
- Introduction to Bachelor’s Degree in Nursing
- Curriculum and Coursework
- Clinical Experiences and Practicums
- Admission Requirements and Application Process
- Nursing Skills and Competencies
- Career Paths and Opportunities
- Professional Organizations and Licensure
- The Future of Nursing
- Last Word: Bachelor’s Degree In Nursing
- Question & Answer Hub
A bachelor’s degree in nursing is a gateway to a fulfilling and impactful career in healthcare. It equips individuals with the knowledge, skills, and compassion necessary to provide exceptional patient care. The journey towards becoming a registered nurse (RN) begins with a rigorous academic program that blends theoretical learning with extensive hands-on clinical experience.
Nursing has evolved significantly over time, with the BSN becoming the gold standard for entry-level practice. This degree program prepares graduates for a wide range of roles across diverse healthcare settings, from hospitals and clinics to community health centers and specialized areas like pediatrics, oncology, or critical care. The demand for skilled and compassionate nurses continues to rise, making this career path both rewarding and in high demand.
Introduction to Bachelor’s Degree in Nursing
The Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) degree is a foundational qualification for aspiring nurses, equipping them with the knowledge, skills, and ethical framework necessary to provide safe and effective patient care. It represents a significant investment in one’s future, opening doors to a fulfilling and impactful career in healthcare.
Historical Evolution of Nursing Education
The evolution of nursing education has been intertwined with the changing landscape of healthcare, reflecting advancements in medical knowledge and the evolving role of nurses. Nursing education initially emerged as apprenticeship programs, where aspiring nurses learned practical skills under the guidance of experienced nurses.
- In the late 19th century, the first formal nursing schools were established, offering structured curricula and theoretical knowledge alongside clinical practice. These schools were often affiliated with hospitals, providing students with hands-on experience in various healthcare settings.
- The 20th century saw a shift towards higher education in nursing, with the establishment of baccalaureate programs. The American Nurses Association (ANA) advocated for the BSN as the minimum educational standard for professional nursing practice, recognizing the need for nurses with advanced knowledge and critical thinking skills to navigate complex healthcare environments.
- Today, the BSN is widely recognized as the gold standard for nursing education, preparing graduates for diverse roles in hospitals, clinics, community health centers, and research settings.
Diverse Career Paths for BSN Graduates
BSN graduates possess a versatile skill set that opens doors to a wide range of career opportunities in the healthcare field. The BSN curriculum encompasses a broad spectrum of nursing knowledge and practice, enabling graduates to adapt to various healthcare settings and patient populations.
- Direct Patient Care: BSN graduates are highly sought after for direct patient care roles in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities. They provide comprehensive care, administer medications, educate patients and families, and advocate for their well-being. Examples include registered nurses (RNs), critical care nurses, emergency room nurses, and operating room nurses.
- Specialized Nursing Roles: The BSN degree serves as a foundation for specialization in various areas of nursing. Graduates can pursue advanced training and certification in fields such as pediatrics, oncology, geriatrics, mental health, and critical care.
- Management and Leadership: BSN graduates with experience and leadership qualities can advance to management positions within healthcare organizations. They oversee nursing staff, develop care plans, manage budgets, and ensure quality patient care.
- Education and Research: BSN graduates with a passion for education can pursue careers as nursing educators, teaching future generations of nurses. Others may choose to engage in nursing research, contributing to advancements in healthcare practice and patient outcomes.
- Public Health and Advocacy: BSN graduates can work in public health organizations, promoting health and wellness within communities. They may develop health programs, conduct outreach initiatives, and advocate for policies that improve healthcare access and quality.
Curriculum and Coursework
A Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) program provides a comprehensive curriculum designed to equip aspiring nurses with the necessary knowledge, skills, and values to practice effectively in diverse healthcare settings. The curriculum is a carefully structured blend of theoretical and practical components, fostering a deep understanding of nursing principles and their application in real-world situations.
