard credit hour requirement for a bachelor’s degree in the United States is 120, but this number can fluctuate depending on the specific field of study, university, and even the intensity of individual courses.
Factors like course difficulty, program requirements, and the type of degree (arts versus science) can all impact the total credit hours needed for graduation. Transferring credits from previous institutions also plays a significant role, as each institution has its own system for evaluating and awarding credit hour equivalency. Ultimately, understanding the credit hour requirements for your chosen field of study and university is essential for planning your academic path and ensuring a smooth graduation process.
General Overview of Bachelor’s Degrees: How Many Credit Hours For A Bachelor Degree
A bachelor’s degree is a four-year undergraduate degree that is typically required for entry-level positions in many professions. In the United States, the standard credit hour requirement for a bachelor’s degree is 120 credit hours. This translates to approximately 40 courses, each typically worth 3 credit hours.
Credit Hour Requirements for Bachelor’s Degrees
The specific credit hour requirements for a bachelor’s degree can vary depending on the institution, the major, and the specific degree program. For example, some universities may require a minimum of 124 credit hours, while others may require only 116. Some majors, such as engineering or nursing, may have more stringent requirements than others, such as liberal arts or humanities.
Variations in Credit Hour Requirements
The following are some examples of how credit hour requirements can vary based on academic field:
- Engineering: Engineering programs often require more credit hours than other majors because of the rigorous coursework and laboratory requirements. For example, a bachelor’s degree in mechanical engineering may require 130 credit hours.
- Nursing: Nursing programs also require more credit hours than other majors because of the clinical requirements and the need for specialized coursework. A bachelor’s degree in nursing may require 128 credit hours.
- Liberal Arts: Liberal arts programs often have more flexible credit hour requirements. A bachelor’s degree in liberal arts may require 120 credit hours, but students may be able to take more elective courses or pursue a double major.
Credit Hour Requirements Across Universities
Credit hour requirements can also vary across universities. For example, a bachelor’s degree in business administration at one university may require 120 credit hours, while the same degree at another university may require 124 credit hours. This is because universities have different course structures and credit hour systems.
Factors Influencing Credit Hour Requirements
While the standard number of credit hours for a bachelor’s degree is generally 120, various factors can influence this requirement. These factors encompass the complexity of the chosen program, specific program requirements, and the institution’s policies.
Course Intensity and Difficulty
The intensity and difficulty of courses can significantly impact credit hour requirements. Courses with a higher workload, demanding assignments, or more rigorous content may be assigned more credit hours. For instance, a laboratory science course with extensive hands-on work might carry more credit hours than a lecture-based humanities course.
Program-Specific Requirements
Specific program requirements can also influence credit hour requirements. Programs that include internships, research projects, or capstone projects may necessitate additional credit hours beyond the standard 120. For example, an engineering program requiring a mandatory internship might add 3-6 credit hours to the overall degree requirement.
Types of Bachelor’s Degrees
The credit hour requirements can vary across different types of bachelor’s degrees. Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) degrees often require a greater number of credit hours due to the demanding nature of their coursework and the inclusion of laboratory experiences. Conversely, arts and humanities degrees may have fewer credit hour requirements, focusing more on theoretical and conceptual learning.
Transfer Credits and Credit Hour Equivalency

Transferring credits from previous institutions can be a valuable way to reduce the time and cost of earning a bachelor’s degree. However, understanding the process of transferring credits and how credit hour equivalency is determined is crucial.
Transfer Credit Evaluation
When you apply to transfer credits, the receiving institution will evaluate your previous coursework to determine if it meets the requirements for your chosen degree program. This evaluation process involves comparing your previous courses to the courses offered at the new institution.
- Course Content: The receiving institution will examine the course syllabus, learning objectives, and course content to ensure it aligns with their own courses.
- Grade: The receiving institution may have minimum grade requirements for transferring credits. For example, they may only accept courses with a grade of C or higher.
- Course Level: Transfer credits are typically only accepted for courses at the college level (typically 100-level or higher).
Credit Hour Equivalency
Credit hour equivalency refers to the process of determining how many credit hours at the receiving institution are equivalent to the credit hours you earned at your previous institution. This is important because different institutions may have different credit hour systems.
For example, a 3-credit hour course at one institution might be equivalent to a 4-credit hour course at another institution.
Impact on Total Credit Hours
The number of transfer credits you are able to receive can significantly impact the total number of credit hours you need to earn a bachelor’s degree. If you are able to transfer a significant number of credits, you may be able to graduate sooner and potentially save on tuition costs.
For example, if you transfer 30 credit hours from a previous institution, you may only need to take an additional 60 credit hours to earn your bachelor’s degree, rather than the standard 120 credit hours.
Credit Hour Requirements for Specific Majors

The number of credit hours required for a bachelor’s degree can vary significantly depending on the specific major. Some majors may require more credit hours than others, and some universities may have different credit hour requirements for the same major.
This section explores the credit hour requirements for specific majors, providing insights into the average credit hour requirements for popular majors, comparing credit hour requirements across different universities for a chosen major, and detailing the specific courses and their corresponding credit hours for a specific major.
Average Credit Hour Requirements for Popular Majors, How many credit hours for a bachelor degree
This table displays the average credit hour requirements for some popular majors.
| Major | Average Credit Hours |
|—|—|
| Business Administration | 120-130 |
| Engineering | 128-132 |
| Nursing | 120-124 |
| Education | 120-128 |
| Computer Science | 120-124 |
| Psychology | 120-124 |
| Biology | 120-124 |
| Chemistry | 120-124 |
| English | 120-124 |
| History | 120-124 |
These are just average credit hour requirements, and the actual number of credit hours required may vary depending on the specific university and the chosen course of study.