Core Nursing Courses
The core nursing courses form the foundation of the BSN program, covering essential areas of nursing practice. These courses provide a comprehensive understanding of nursing theory, principles, and skills.
- Fundamentals of Nursing: This course introduces students to the basic concepts of nursing, including the nursing process, patient assessment, vital signs, medication administration, and basic nursing procedures. It also covers the ethical and legal principles of nursing practice.
- Medical-Surgical Nursing: This course focuses on the care of patients with a wide range of medical and surgical conditions. Students learn about common diseases, treatments, and nursing interventions for various medical and surgical specialties.
- Maternal-Newborn Nursing: This course explores the physiological and psychological aspects of pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum care. Students learn about the care of mothers and newborns during the antepartum, intrapartum, and postpartum periods.
- Pediatric Nursing: This course focuses on the unique health needs of children and adolescents. Students learn about common childhood illnesses, developmental milestones, and nursing interventions for pediatric patients.
- Mental Health Nursing: This course examines the principles of mental health nursing, including assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of mental health disorders. Students learn about various mental health conditions, therapeutic interventions, and the role of nurses in promoting mental well-being.
- Community Health Nursing: This course explores the role of nurses in promoting health and preventing disease within communities. Students learn about community health assessment, health education, and various community health programs.
Integration of Theory and Practice
A key feature of BSN programs is the seamless integration of theoretical knowledge with clinical practice. This integration is achieved through various methods, including:
- Clinical Rotations: Students participate in supervised clinical rotations in different healthcare settings, such as hospitals, clinics, and community health centers. These rotations provide hands-on experience in applying theoretical concepts to real-life situations.
- Simulation Labs: BSN programs often incorporate simulation labs, where students practice nursing skills in a safe and controlled environment. These labs use high-fidelity mannequins and advanced technology to create realistic scenarios that mimic real-world patient care.
- Case Studies: Students analyze real-life patient cases to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This approach helps them apply theoretical knowledge to complex clinical situations.
Importance of Elective Courses
Elective courses provide students with the opportunity to specialize in areas of nursing practice that align with their interests and career goals. These courses allow students to delve deeper into specific areas of nursing, such as:
- Critical Care Nursing: This specialization focuses on the care of critically ill patients in intensive care units (ICUs). Students learn about advanced life support techniques, hemodynamic monitoring, and complex medical interventions.
- Oncology Nursing: This specialization focuses on the care of patients with cancer. Students learn about cancer biology, treatment modalities, and the psychosocial needs of cancer patients and their families.
- Emergency Nursing: This specialization focuses on the care of patients in emergency departments. Students learn about triage, trauma management, and advanced emergency medical procedures.
Clinical Experiences and Practicums
Nursing students gain essential practical skills and knowledge through hands-on experiences in various clinical settings. These experiences provide opportunities to apply theoretical concepts learned in the classroom to real-life situations, fostering critical thinking and decision-making skills.
Clinical Settings for Nursing Students, Bachelor’s degree in nursing
Clinical experiences are a crucial part of a nursing education, allowing students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations and develop essential skills. Students typically rotate through various clinical settings, gaining exposure to diverse patient populations and healthcare environments. Common clinical settings for nursing students include:
- Hospitals: Hospitals provide a wide range of clinical experiences, including acute care, critical care, emergency medicine, and specialized units like cardiology, oncology, and pediatrics.
- Community Health Centers: Community health centers focus on providing healthcare services to underserved populations in local communities. Students gain experience in preventive care, health education, and outreach programs.
- Long-Term Care Facilities: Nursing homes and assisted living facilities provide students with experience in caring for older adults with chronic illnesses and disabilities. Students learn about geriatric care, rehabilitation, and end-of-life care.
- Mental Health Facilities: Psychiatric hospitals and community mental health centers offer opportunities to learn about mental health disorders, therapeutic interventions, and patient advocacy.
- Schools: School nurses provide healthcare services to students and staff, including health screenings, medication administration, and emergency care. Students gain experience in pediatric health and wellness.
- Home Health Agencies: Home health nurses provide care to patients in their homes. Students learn about patient education, medication management, and coordinating care with other healthcare providers.
Role of Clinical Instructors
Clinical instructors play a vital role in guiding and assessing student performance in clinical settings. They provide mentorship, supervision, and feedback to ensure students develop the necessary skills and knowledge. The key responsibilities of clinical instructors include:
- Providing instruction and guidance: Clinical instructors guide students through clinical procedures, patient assessments, and medication administration, ensuring they understand the rationale behind each action.
- Supervising and evaluating student performance: Clinical instructors observe students’ interactions with patients, assess their decision-making skills, and provide feedback on their performance. This ensures students meet the required standards and develop proficiency in clinical practice.
- Promoting critical thinking and decision-making: Clinical instructors encourage students to analyze patient situations, consider different options, and make informed decisions based on their knowledge and assessment findings.
- Facilitating learning experiences: Clinical instructors create opportunities for students to learn from real-life situations, participate in case studies, and engage in reflective practice.
- Ensuring student safety and patient well-being: Clinical instructors prioritize the safety of both students and patients, providing clear guidelines and supervision to ensure appropriate care is delivered.
Developing Critical Thinking and Decision-Making Skills
Clinical experiences provide a dynamic environment for developing critical thinking and decision-making skills. Students learn to:
- Analyze patient data: Students gather information from patients, medical records, and diagnostic tests to identify relevant data and develop a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s condition.
- Synthesize information: Students integrate various pieces of information, including patient history, physical assessment findings, and laboratory results, to form a holistic picture of the patient’s situation.
- Evaluate options and make informed decisions: Students learn to consider different treatment options, weigh the risks and benefits, and make evidence-based decisions that prioritize patient safety and well-being.
- Reflect on their practice: Students are encouraged to reflect on their clinical experiences, identify areas for improvement, and seek guidance from clinical instructors.
Admission Requirements and Application Process

Gaining admission to a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) program is a competitive process that requires careful planning and preparation. Nursing schools seek candidates who demonstrate strong academic abilities, a genuine passion for nursing, and the necessary personal qualities to succeed in this demanding field. This section Artikels the typical admission requirements and the application process for BSN programs.
Academic Prerequisites
BSN programs typically require applicants to have completed specific prerequisite courses before applying. These courses provide a foundation in the sciences and humanities that are essential for understanding nursing concepts and principles. Common prerequisites include:
- Biology
- Chemistry
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Microbiology
- Psychology
- Sociology
- English Composition
- Statistics
The specific prerequisites and their minimum grade requirements may vary depending on the individual nursing school. It is crucial to review the program’s website or contact the admissions office directly to confirm the exact requirements.
Application Process
The application process for BSN programs typically involves the following steps:
- Submit an Application: Most nursing schools use online application systems. Applicants will need to create an account, provide personal information, and submit academic transcripts.
- Complete Prerequisite Courses: Ensure all prerequisite courses are completed with a minimum grade requirement.
- Write an Essay: The essay is an opportunity for applicants to demonstrate their writing skills, explain their reasons for pursuing nursing, and showcase their passion for the profession. It’s crucial to be genuine and highlight personal experiences that demonstrate commitment to serving others.
- Submit Letters of Recommendation: Applicants are usually required to submit letters of recommendation from professors, employers, or other individuals who can attest to their academic abilities, work ethic, and personal qualities.
- Take Standardized Exams: Some nursing schools require applicants to take standardized exams, such as the Test of Essential Academic Skills (TEAS) or the Health Education Systems Incorporated (HESI) exam. These exams assess critical thinking, reading comprehension, math, and science skills.
- Attend an Interview: Many nursing schools conduct interviews as part of the admission process. Interviews allow the admissions committee to assess an applicant’s communication skills, personality, and suitability for the program.