Credit Hour Requirements for a Specific Major Across Different Universities
This table compares the credit hour requirements for a Bachelor of Science in Computer Science across several universities.
| University | Credit Hours Required |
|—|—|
| Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) | 128 |
| Stanford University | 124 |
| University of California, Berkeley | 124 |
| Carnegie Mellon University | 128 |
| Georgia Institute of Technology | 128 |
As you can see, the credit hour requirements for a Bachelor of Science in Computer Science can vary slightly across different universities. It’s important to note that these are just a few examples, and the actual credit hour requirements may vary depending on the specific program and course of study.
Specific Courses and Credit Hours for a Chosen Major
This section provides a detailed overview of the specific courses and their corresponding credit hours for a Bachelor of Science in Computer Science at a specific university, such as the University of California, Berkeley.
Required Courses
* Introduction to Computer Science (4 credit hours)
* Data Structures and Algorithms (4 credit hours)
* Object-Oriented Programming (4 credit hours)
* Software Engineering (4 credit hours)
* Computer Systems (4 credit hours)
* Operating Systems (4 credit hours)
* Databases (4 credit hours)
* Artificial Intelligence (4 credit hours)
* Computer Graphics (4 credit hours)
* Network Security (4 credit hours)
Electives
* Students are required to take a certain number of elective courses in their major, such as:
* Machine Learning
* Web Development
* Mobile App Development
* Cybersecurity
* Data Science
The specific courses and credit hours may vary depending on the specific program and course of study. It’s important to consult the university’s catalog for the most up-to-date information.
The Importance of Credit Hours for Graduation
Credit hours are the fundamental units that measure the amount of academic work undertaken by a student. They are not just a number on a transcript; they represent the time, effort, and learning acquired throughout a student’s academic journey. Understanding the importance of credit hours is crucial for navigating the path to graduation successfully.
Credit Hours and the Learning Experience
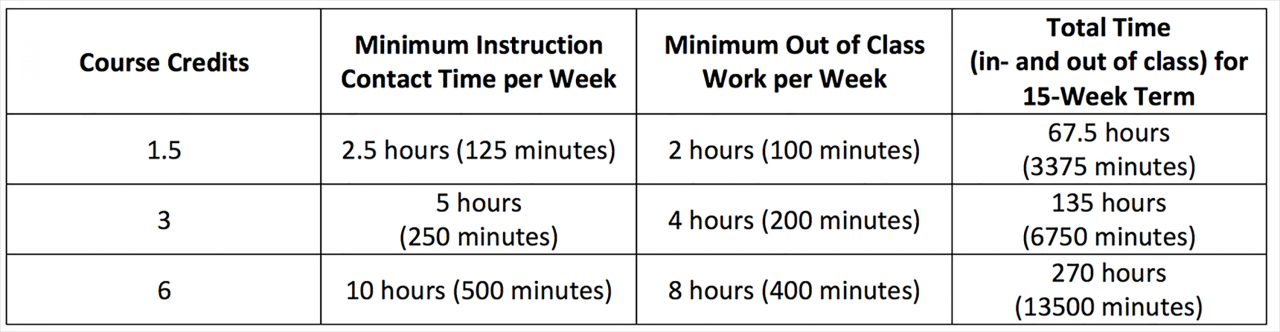
Credit hours are directly linked to the learning experience. Each credit hour represents a specific amount of time dedicated to instruction, assignments, and independent study. For instance, a three-credit hour course typically involves approximately 45 hours of combined classroom time, homework, and study. This structured approach ensures students engage in a sufficient depth of learning and develop the necessary skills and knowledge.
Credit Hours and GPA Calculation
Credit hours are essential for calculating a student’s Grade Point Average (GPA). The GPA is a numerical representation of a student’s academic performance, reflecting the grades earned in each course and the corresponding credit hours. The GPA is calculated by dividing the total grade points earned by the total credit hours attempted.
For example, if a student earns an A (4.0 grade points) in a 3-credit hour course and a B (3.0 grade points) in a 4-credit hour course, their GPA would be calculated as follows:
Total Grade Points = (4.0 x 3) + (3.0 x 4) = 24
Total Credit Hours = 3 + 4 = 7
GPA = 24 / 7 = 3.43
Consequences of Insufficient Credit Hours
Failing to meet the required credit hour threshold for graduation can have significant consequences. Students who fall short of the required credit hours may be unable to graduate, even if they have met all other academic requirements. This can delay career aspirations, affect job prospects, and require additional semesters or summer courses to complete the degree.
Last Word
Navigating the world of credit hours can feel overwhelming, but with careful planning and research, you can confidently map out your academic journey. Understanding the factors that influence credit hour requirements, exploring the transfer credit process, and researching specific program requirements will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and achieve your academic goals.
FAQ Section
What happens if I don’t meet the required credit hour threshold for graduation?
You won’t be eligible to graduate until you complete the required number of credit hours. You may need to take additional courses or explore alternative options, such as summer school or independent study.
Can I take more than the required credit hours for a bachelor’s degree?
Yes, you can take more than the required credit hours. This can be beneficial if you want to explore additional areas of interest or prepare for graduate studies. However, be mindful of the potential financial implications.
Are credit hours the same across all universities?
No, credit hours can vary slightly across different universities. It’s important to check the specific requirements of the institution you plan to attend.