Standardized Exams
Standardized exams like the TEAS and HESI are commonly used by nursing schools to assess an applicant’s academic preparedness for nursing studies. These exams evaluate skills that are crucial for success in nursing school, including:
- Reading Comprehension: The ability to understand and interpret written materials, which is essential for comprehending medical literature and patient charts.
- Mathematics: Proficiency in basic math skills, such as fractions, decimals, percentages, and ratios, is essential for calculating dosages and understanding medical data.
- Science: A strong foundation in biology, chemistry, and anatomy and physiology is crucial for understanding the human body and disease processes.
- Critical Thinking: The ability to analyze information, solve problems, and make sound judgments is essential for clinical decision-making in nursing.
While the TEAS and HESI are widely used, some nursing schools may have their own standardized exams or may not require any standardized testing at all. It’s essential to check the specific requirements of the program you are applying to.
Nursing Skills and Competencies
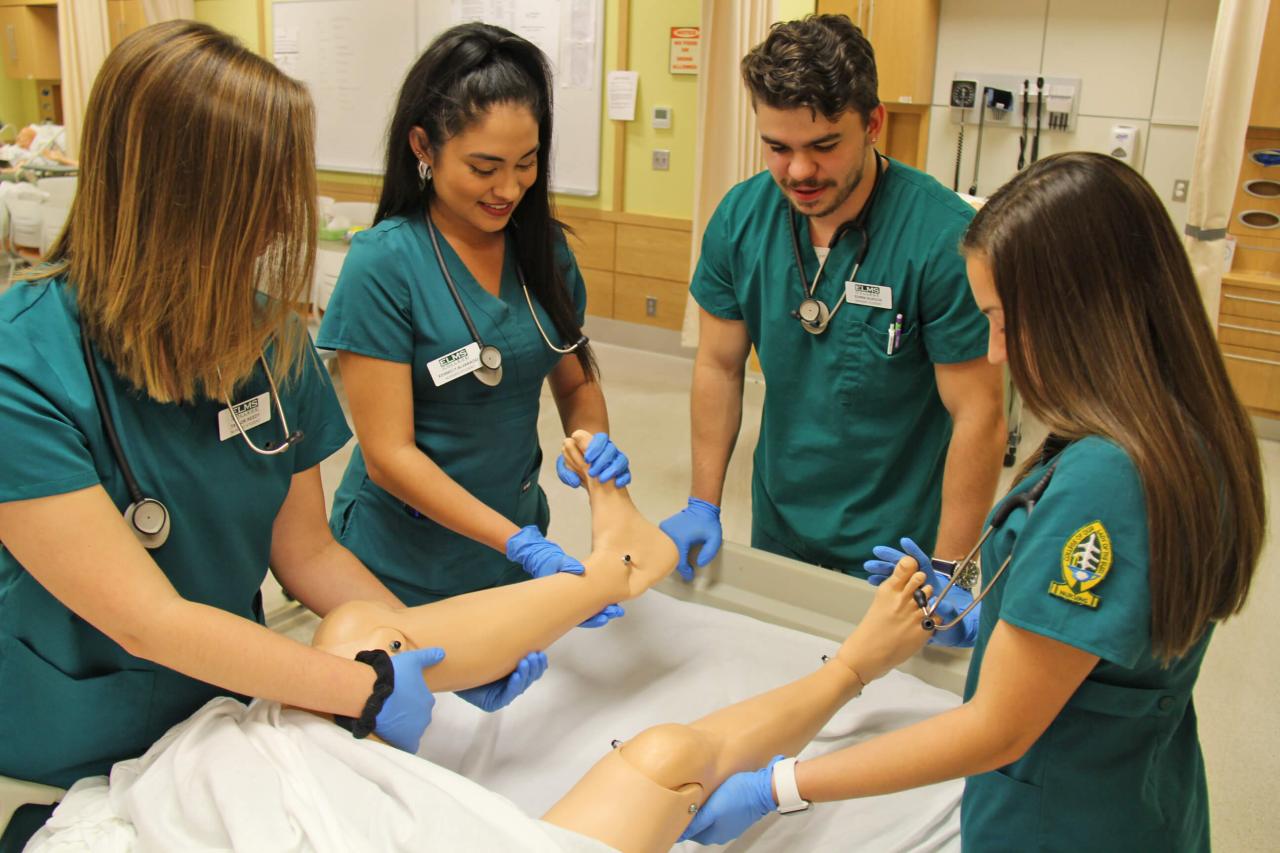
Nurses are essential members of the healthcare team, providing a wide range of services to patients. Their ability to effectively care for patients relies on a solid foundation of knowledge, skills, and competencies. This section will explore the core skills and competencies that are essential for successful nursing practice.
Core Nursing Skills and Competencies
Nurses require a diverse set of skills and competencies to effectively care for patients in various settings. These skills can be broadly categorized into technical, interpersonal, and critical thinking skills.
- Technical Skills: These skills are the hands-on abilities nurses need to perform their duties. They include:
- Assessment: Nurses gather and interpret patient information, including vital signs, physical assessments, and medical history, to identify health issues and develop care plans.
- Medication Administration: Nurses administer medications safely and accurately, understanding dosages, routes, and potential side effects.
- Wound Care: Nurses provide wound care, including cleaning, dressing changes, and monitoring for signs of infection.
- IV Therapy: Nurses administer intravenous fluids and medications, ensuring proper technique and monitoring for complications.
- Basic Life Support (BLS): Nurses are trained in basic life support procedures, including CPR and the use of a defibrillator.
- Interpersonal Skills: Effective communication and interpersonal skills are crucial for building rapport with patients and their families. These skills include:
- Communication: Nurses communicate effectively with patients, families, and other healthcare professionals, using clear and concise language, active listening, and empathy.
- Active Listening: Nurses actively listen to patients, demonstrating empathy and understanding their concerns, needs, and preferences.
- Teamwork: Nurses collaborate effectively with other healthcare professionals, including doctors, pharmacists, and social workers, to ensure comprehensive patient care.
- Critical Thinking Skills: Nurses must be able to analyze patient information, identify problems, and develop solutions. These skills include:
- Problem-Solving: Nurses use critical thinking skills to identify and solve problems, making informed decisions based on evidence and patient needs.
- Decision-Making: Nurses make decisions based on their knowledge, assessment findings, and patient preferences, ensuring safety and effectiveness of care.
- Clinical Reasoning: Nurses use clinical reasoning to interpret patient data, analyze potential risks, and develop appropriate interventions.
Communication, Critical Thinking, and Problem-Solving Skills
Effective communication, critical thinking, and problem-solving are essential for nurses to provide safe and effective care.
- Communication: Nurses use clear and concise language to communicate with patients, families, and other healthcare professionals. This includes:
- Active Listening: Nurses actively listen to patients, demonstrating empathy and understanding their concerns, needs, and preferences.
- Providing Information: Nurses provide patients and families with clear and understandable information about their health condition, treatment plan, and potential risks and benefits.
- Explaining Procedures: Nurses explain medical procedures to patients in a way they can understand, addressing their questions and concerns.
- Advocating for Patients: Nurses advocate for patients’ rights and needs, ensuring they receive the care they deserve.
- Critical Thinking: Nurses use critical thinking skills to analyze patient information, identify problems, and develop solutions. This includes:
- Data Analysis: Nurses gather and analyze patient data, including vital signs, lab results, and medical history, to identify potential problems.
- Identifying Patterns: Nurses recognize patterns in patient data, helping them anticipate potential complications and develop appropriate interventions.
- Evaluating Evidence: Nurses evaluate evidence-based practices and research findings to ensure they are providing the best possible care.
- Problem-Solving: Nurses use problem-solving skills to identify and address patient issues, making informed decisions based on evidence and patient needs. This includes:
- Developing Solutions: Nurses develop creative and effective solutions to address patient problems, taking into account their individual needs and preferences.
- Evaluating Outcomes: Nurses evaluate the effectiveness of their interventions, making adjustments as needed to improve patient outcomes.
- Seeking Consultation: Nurses seek consultation from other healthcare professionals when necessary, ensuring patients receive comprehensive and coordinated care.
Technology and Informatics in Nursing Practice
Technology and informatics play a crucial role in modern nursing practice, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and patient safety.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): EHRs are electronic systems that store and manage patient medical information. Nurses use EHRs to document patient care, track medications, and access medical history.
- Telehealth: Telehealth technologies allow nurses to provide care remotely, using video conferencing, mobile apps, and other tools. This expands access to care, particularly in rural or underserved areas.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): CDSSs provide nurses with real-time clinical guidance, helping them make informed decisions about patient care.
- Data Analytics: Nurses use data analytics to identify trends, track outcomes, and improve the quality of care. This involves analyzing data from EHRs, patient surveys, and other sources.
Career Paths and Opportunities
A Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) degree opens doors to a wide range of career paths in healthcare, offering both traditional and specialized roles. The BSN prepares graduates to be adaptable and skilled nurses, ready to contribute to diverse healthcare settings.
Roles and Responsibilities of Registered Nurses
Registered Nurses (RNs) play a vital role in providing patient care and ensuring their well-being. Their responsibilities vary depending on their work setting, but generally include:
- Assessing patients’ health conditions and needs
- Developing and implementing individualized care plans
- Administering medications and treatments
- Monitoring patients’ vital signs and progress
- Educating patients and their families about health conditions and treatments
- Collaborating with other healthcare professionals
- Advocating for patients’ rights and needs
- Maintaining accurate patient records
Hospital Settings
Hospitals are the most common work environment for RNs, providing a diverse range of care specialties. RNs in hospital settings may work in:
- Medical-Surgical Units: Providing care to patients with a variety of medical and surgical conditions.
- Intensive Care Units (ICUs): Caring for critically ill patients who require close monitoring and specialized treatments.
- Emergency Departments: Providing immediate care to patients with urgent medical needs.
- Operating Rooms: Assisting surgeons during surgical procedures.
- Labor and Delivery Units: Providing care to mothers and newborns during childbirth.
- Pediatric Units: Caring for children with various health conditions.
Community Health
Community health nurses work outside of traditional hospital settings, providing care to individuals and families in their communities. They may work in:
- Public Health Departments: Promoting health and preventing disease through education, screenings, and outreach programs.
- Home Health Agencies: Providing care to patients in their homes, assisting with activities of daily living, and managing chronic conditions.
- Schools: Providing health education and care to students.
- Clinics and Health Centers: Providing primary care and specialized services to underserved populations.
Specialized Areas
BSN graduates can pursue specialized areas of nursing practice, requiring advanced education and certification. Some common specialties include:
- Critical Care Nursing: Caring for critically ill patients in intensive care units.
- Oncology Nursing: Providing care to patients with cancer.
- Pediatric Nursing: Caring for children with various health conditions.
- Geriatric Nursing: Caring for older adults.
- Mental Health Nursing: Providing care to individuals with mental health conditions.
- Nurse Anesthesia: Administering anesthesia to patients during surgical procedures.
- Nurse Midwifery: Providing prenatal, labor, and postpartum care to women.
Opportunities for Advancement and Specialization
The nursing profession offers various opportunities for advancement and specialization. RNs can pursue:
- Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) Roles: These roles require a Master’s or Doctoral degree in Nursing and specialized certification. APRNs can provide a wider range of services, including diagnosing and treating illnesses, prescribing medications, and conducting research.
- Leadership Positions: RNs can advance into leadership roles, such as nurse managers, directors, and chief nursing officers, overseeing the delivery of nursing care and managing nursing departments.
- Teaching Positions: RNs with advanced degrees can teach nursing students in colleges and universities, sharing their expertise and preparing future generations of nurses.
- Research Positions: RNs with a strong research background can contribute to the advancement of nursing knowledge and practice through clinical trials and research studies.
Professional Organizations and Licensure
Nurses are a vital part of the healthcare system, providing direct patient care and contributing to overall health outcomes. To support the profession and ensure the highest standards of practice, various professional organizations and licensing bodies play a crucial role. This section explores these organizations, their importance, and the licensing requirements for registered nurses (RNs).
Professional Organizations for Nurses
Professional organizations provide a platform for nurses to connect, collaborate, and advocate for their profession. These organizations offer numerous benefits, including networking opportunities, professional development resources, and support for advancing nursing practice.
- American Nurses Association (ANA): The ANA is the largest professional organization for registered nurses in the United States. It advocates for nurses’ rights and interests, promotes high standards of nursing practice, and provides resources for professional development.
- National League for Nursing (NLN): The NLN focuses on nursing education, promoting excellence in nursing education programs and supporting faculty development. It offers accreditation services for nursing schools and provides resources for nursing educators.
- American Association of Critical-Care Nurses (AACN): The AACN is dedicated to the advancement of critical care nursing. It offers certifications for critical care nurses, provides resources for professional development, and advocates for policies that improve critical care.
Importance of Professional Development and Continuing Education
Professional development and continuing education are crucial for nurses to stay current with the latest advancements in healthcare and maintain their skills. This includes:
- Keeping Up with New Technologies and Treatments: Healthcare is constantly evolving with new technologies and treatments. Nurses must stay informed about these changes to provide safe and effective care.
- Improving Clinical Skills: Continuous learning helps nurses refine their clinical skills and develop new ones. This includes attending workshops, conferences, and online courses.
- Maintaining Licensure Requirements: Many states require nurses to complete continuing education units (CEUs) to maintain their licenses.
Licensing Requirements for Registered Nurses
Becoming a registered nurse requires passing the NCLEX-RN exam and meeting the licensing requirements of the state where you plan to practice. These requirements vary by state but typically include:
- Graduation from an Accredited Nursing Program: Nurses must graduate from a nursing program accredited by a recognized accrediting body.
- Passing the NCLEX-RN Exam: The NCLEX-RN is a national examination that tests nursing knowledge and skills.
- Background Check and Criminal History Review: Most states require a background check and criminal history review to ensure the safety of patients.
- Continuing Education Requirements: Nurses must complete continuing education units (CEUs) to maintain their licenses.
The Future of Nursing
The nursing profession is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, shifting healthcare priorities, and a growing demand for skilled professionals. Understanding these trends is crucial for aspiring nurses who want to make a meaningful impact in the healthcare landscape.
Evolving Trends and Challenges
The nursing profession faces a multitude of evolving trends and challenges, including:
- Aging Population: As the population ages, the demand for nurses to care for chronic conditions and geriatric patients will increase significantly. This will require nurses to specialize in gerontology and palliative care, and to develop expertise in managing complex medical needs.
- Technological Advancements: The integration of technology in healthcare is transforming nursing practice. Nurses are expected to be proficient in using electronic health records (EHRs), telehealth platforms, and various medical devices to deliver safe and efficient care.
- Healthcare Reform: Policies aimed at improving healthcare accessibility and affordability, such as the Affordable Care Act (ACA), have influenced nursing practice. Nurses play a vital role in navigating these changes and advocating for patients’ rights and access to quality care.
- Nurse Shortages: The nursing profession faces a persistent shortage of qualified professionals, particularly in rural and underserved areas. Addressing this challenge requires attracting and retaining nurses through competitive salaries, improved working conditions, and opportunities for professional development.
- Increased Focus on Prevention and Wellness: The healthcare system is shifting towards a more preventative approach, emphasizing health education, disease prevention, and promoting healthy lifestyles. Nurses are at the forefront of this shift, providing health screenings, counseling, and community outreach programs.
Impact of Technology and Healthcare Reform
Technology and healthcare reform have a profound impact on nursing practice, shaping the future of the profession.
Technology
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): EHRs have revolutionized the way nurses document patient care, track vital signs, and access medical information. Nurses must be proficient in using EHRs to ensure accurate data entry, patient safety, and efficient communication with other healthcare professionals.
- Telehealth: Telehealth platforms allow nurses to provide remote patient care, offering consultations, monitoring, and education. This technology expands access to healthcare services, especially in rural areas, and allows nurses to connect with patients in new ways.
- Medical Devices: Advancements in medical devices, such as wearable health monitors, remote patient monitoring systems, and robotic surgery, are changing the role of nurses. Nurses are expected to understand the operation of these devices, monitor patient responses, and ensure safe and effective use.
Healthcare Reform
- Affordable Care Act (ACA): The ACA has expanded access to healthcare for millions of Americans, increasing the demand for nurses. Nurses play a crucial role in implementing the ACA’s provisions, ensuring patient access to preventive care, primary care services, and mental health support.
- Value-Based Care: The shift towards value-based care models emphasizes quality outcomes and patient satisfaction. Nurses are key players in achieving these goals, collaborating with healthcare teams to improve patient experiences and reduce hospital readmissions.
- Population Health Management: Healthcare is increasingly focusing on managing the health of entire populations, rather than treating individual illnesses. Nurses are well-positioned to lead community health initiatives, promote healthy behaviors, and manage chronic conditions within communities.
Ethical Considerations in Nursing Care
Ethical considerations are paramount in nursing practice, guiding nurses in making responsible and compassionate decisions.
- Patient Autonomy: Nurses must respect patient autonomy and their right to make informed decisions about their healthcare. This includes providing patients with accurate information, supporting their choices, and advocating for their needs.
- Beneficence and Non-Maleficence: Nurses are ethically obligated to act in the best interests of their patients, promoting their well-being and avoiding harm. This principle requires nurses to be vigilant in providing safe and effective care, while also considering the potential risks and benefits of treatment options.
- Confidentiality and Privacy: Nurses must maintain patient confidentiality and protect their personal information. This principle ensures that patients feel comfortable sharing sensitive information and builds trust in the healthcare system.
- Professional Integrity: Nurses are expected to maintain professional integrity, upholding ethical standards and demonstrating honesty, accountability, and trustworthiness. This includes adhering to professional codes of conduct and reporting any breaches of ethical behavior.
Last Word: Bachelor’s Degree In Nursing

Earning a bachelor’s degree in nursing is a commitment to a profession that requires dedication, empathy, and a lifelong pursuit of knowledge. Nurses play a vital role in the lives of patients and their families, providing support, guidance, and advocacy throughout their healthcare journey. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, nurses will remain at the forefront of innovation and progress, ensuring the delivery of quality care for generations to come.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the average salary for a registered nurse with a BSN?
The average salary for a registered nurse with a BSN varies depending on location, experience, and specialization. However, RNs with a BSN typically earn a higher salary than those with an associate’s degree.
How long does it take to complete a BSN program?
A typical BSN program takes four years to complete, but some accelerated programs can be completed in less time. The length of the program may vary depending on the institution and the student’s prior education.
What are the best online BSN programs?
There are many reputable online BSN programs available. It’s important to research programs carefully and consider factors such as accreditation, faculty qualifications, and clinical placement opportunities.
What are the job prospects for BSN graduates?
The job outlook for registered nurses is excellent. The demand for qualified nurses is expected to grow significantly in the coming years due to an aging population and increasing healthcare needs.




